Giant electrocaloric effect in a molecular ceramic†
Hao-Ran
Ji‡
a,
Ru-Jie
Zhou‡
a,
Jie
Yao‡
a,
Xiao-Xing
Cao
a,
Zheng-Yin
Jing
a,
Qiang
Pan
a,
Zi-Jie
Feng
a,
Zhu-Xiao
Gu
*ab and
Yu-Meng
You
 *a
*a
aJiangsu Key Laboratory for Science and Applications of Molecular Ferroelectrics, Southeast University, Nanjing, 211189, P. R. China. E-mail: youyumeng@seu.edu.cn; gzx@ufl.edu
bAffiliated Drum Tower Hospital, Medical School of Nanjing University, Nanjing, 210008, P. R. China
First published on 22nd December 2022
Abstract
The electrocaloric effect (ECE) is an efficient and environmentally friendly method for solid-state refrigeration driven by an electric field. However, disregarding the ECE performance, the mass of materials also limits the amount of energy transferred in the cooling process. While molecular ECE materials have been attracting intensive attention with their excellent ECE properties, most reported molecular compounds can only be utilized in the form of thin films or single crystals. Unlike inorganic ceramics, molecular thin films and single crystals are very difficult to prepare in a large amount, which greatly restrains the future application of those materials. In this work, we report an excellent molecular ECE material in the form of polycrystalline molecular ceramics. Such molecular ceramics are composed of plastic molecular ferroelectrics, and can fulfil the requirement of large mass, easy processing, excellent performance and low energy consumption. Our molecular ceramic of HQReO4 (HQ: protonated quinuclidine) demonstrates an isothermal entropy change of 5.8 J K−1 kg−1 and an adiabatic temperature change of 3.1 K. Notably, by a simple low-temperature pressing process without added adhesives (about 373 K), an HQReO4 molecular ceramic block can be obtained, and its ECE performance is observed to be comparable to that of single crystals, for the first time. This work proposes a new application form for molecular electrocaloric materials, which opens up new ideas for solid-state refrigeration.
New conceptsIn this work, a molecular ceramic of the molecular ferroelectric HQReO4 (HQ: protonated quinuclidine) was prepared to demonstrate its potential electrocaloric effect. Different from conventional inorganic ferroelectric ceramics, which are fabricated by a high processing temperature and a rigid structure, the molecular ceramic possesses outstanding mechanical deformability (Vickers hardness: 12.8 HV) thanks to the weak intermolecular interactions of plastic ferroelectrics. Molecular ceramic blocks can be obtained with no adhesive added and just simple low-temperature pressing, while traditional inorganic ferroelectric ceramics require high processing temperature and energy-intensive manufacturing. More importantly, compared to inorganic ceramics, the molecular ceramic shows better quality with less defects. This work provides a simple and feasible approach to obtain massive molecular electrocaloric materials with qualities comparable to those of single crystals. |
Introduction
With the rapid development of modern technologies, refrigeration is playing an increasingly important role in industries and daily life, but the resulting energy crisis and environmental problems are becoming increasingly serious. Refrigerators and air conditioners utilizing traditional compressors consume more than 20% of the daily energy consumption.1 Not only does the traditional refrigeration method have a low energy conversion efficiency but also the leaked refrigerant will destroy the ozone layer and cause extreme weather.2 Additionally, the development of the microelectronics field has raised the demand for microrefrigeration devices, but the refrigeration method of traditional compressors cannot be used for the refrigeration of small equipment due to the excessive volume and weight. Electrocaloric (EC) cooling has the advantages of environmental friendliness, easy miniaturization and light weight, so it has received extensive attention.The electrocaloric effect (ECE) is the phenomenon in which the temperature of a material changes due to the entropy change of the material when an electric field is applied and removed, achieving heat transfer.3 In recent years, major breakthroughs have been made in the EC field, which have drawn attention to this promising solid-state cooling method.4–12 The entropy change (ΔS) and temperature change (ΔT) are the key parameters used to evaluate the ECE. According to the Maxwell relation, EC refrigeration raises the requirements of a large pyroelectric coefficient, a low coercive field, a high breakdown electric field, a small heat capacity, etc. Most of the studies on the applications of ferroelectrics are based on inorganic ferroelectrics.13–16 Recently, molecular ferroelectrics have become a hotspot due to their environmental friendliness and low-temperature processing, mechanical flexibility and light weight, which are attractive for materials science and technology applications.17–26 From the ECE aspect, molecular ferroelectric materials have attracted increasing attention due to their excellent related properties. For example, [Hdabco]ClO4 (dabco = diazabicyclo[2.2.2]octane) was reported to have a large pyroelectric coefficient of 48![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 μC m−2 K−1, and Mdabco–NH4I3 (Mdabco = N-methyl-N′-diazabicyclo[2.2.2]octonium) has a coercive field (Ec) of 1 MV m−1, which is two orders of magnitude smaller than that of traditional EC materials.27,28 In addition to intrinsic properties that lead to large ΔS and temperature change ΔT, in real applications, an effective cooling power should be required, which is closely related to the mass of the material used.29 However, recent reports on molecular EC materials have involved either single crystal or thin film forms. The ECE achieved with single crystals suffers from the high cost and time consumption of growing large single crystals. Although these films are easy to prepare, the micrometre film thickness makes achieving a large mass almost impossible. On the other hand, traditional inorganic ferroelectric ceramics are accompanied by high processing temperatures, rigid structures, and energy-intensive manufacturing, which do not meet the current demands of energy conservation and emission reduction.25
000 μC m−2 K−1, and Mdabco–NH4I3 (Mdabco = N-methyl-N′-diazabicyclo[2.2.2]octonium) has a coercive field (Ec) of 1 MV m−1, which is two orders of magnitude smaller than that of traditional EC materials.27,28 In addition to intrinsic properties that lead to large ΔS and temperature change ΔT, in real applications, an effective cooling power should be required, which is closely related to the mass of the material used.29 However, recent reports on molecular EC materials have involved either single crystal or thin film forms. The ECE achieved with single crystals suffers from the high cost and time consumption of growing large single crystals. Although these films are easy to prepare, the micrometre film thickness makes achieving a large mass almost impossible. On the other hand, traditional inorganic ferroelectric ceramics are accompanied by high processing temperatures, rigid structures, and energy-intensive manufacturing, which do not meet the current demands of energy conservation and emission reduction.25
Here, to meet the material's mass requirement, we report a new application form of molecular EC materials – molecular ceramics. Different from traditional inorganic ferroelectric ceramics, which are accompanied by a high processing temperature and a rigid structure,25 a molecular ceramic with a performance comparable to that of a single crystal can be obtained by simply applying the low-temperature powder press method due to the plastic phase.30 The plastic phase refers to an intermediate state between liquid and solid and usually occurs in globular cationic compounds. The weaker intermolecular interactions contribute to the mechanical deformability of the ceramic, while ordinary crystals are normally nonflexible and brittle.31 The thickness and shape of the ceramic can be easily adjusted by adapting different moulding methods. To demonstrate the potential, we prepared a molecular ceramic of the molecular ferroelectric HQReO4 (HQ: protonated quinuclidine) with excellent EC performance, which is the first application attempt of molecular ceramics for the ECE. Compared with the thickness of ferroelectric thin films (micron scale), molecular ceramics do not have a thickness limitation, which has a crucial impact on the actual cooling power of the ECE.32 Additionally, the coercive field of HQReO4 is only approximately 10 kV cm−1, which is much smaller than that of poly(vinylidene fluoride trifluoroethylene) [P(VDF-TrFE)].33 Giant EC strengths of 1.7 J mm K−1 kg−1 kV−1 (ΔS/ΔE) and 0.91 K mm kV−1 (ΔT/ΔE) can be reached with a low electric field of 34 kV cm−1, which exceed those of most traditional inorganic ferroelectric ceramics.34–37 The maximum ΔS is 5.8 J K−1 kg−1, and the maximum ΔT is 3.1 K. This work proves the very large ECE in plastic molecular ceramics and opens up new ideas for EC solid-state refrigeration technology.
Results and discussion
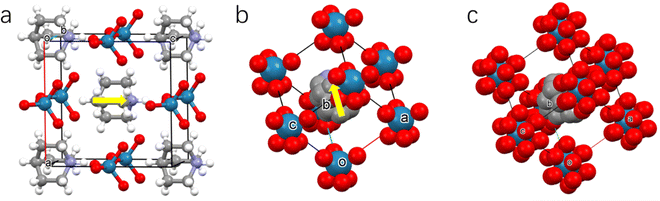
The crystalline salt of HQReO4 was obtained by evaporating equimolar solutions of perrhenic acid and quinuclidine (Fig. S1, ESI†), as previously described.38 In the low-temperature phase (LTP), HQReO4 crystallizes in the polar space group Pmn21 (point group mm2). The basic structure is composed of two ordered components, the [HQ]+ cation and the [ReO4]− anion, which promotes spontaneous ferroelectric polarization along the [001] direction (Fig. 1a). When the temperature is 350 K, HQReO4 in the intermediate-temperature phase (ITP) adopts the polar space group R3m (point group 3m). In the rhombohedral unit cell of the ITP, the polar [HQ]+ cation rotates along the molecular axis, inducing spontaneous polarization of the crystal along the polar threefold axis (Fig. 1b). At 380 K, in the high-temperature phase (HTP), [HQ]+ cations have a significant degree of rotational freedom, causing HQReO4 to crystallize in the nonpolar space group Pm![[3 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0033_0304.gif) m (point group m
m (point group m![[3 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0033_0304.gif) m). The structure shows a CsCl-type cubic packing with the [HQ]+ cation located in the centre and the [ReO4]− anion located at the eight corners of the cube, which suggests the plastic crystal phase for the HTP (Fig. 1c).
m). The structure shows a CsCl-type cubic packing with the [HQ]+ cation located in the centre and the [ReO4]− anion located at the eight corners of the cube, which suggests the plastic crystal phase for the HTP (Fig. 1c).
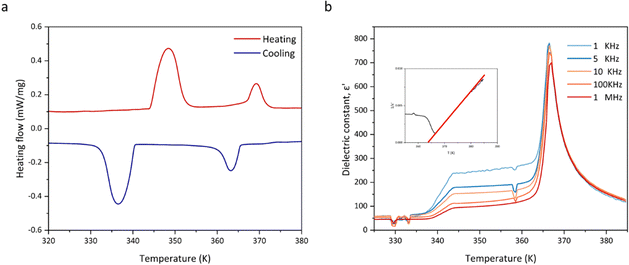
Because the maximum value of the ECE often occurs near the phase transition temperature, we focused on the analysis of the phase transition behaviour of HQReO4. Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) analysis and the temperature-dependent dielectric constant show that HQReO4 undergoes reversible solid–solid transitions at 348 K and 369 K upon heating (Fig. 2a and b). Fig. 2b describes the temperature dependence of the real part (ε′) of the complex permittivity. The sharp peak that occurs at 369 K represents a ferroelectric-to-paraelectric transition. The value of ε′ obeys the Curie–Weiss law above 369 K. The linear fit to the Curie–Weiss law is inserted in Fig. 2b. The LTP and ITP are ferroelectric phases, while the HTP is a paraelectric phase. The wide thermal hysteresis of 11 K indicates that the ferroelectric–paraelectric phase transition is a first-order phase transition, which can be confirmed by the polarization mutation displayed by its spike temperature-dependent dielectric constant (Fig. 2b). The pyroelectric effect and ECE are inverse effects, and the polarization caused by the first-order phase transition brings a large pyroelectric coefficient to HQReO4, which also has positive implications for the ECE.39,40
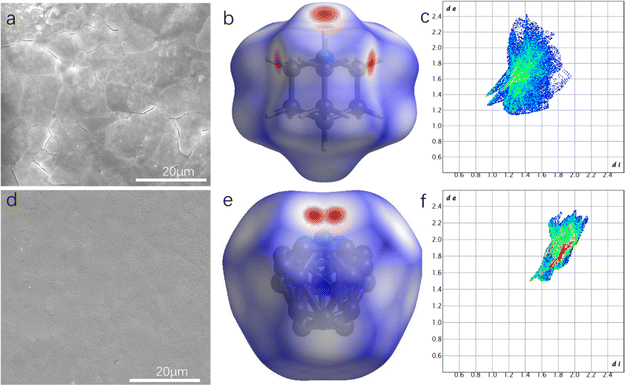
The molecular ceramic of HQReO4 was prepared in circular heated moulds at 373 K with a pressure of 454 MPa. The pressure holding time was set at 15 minutes to ensure shaping of the molecular ceramics. We obtained a molecular ceramic cylinder with a diameter of 13 mm and a thickness of 0.3 mm by this method. At present, a bottleneck in the application of thick films or bulk materials of EC materials is that the breakdown electric field is too close to the coercive field, which leads to easy breakdown and damage of materials under high cycling in practical applications.29,41 Reducing the porosity and microcracks of a bulk material is considered to be an important method to improve the breakdown electric field of the material.42 To intuitively study the plastic properties of the materials, scanning electron microscopy (SEM) was conducted. As shown in Fig. 3d, no crystal grains can be observed in the molecular ceramic in the HTP, and its pores and microcracks are quite few, much fewer than those in the LTP (Fig. 3a). The densification degree of the HQReO4 molecular ceramic has unparalleled advantages compared to inorganic materials such as BTO.43 To explore the internal causes of such advantages, a Nanoindenter was used to check the hardness. The Vickers hardness is only 12.8 HV, endowing HQReO4 with unique mechanical properties. This characteristic of quinuclidine perrhenate benefits from the spherical quinuclidine molecule and perrhenic acid. The spherical cations HQ+ and anions ReO4− rotate at high speed in the HTP, showing CsCl-type cubic packing, and their intermolecular forces are relatively weak. The Hirshfeld surfaces of HQReO4 at 300 K and 350 K are demonstrated in Fig. 3b and e, where the normalized contact distance is coloured differently based on the location and magnitudes of intermolecular interactions.44 The intermolecular contacts are marked in red when they are smaller than the sum of the van der Waals radii, while the longer contacts are marked in blue. The decoded two-dimensional (2D) fingerprint plot shifts in the longer contact direction with increasing temperature, indicating relaxed intermolecular interactions45 (Fig. 3c and f). In this state, quinuclidine perrhenate exhibits properties similar to those of liquids. The weak intermolecular forces prevent the crystallites from breaking when squeezed, and the crystallites exhibit a certain “fluidity”, which allows fewer pores and microcracks in the molecular ceramic. Excitingly, the HQReO4 molecular ceramic still maintains considerable ferroelectricity after 105 cycles,38 which lays the foundation for its application.
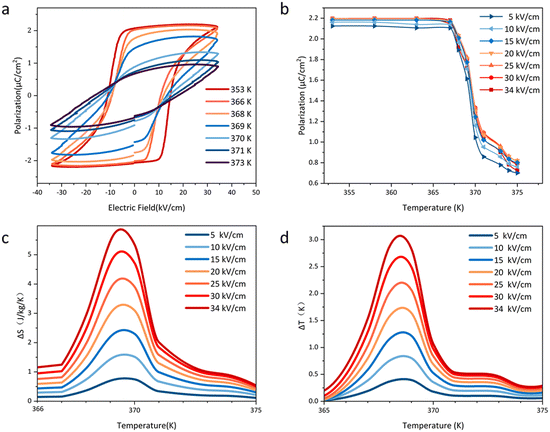
The temperature-dependent polarization–electric field (P–E) hysteresis loops of the molecular ceramic were measured with an electric field of 100 Hz to investigate its EC performance. Fig. 4a shows the P–E loop of HQReO4 from 353 K to 373 K. At 353 K, a saturated polarization of 2.1 μC cm−2 can be observed. Fig. 4b shows the temperature-dependent polarization obtained from Fig. 4a. With increasing temperature, the hysteresis loop abruptly changes, implying a sharp first-order phase transition at TC, which corresponds to the pyroelectric and DSC results. Notably, the coercive field of HQReO4 is only approximately 10 kV cm−1, which is much smaller than that of P(VDF-TrFE) (∼50 kV cm−1).33
The ECE of the HQReO4 molecular ceramic was calculated according to the Maxwell relation (dP/dT)E = (dS/dE)T. ΔS and ΔT were obtained from the equations:3
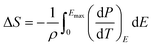 | (1) |
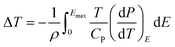 | (2) |
For further verification of the ECE, a thermodynamic calculation was proposed. The Landau theory of phase transition was developed to describe the phase transition behaviour of ferroelectrics near the transition point.46 A modified theory named Landau–Ginzburg–Devonshire (LGD) theory is used here to describe the behaviour of quinuclidine perrhenate near the phase transition point. According to LGD theory, the free energy of HQReO4 is expressed as:47
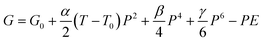 | (3) |
Conclusions
In summary, the EC application has raised the requirement for the quality of the material to ensure the cooling power of the EC module. We prepared a high-quality plastic molecular ferroelectric HQReO4 molecular ceramic by hot pressing. Giant EC strengths of 1.7 J mm K−1 kg−1 kV−1 (ΔS/ΔE) and 0.91 K mm kV−1 (ΔT/ΔE) were reached under a low electric field of 34 kV cm−1, which exceed those of most traditional inorganic ferroelectric ceramics; the maximum ΔS is 5.8 J K−1 kg−1, and the maximum ΔT is 3.1 K. The low porosity of the plastic molecular material allows the HQReO4 molecular ceramic to maintain good performance after 105 electric field cycles. The HQReO4 molecular ceramic with its excellent characteristics, such as a very large ECE, a high refrigeration power, a long working life and a simple preparation method, has provided ideas for new application forms of EC materials and has become a strong candidate for EC materials.Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.References
- F. Birol, International Energy Agency, 2018 Search PubMed.
- G. J. M. Velders, D. W. Fahey, J. S. Daniel, M. McFarland and S. O. Andersen, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2009, 106, 10949–10954 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. Correia and Q. Zhang, New Generation of Coolers, 2014, 34, 6–10 Search PubMed.
- A. S. Mischenko, Q. Zhang, J. F. Scott, R. W. Whatmore and N. D. Mathur, Science, 2006, 311, 1270–1271 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. Neese, B. Chu, S.-G. Lu, Y. Wang, E. Furman and Q. M. Zhang, Science, 2008, 321, 821–823 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Qian, D. Han, L. Zheng, J. Chen, M. Tyagi, Q. Li, F. Du, S. Zheng, X. Huang, S. Zhang, J. Shi, H. Huang, X. Shi, J. Chen, H. Qin, J. Bernholc, X. Chen, L.-Q. Chen, L. Hong and Q. M. Zhang, Nature, 2021, 600, 664–669 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X.-S. Qian, H.-J. Ye, Y.-T. Zhang, H. Gu, X. Li, C. A. Randall and Q. M. Zhang, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2014, 24, 1300–1305 CrossRef CAS.
- S. G. Lu, B. Rožič, Q. M. Zhang, Z. Kutnjak, X. Li, E. Furman, L. J. Gorny, M. Lin, B. Malič, M. Kosec, R. Blinc and R. Pirc, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2010, 97, 162904 CrossRef.
- G. Dai, S. Wang, G. Huang, G. Chen, B. Lu, D. Li, T. Tao, Y. Yao, B. Liang and S.-G. Lu, Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol., 2020, 17, 1354–1361 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Valant, Prog. Mater. Sci., 2012, 57, 980–1009 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Wu, F. Zhuo, H. Qiao, L. Kodumudi Venkataraman, M. Zheng, S. Wang, H. Huang, B. Li, X. Mao and Q. Zhang, Energy Environ. Mater., 2022, 5, 486–514 CrossRef CAS.
- H.-H. Wu, J. Zhu and T.-Y. Zhang, Nano Energy, 2015, 16, 419–427 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Wang, X. Wen, Y. Jia, M. Huang, F. Wang, X. Zhang, Y. Bai, G. Yuan and Y. Wang, Nat. Commun., 2020, 11, 1328 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. You, Z. Wu, L. Zhang, Y. Ying, Y. Liu, L. Fei, X. Chen, Y. Jia, Y. Wang, F. Wang, S. Ju, J. Qiao, C.-H. Lam and H. Huang, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2019, 58, 11779–11784 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Wang, S. Wang, Y. Meng, Z. Liu, D. Li, Y. Bai, G. Yuan, Y. Wang, X. Zhang, X. Li and X. Deng, Nat. Commun., 2022, 13, 4419 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. L. Yuan and S. W. Or, J. Appl. Phys., 2006, 100, 024109 CrossRef.
- Y.-M. You, W.-Q. Liao, D. Zhao, H.-Y. Ye, Y. Zhang, Q. Zhou, X. Niu, J. Wang, P.-F. Li, D.-W. Fu, Z. Wang, S. Gao, K. Yang, J.-M. Liu, J. Li, Y. Yan and R.-G. Xiong, Science, 2017, 357, 306–309 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y.-Y. Tang, Y.-L. Zeng and R.-G. Xiong, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2022, 144, 8633–8640 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Yao, Q. Pan, Z.-J. Feng, Y.-A. Xiong, T.-T. Sha, H.-R. Ji, Z.-X. Gu and Y.-M. You, APL Mater., 2021, 9, 040901 CrossRef CAS.
- W.-Q. Liao, D. Zhao, Y.-Y. Tang, Y. Zhang, P.-F. Li, P.-P. Shi, X.-G. Chen, Y.-M. You and R.-G. Xiong, Science, 2019, 363, 1206–1210 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H.-Y. Ye, Y.-Y. Tang, P.-F. Li, W.-Q. Liao, J.-X. Gao, X.-N. Hua, H. Cai, P.-P. Shi, Y.-M. You and R.-G. Xiong, Science, 2018, 361, 151–155 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D.-W. Fu, H.-L. Cai, Y. Liu, Q. Ye, W. Zhang, Y. Zhang, X.-Y. Chen, G. Giovannetti, M. Capone, J. Li and R.-G. Xiong, Science, 2013, 339, 425–428 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H.-Y. Zhang, X.-J. Song, X.-G. Chen, Z.-X. Zhang, Y.-M. You, Y.-Y. Tang and R.-G. Xiong, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2020, 142, 4925–4931 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Ai, Y.-L. Zeng, W.-H. He, X.-Q. Huang and Y.-Y. Tang, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2020, 142, 13989–13995 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H.-Y. Liu, H.-Y. Zhang, X.-G. Chen and R.-G. Xiong, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2020, 142, 15205–15218 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H.-Y. Zhang, Z.-X. Zhang, X.-G. Chen, X.-J. Song, Y. Zhang and R.-G. Xiong, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2021, 143, 1664–1672 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J.-J. Wang, D. Fortino, B. Wang, X. Zhao and L.-Q. Chen, Adv. Mater., 2020, 32, 1906224 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W. Li, G. Tang, G. Zhang, H. M. Jafri, J. Zhou, D. Liu, Y. Liu, J. Wang, K. Jin, Y. Hu, H. Gu, Z. Wang, J. Hong, H. Huang, L.-Q. Chen, S. Jiang and Q. Wang, Sci. Adv., 2021, 7, eabe3068 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Valant, A.-K. Axelsson, F. Le Goupil and N. M. Alford, Mater. Chem. Phys., 2012, 136, 277–280 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Harada, APL Mater., 2021, 9, 020901 CrossRef CAS.
- Q. Pan, Y.-A. Xiong, T.-T. Sha and Y.-M. You, Mater. Chem. Front., 2021, 5, 44–59 RSC.
- Y.-Y. Tang, P.-F. Li, P.-P. Shi, W.-Y. Zhang, Z.-X. Wang, Y.-M. You, H.-Y. Ye, T. Nakamura and R.-G. Xiong, Phys. Rev. Lett., 2017, 119, 207602 CrossRef PubMed.
- S. Horiuchi and Y. Tokura, Nat. Mater., 2008, 7, 357–366 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. A. Hamad, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2013, 102, 142908 CrossRef.
- B. Rožič, B. Malič, H. Uršič, J. Holc, M. Kosec and Z. Kutnjak, Ferroelectrics, 2011, 421, 103–107 CrossRef.
- Y. Bai, G.-P. Zheng and S.-Q. Shi, Mater. Res. Bull., 2011, 46, 1866–1869 CrossRef CAS.
- S.-B. Wang, G.-Z. Dai, Y.-B. Yao, X.-B. Zhao, T. Tao, B. Liang and S.-G. Lu, Scr. Mater., 2021, 193, 59–63 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Harada, T. Shimojo, H. Oyamaguchi, H. Hasegawa, Y. Takahashi, K. Satomi, Y. Suzuki, J. Kawamata and T. Inabe, Nat. Chem., 2016, 8, 946–952 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Liu, Z. Wu, T. Guan, H. Jiang, P. Long, X. Li, C. Ji, S. Chen, Z. Sun and J. Luo, Nat. Commun., 2021, 12, 5502 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Li, X.-S. Qian, H. Gu, X. Chen, S. G. Lu, M. Lin, F. Bateman and Q. M. Zhang, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2012, 101, 132903 CrossRef.
- M. Valant, A.-K. Axelsson, F. Le Goupil and N. M. Alford, Mater. Chem. Phys., 2012, 136, 277–280 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Gerson and T. C. Marshall, J. Appl. Phys., 1959, 30, 1650–1653 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Y. Lee, K. H. Cho and H. D. Nam, Ferroelectrics, 2006, 334, 165–169 CrossRef CAS.
- J. J. McKinnon, D. Jayatilaka and M. A. Spackman, Chem. Commun., 2007, 37, 3814–3816 RSC.
- Y. Xie, Y. Ai, Y.-L. Zeng, W.-H. He, X.-Q. Huang, D.-W. Fu, J.-X. Gao, X.-G. Chen and Y.-Y. Tang, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2020, 142, 12486–12492 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. F. Devonshire, London, Edinburgh Dublin Philos. Mag. J. Sci., 1949, 40, 1040–1063 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Huang, G. Zhang, X. Ma, D. Liang, J. Wang, Y. Liu, Q. Wang and L.-Q. Chen, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2018, 101, 1566–1575 CrossRef CAS.
Footnotes |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available. See DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/d2mh01296k |
| ‡ Hao-Ran Ji, Ru-Jie Zhou and Jie Yao contributed equally. |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2023 |