Electric control of magnetization in an amorphous Co–Fe–Ta–B–O film by resistive switching
Abstract
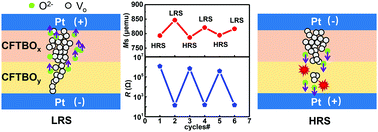
Electric control of magnetism by resistive switching is a simple and efficient approach to manipulate magnetism. However, the mechanism of magnetism manipulation by resistive switching is not well understood. Detailed characterization was performed to investigate the mechanism of magnetization changes with resistance state. We achieved a reversible and nonvolatile control of magnetization in a Co–Fe–Ta–B–O film at room temperature by resistive switching. It is found that a higher saturation magnetization could be attributed to the formation of a conducting filament rich in the reductive state of iron when the device is switched to low resistance. This work might provide a new insight to achieve magnetoelectric coupling.
- This article is part of the themed collection: PCCP Editor’s Choice, 2020


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...