Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleCreative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported Licence
Recent advances in CO2 hydrogenation to methane using single-atom catalysts
Neha
Choudhary†
a,
Kallayi
Nabeela†
a,
Nirmiti
Mate
a and
Shaikh M.
Mobin
 *ab
*ab
aDepartment of Chemistry, Indian Institute of Technology Indore, Simrol, Khandwa Road, 433552, India. E-mail: xray@iiti.ac.in
bCenter for Advanced Electronics (CAE), Indian Institute of Technology Indore, Simrol, Khandwa Road, 433552, India
First published on 19th April 2024
Abstract
Single-atom catalysts (SACs) with isolated metal atoms dispersed on a solid support have been a hot topic in the last decade in heterogeneous catalysis. In a comprehensive attempt to minimize CO2 emissions with a persisting effect on global warming, the catalytic conversion of CO2 to methane can facilitate the convenient storage of excess energy as a green natural gas. Herein, we narrow the scope of this review by focusing on recent reports on thermocatalytic CO2 methanation using SACs with a special focus on the design and optimization strategies and existing challenges to overcome to get high selectivity and activity. It is highlighted that for higher selectivity towards methane over the CO product in CO2 hydrogenation, H2 dissociation and strong CO binding as an intermediate over the catalyst surface are the key steps. These insights are vital for determining the design principles of upcoming SACs to make them more efficient and selective in CO2 methanation.
Sustainability spotlightSingle-atom catalysts (SACs) are among the most important tools of the new era for commercializing CO2 emissions. Among CO2RR products, methane (CH4), being a renewable fuel hydrocarbon, has attracted significant attention, and its storage, transportation, and applications have been well researched. The invention of SACs on the whole greatly alleviates the obstacle of scaling-up processes that previously used precious metals as catalysts that are highly selective and effective toward CO2 methanation. In this review, the issue of product selectivity in CO2 hydrogenation, with a focus on mentioning the synthesis strategies of SACs and their utilization for CO2 methanation reactions, is highlighted. We strongly believe that this review will enlighten ongoing and future catalyst research, offering fundamental guidance to design multifarious SACs for CO2 methanation. |
1. Introduction
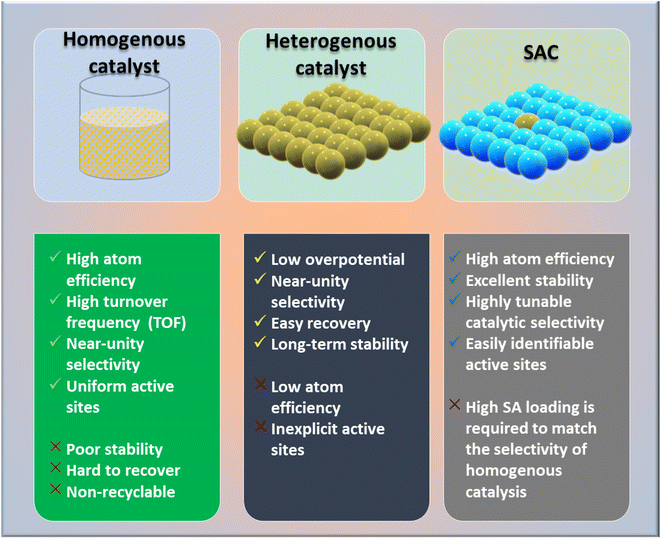
The global demand for modern material designs with redefined catalytic efficiency is driving the circular economy to new heights. As the need for carbon neutrality intensifies, newly invented catalysts for the conversion of CO2 by CO2 reduction reactions (CO2RR) or CO2 hydrogenation to value-added chemicals must be able to surpass the bottlenecks of the existing catalytic chemistry.1,2 Based on the actual requirements, diverse subcategories and plentiful designs of heterogeneous catalysts have been developed and applied by global industries. The most explored classes include metal oxides,3–8 metal sulfides,9–11 metal–organic frameworks (MOFs),12–17 covalent organic frameworks (COFs),18,19 carbonaceous materials20 (such as carbon nanofibers,21–24 graphene,25,26 and carbon nanotubes (CNTs)27–29), and conjugated microporous polymers (CMPs).30 In this context, single-atom catalysts (SACs) are one of the most promising classes of catalysts, and have shown good potential due to offering high catalytic activity and a high exposure to active sites together with good recyclability and reusability.Recently, SACs have been receiving much attention from the scientific community owing to their extraordinary properties of both homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysts (Fig. 1). SACs can solve the common issues of homogeneous catalysts, in term of their recyclability and high cost and difficult synthetic procedure, without compromising the product selectivity.31,32 Since SACs are considered one of the most important tools of the new era for commercializing CO2 emissions, considerable efforts have been made in the last decades to achieve the selective hydrogenation of CO2 for ensuring the desired products.33–37 Among CO2RR products, methane (CH4), being a renewable fuel hydrocarbon, has attracted much attention, and its storage, transportation, and applications have been well researched. To date, it has been reported that conventional catalysts can achieve a maximum 50% selectivity, but with an unsatisfactory practical current density (>100 mA cm−2).33 Herein, we highlight the issue of product selectivity in CO2 hydrogenation by considering the synthesis strategies of SACs and their utilization for CO2 methanation reactions.
1.1. Scope of the review
Owing to the meteoric rise in publications in SACs over the last few years, several attempts were previously made to review SACs, including the fundamentals,38,39 various advancements made in designing SACs,37 and theoretical insights40 into the electronic structure and mechanistic aspects of catalysis in various organic reactions.41 Many reviews have discussed the scope of SACs for CO2 hydrogenation transformation alone.36,42–50 Quite a large number of progress reports have also been made on SACs for the electrochemical reduction of CO2.36,42–47 Herein, we narrow the scope of this review by focusing on CO2RR methanation using SACs in light of relevant reports. For the sake of understanding, we provide a brief overview of the general aspects of SACs, including the theory, their structures, and common synthetic strategies. Afterward, we discuss how SACs have been employed for CO2 hydrogenation into useful products, further narrowing the discussion down to the methanation of CO2 in particular. Additionally, an earnest attempt is made to give the reader a comprehensive understanding of the mechanistic aspects of SAC methanation. It is remarkable that around one-third of reports on SACs are based on theoretical conceptualization,40 while a majority of the experimental reports endorsed their results based on theoretical grounds. We strongly believe that this review will enlighten ongoing and future catalyst research, offering fundamental guidance to aid the design of multifarious SACs for CO2 methanation.1.2. SACs: evolution, structure, and theory
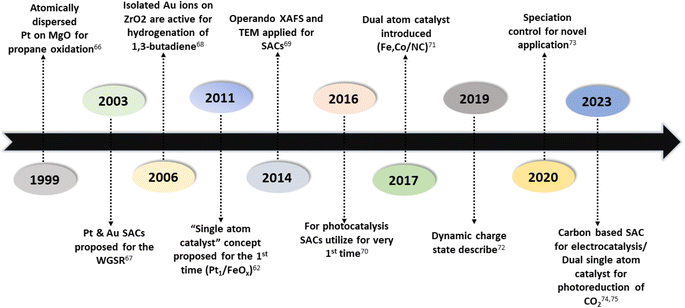
Numerous studies and observations have shown that the efficiency and selectivity of a heterogeneous catalyst are directly related to its size.51–56 It is evident that as a catalyst's size is decreased from the micron to cluster to atomic size, more catalytic access points are created or more active sites can be accessed, which leads to an increase in catalytic efficiency.57,58 It is noteworthy that even though downsizing catalysts into (sub)nanoclusters is highly desirable for catalysis, stabilizing such systems under realistic reaction conditions still requires significant effort, despite the advancements accomplished in nanotechnology. For example, metal nanoclusters characteristically display instability, especially under thermocatalytic conditions, which prompts sintering them into larger particles (such as nanoparticles, and nano aggregates).59–61 However, over time, it has been established that these clusters could better withstand extreme conditions by encapsulating them into molecular frameworks or cage-like structures, like zeolites, COFs, and MOFs.59 Nevertheless, reducing a catalytic active element to the atomic level (equivalent to a homogenous catalyst) can lead to improvements in catalytic efficiency, but these would still be highly unstable under real-time reaction conditions. This is because free atoms or active elements with unsaturated coordination sites are too reactive.62 Moreover, it has been revealed that the existence of an isolated atom can restrain such a risk when it is bound to a suitable support in a crystal lattice. A heterogeneous catalyst so formulated is called a single-atom catalyst (SAC) and can overcome many of the drawbacks of a typical heterogeneous catalyst.The term ‘single-atom catalyst’ was first coined by Qiao et al.62 in 2011. SACs can be defined as an ensemble of any catalytically active atom spatially secluded from its own species by directly bonding with a solid carrier host of another entity. The terminology SAC should not be confused with the isolated active elements immobilized with the linker functionalities of carriers.63 It is worth mentioning that, even before introducing the terminology SAC, many groups had already reported the exceptional catalytic features of SAC systems but variously termed these as ‘isolated atom’, ‘atomically dispersed’, or ‘single site catalysts’, where the single metal atoms were isolated on a metal oxide support.64,65 Seemingly, SACs stand as a bridge between both types of catalysts. A heterogeneous catalyst has a bad reputation for its less viable active sites for molecular transformation. Unlike a homogenous catalyst, a heterogeneous catalyst, however, offers better thermal stability and easy recovery. SACs provide a solid insoluble platform that is viable for easy recovery with enough chemical stability but with possibly 100% exposed active sites. The evolution of SACs right after heterogeneous catalysts is illustrated in Fig. 2.62,66–75
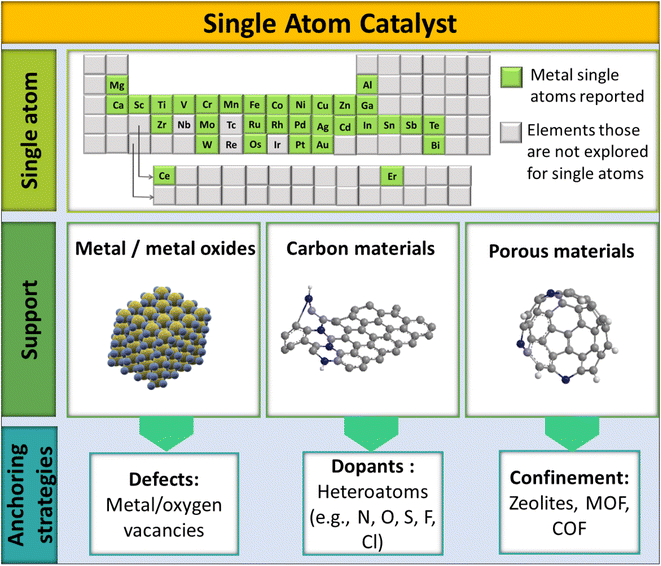
Typically, the design of SACs has three main components: (i) active single atom (SA) entity, (ii) SAC support, and (iii) anchoring sites and anchoring strategies, as shown in Fig. 3. Being highly selective and effective for CO2 methanation, the active SA entity of SACs is the part responsible for the catalytic action. Ru, Rh, and Pd are the most explored noble metals and are known for the selective methanation of CO2.76,77 A prudent and maximal utilization of these SAs in SACs would help economize CO2 methanation to a significant extent by reducing the overall consumption of precious metals. Besides, providing a proper coordination environment and electronic structure of a SA could, on the other hand, also address the limited activity and deactivation issue of low-cost metals, like Ni, toward the methanation of CO2. The SAC support, as the second major component of SACs, helps to stabilize the SA entity. The stability of the SA in SACs largely depends on how the SA is bonded to the support. Typically, there are 3 classes of support: metal oxides, carbon materials, and porous structures (zeolites, MOF, COF, etc.). The porous structures help to significantly increase SA loading onto the support matrix.78
The third designating entity in SACs is their anchoring strategy, which plays a decisive role in the SAC accomplishing a particular reaction out of a certain SA–support combination. The anchoring of the SA onto the support could be achieved using dopants, defects, or confinements. The heteroatom dopants in SACs can enhance the catalytic activity by creating surface defects to stabilize the structure.79–81 In such cases, single atom stabilization usually occurs through covalent/ionic interactions with the support surface.33,50 Doping can be done by introducing non-metals into the lattices or interstitial sites of a host system. Non-metallic elements with lone pairs (such as N, S, or O) doped in a host system can provide anchoring centers for metallic SAs, leading to the stabilization of the SAC.82–85 Defect engineering is another strategy to introduce vacancies onto a host material, which otherwise would not be introduced by doping.86 Surface step edge defects, unsaturated coordination sites, and cation vacancies are important anchoring centers for single atoms.87–89 A high SA loading can also be achieved by confining the active elements spatially in the pores of perforated materials (COFs, zeolites, MOFs) or by linking with coordination sites. For example, 20% atom dispersion was achieved by using melamine sponges with a carbon nitride backbone, which apparently helped to effectively disperse SAs throughout the host system.63 Thus the electronic structure of SACs will be governed by the coordination environment of the SA.40 Apparently, the electronic structure of SACs will differ from their bulk counterparts. Since SACs have a regular crystal lattice, simulating equivalent models largely gives insights into the electronic features of the anticipated structure. This is also vital to decide the design principles of SACs to make them selective toward a particular reaction, like the hydrogenation of CO2.
1.3. Synthesis
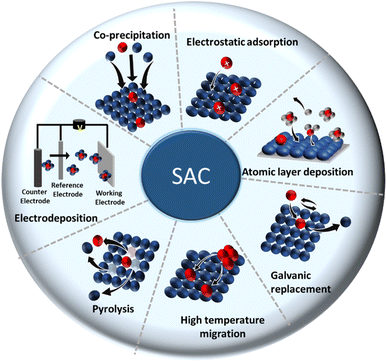
The bottleneck for acquiring SACs is the controlled growth of a SA on a support phase without compromising the atomic catalytic activity of the active phase. Common strategies that can be adopted to prepare SACs are: (1) lowering the active phase loading, (2) increasing the metal–support interactions, and (3) exploring vacancy defects on the support. Measures like mass-selected soft-landing and atomic layer deposition are helpful in establishing the above scenarios, enabling the precise regulation of the growth of SACs. Nevertheless, scaling up these methods and their economization pose problems. Recently, many wet chemical methods, which are usually simple and easy to implement, have been introduced as alternatives.41,62 However, most wet chemical processes rely on typically trial-and-error principles. Altogether, any synthetic routes that already exist or that are being constantly evolved can be classified broadly into bottom-up strategies (direct synthesis) and top-down strategies (post synthesis).Bottom-up strategies (direct synthesis) are the most common approach to achieve metal SACs. When the minority element precursor is adsorbed, reduced, and/or confined by the vacancy defects or voids present in the host material, single metals can be stabilized in solitary sites by surrounding them with the host material. This can happen during the preparation of the host material. Stabilizing isolated atoms gets the prime focus, which decides the ultimate thermodynamic stability of SACs. For further in-depth information, we refer to recent reviews dealing with preparation strategies.90,91
In top-down approaches (post synthesis), an isolated single metal of interest is introduced and gets stabilized in the bulk catalyst right after preparation.91–94 Many SACs are prepared by incorporating/depositing the active SA in pre-synthesized support having appropriate coordination sites. Common strategies are gas-phase, electrochemical, and wet chemical deposition.18 More strategies have been constantly evolving over time. The most common methods are discussed below. A concise illustration of the synthetic strategies is presented in Fig. 4. The major merits and demerits of the existing synthesis methods for SACs are listed in Table 1.
| Type of synthesis | Process | Advantages | Disadvantages | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coprecipitation | Precipitation of host precursor in parallel with SA precursor | • Simple operation | • Control over single atom loading is less | 62 and 107 |
| • Requires no complicated steps or any special equipment | • Heterogeneous active sites | |||
| • Post-treatments are required to limit the aggregation of isolated SA | ||||
| Electrostatic adsorption | Single metal species is adsorbed and stabilized on the support by a strong electrostatic interaction | • Simple operation | • Limited control over the SAC structure | 96 |
| • Scalable | • Heterogeneous active sites | |||
| • Post/pre-treatments are required to limit the aggregation of isolated SA | ||||
| Atomic layer deposition | Controlled single-atom-thick-layer deposition of a gas-phase precursor on a solid support | • Sub-nano level thickness control | • Low deposition rate | 97 and 98 |
| • Scalable | • Expensive | |||
| • Surface chemical selectivity | ||||
| • Applicable for the fabrication of SACs with a complex micropattern | ||||
| Electrodeposition | Deposition of an active metal containing an electrolyte onto the solid support | • Scalability | • Possible inhomogeneous coating of SA on the host | 99 |
| • Economical | ||||
| • Better control over the extent of the active element deposition | ||||
| Galvanic replacement | Oxidation of one metal (support) as a sacrificial template by other metal ions (SA component) that have a higher reduction potential | • Better control over the morphology (size and shape, composition) of the SAC | • Suitable for SA metals with a higher reduction potential than that of the host metal | 79, 100–102 and 104 |
| Pyrolysis | Metal on the C-based host at pyrolysis temperature removes its sacrificial host template, leaving SA on the C support | • Robust precursors | • Requires high-temperature (>800 °C) | 34 |
| • Good thermal stability and recyclability | • Applicable only for an SA on a C support | |||
| • Less control over the SA loading | ||||
| High-temperature atomic migration | Subjecting SA species from the precursor to high-temperature so they get trapped and stabilized onto the support phase by atomically migrating under elevated temperature (≥800 °C) | • Sinter resistant | • Choice of the SA is restricted to metals with a low free energy | 106 |
| • Suitable for thermocatalysis under elevated temperature conditions | • Support must be sinter resistant or must be able to undergo stable phase transition without affecting the ability to stabilize the SA |
(1) Coprecipitation approach: this is a wet chemical method that is known for its straightforwardness. The method needs neither complicated steps nor any special equipment and hence could be executed in any wet chemical laboratory. Here, host precursor are precipitated in parallel with the SA active precursor, resulting in the desired SAC. For example, Lin et al. synthesized single-atom Ir species dispersed on a FeOx support by precipitating from H2IrCl6 solution.95 In fact, the first identified SAC was prepared via a coprecipitation method to isolate Pt atoms dispersed in iron oxide.62 Thereafter, researchers devoted efforts to find a reliable root to achieve SACs by adopting different coprecipitation strategies suitable for a wide combination of catalytic active elements in a plethora of supports.91
(2) Electrostatic adsorption: this is a special wet impregnation method, wherein single metal species are adsorbed on the support by a strong electrostatic interaction. Here, a strong metal–support interaction prevents metal–metal interactions, guaranteeing a stable dispersion of the SA phase on the support phase. In some cases, electronic modification of isolated metal atoms by charged ions (cations or anions) helps to stabilize the isolated active species from agglomerating into clusters or nanoparticles. Modification of the precursors and support surface is, therefore, decisive in this method. For example, in SACs, it has been proven that the protection of isolated metal atoms, like Pt and Pd, from aggregation could be accomplished by introducing charged species, like ionic liquids (ILs), on supports, like hydroxyapatite (HAP).96 This will not only enhance the kinetic barrier of forming metal–metal bonds but also decrease the thermodynamic feasibility of metal aggregation.
(3) Atomic layer deposition (ALD): in the ALD process, a cyclic self-limiting reaction between a gas-phase precursor and a solid-host surface enables the controlled deposition of single-atom-thick layers one over other.97,98 The vapor-phase deposition technique provides a scalable way to achieve SACs with good uniformity and conformity. Due to its high surface chemical selectivity, the possibility of impurities from the residual components is less probable, unlike what happens in the simple coprecipitation method.
(4) Electrodeposition: electrodeposition involves the deposition of an active metal containing an electrolyte onto the solid support. Despite the scalability, economic advantages, and better control over the extent of active element deposition (owing to the control over the applied potential and amount of metal ion precursor in the electrolyte), electrodeposition possesses a major drawback of a possible inhomogeneous coating onto the host phase.39 Hence, a universal strategy for realizing SACs for a wider class of SA–support combinations is difficult to formulate, but not impossible. Indeed, Zhang et al.99 demonstrated a universal electrodeposition applicable for the deposition of 4d and 5d metals, like Ru, Rh, Pd, Ag, Pt, and Au, onto a variety of supports, like Co(OH)2, MnO2, MoS2, Co0.8Fe0.2Se2 nanosheets, and nitrogen-doped carbon.
(5) Galvanic replacement method: the process for the galvanic replacement reaction (GRR) involves redox reactions, wherein a metal precursor is oxidized, dissolved, and replaced/deposited by the reduction of another metal precursor with a higher reduction potential. Thus, the standard electrode potential of the precursor ions will decide the nature of pairing two components in a particular SAC.79 Toshima's group has introduced a crown jewel cluster concept to prepare highly active and scalable colloidal nanocatalyst Au/Pd clusters by adopting this method.100,101 Some of the top Pd atoms from Pd nanoclusters (Pd147, considered as a crown) were, thus, galvanically replaced by Au atoms (appeared as a jewel), leaving a high degree of coordinative unsaturation, responsible for high catalytic activity. However, the galvanic replacement in colloidal form often results in dissolution of the non-noble element by depositing the noble metal component. Also, the process is hard to predict, such that the resultant structure of the SAC is governed mainly by the nature of the protective agent and the morphology of the host material.102 Another drawback of this method is that this process is applicable only to those metals whose electrode reduction potential is higher than that of the host.103 Thus, it is speculated that when the reduction potential of the host component is higher than that of the SA component, an alternative way to achieve the SAC or single-atom alloy (SAC) is to downsize the host to promote a reverse replacement reaction.103 Besides, it is worth mentioning that galvanic replacement is not only restricted to noble metals but also can be applied for the replacement of transition metals (e.g., Ni), excluding Cu. For example, Peng et al.104 used Ni nanoparticles sized 4.4 nm as a host for the controlled deposition of single Pt atoms using galvanic replacement.
(6) Pyrolysis: this method forms a metal on a C-based host because of the decomposition of the precursor at pyrolysis temperature or by chemical leaching. On the other hand, this strategy involves a sacrificial host template (removed by acid leaching or oxidative calcination). The sacrificial material could be a MOF, COF, zeolite, or those that can hold metals via a variety of linkers. A uniformly dispersed SA system with enough thermal stability can be realized by the thermal decomposition of various MOFs. As an alternative, the desired active single metal ion can also be ion exchanged post-synthesis of the MOF, followed by high-temperature pyrolysis.35 Single/bimetallic zeolitic imidazolate frameworks (ZIFs) are the most explored MOFs for preparing SACs for CO2 reduction. Wang et al.34 successfully prepared Co-based SACs by high temperature pyrolysis of Co, Zn-based bimetallic ZIF precursors. Pyrolysis at a temperature above Zn metal's boiling point (i.e., >907 °C) facilitated carbonization of the organic linkers, and evaporation of the low boiling Zn, as well as a reduction of Co in the lattice.34 It also enabled control over the coordination numbers by varying pyrolysis temperature. A regular reduction in coordination number 4 to 2 was observed upon the increase in temperature from 800 °C to 1000 °C.
(7) High-temperature atomic migration: this is an outright method to achieve the atomic dispersion of thermally stable SACs by subjecting SA species from the precursor to get them to atomically migrate under elevated temperature (≥800 °C), then trapped and stabilized onto the support phase.105 Generally, a high-temperature treatment will be destructive to the precursor host system. This is because the high-temperature will facilitate the migration of the SA with high free energy in the host system, which then has the tendency to form larger aggregates, clusters, or nanoparticles (otherwise called Ostwald ripening).106 Thus, one way to control the sintering possibility is to use noble metals with a low free energy in defective metal oxides, like CeO2. However, this only works for a low level loading of SA. At higher noble metal loading, it is almost impossible to achieve atomic dispersion due to the uncontrollable formation of defects at elevated temperature. An alternative approach for achieving a higher SA loading on the supports hence can be formulated by considering the thermal behavior of the support material. For instance, Yan et al.106 developed a sintering resistant (thermally stable) SAC by atomically dispersing Pt onto MnOx, taking advantage of its existence in multiple oxidation states and possible structural reconstruction during thermal treatments. During calcination at 800 °C, the initial Mn3O4 lattice support was reformed into Mn2O3 in the presence of O2 and water vapor. In the latter case, the atomic dispersion of Pt SA was further stabilized by the strong interaction existing between the support Mn2O3 (Mn in a high valence state with a possibly increased number of coordination) and Pt atoms.
2. SACs for CO2 hydrogenation
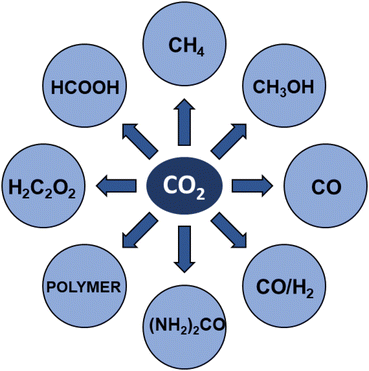
Carbon dioxide is the major greenhouse gas as its emission is leading to increased global warming and unpredictable weather change.108,109 The conversion of CO2 into value-added chemicals is in great demand owing to its harmful impact on the environment and humans. However, the direct conversion of CO2 into value-added chemicals, like methane, methanol, carbon monoxide, urea, formic acid, ethanol, ethylene, ethane, acetic acid, acetone, and propanol (Fig. 5)110–112 is still challenging due to the high thermodynamic stability of CO2. Typically, the structural characteristics of catalysts have a significant impact on the CO2 reduction reaction process. Mainly, CO desorption from a catalyst's surface is the key step for the selective conversion of CO2. If CO desorption is favorable, then the reverse water gas shift reaction (RWGS) is dominant. Otherwise, additional hydrogenation occurs to produce compounds like methane or formic acid.113–115 The formation of CO from CO2 requires a large amount of energy and has a high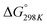 of 28.6 kJ mol−1. However, while the conversion of CO2 to methane is thermodynamically favored
of 28.6 kJ mol−1. However, while the conversion of CO2 to methane is thermodynamically favored 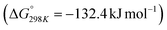 , conversion with high selectivity toward methane at low temperature is a real challenge and requires efforts to improve the catalytic activity at lower temperature.113,116–118 Additionally, CO2 hydrogenation to methanol is also thermodynamicallyfavorable
, conversion with high selectivity toward methane at low temperature is a real challenge and requires efforts to improve the catalytic activity at lower temperature.113,116–118 Additionally, CO2 hydrogenation to methanol is also thermodynamicallyfavorable 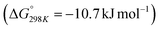 and exothermic, which means it needs to be performed at low reaction temperature. Furthermore, the formation of formic acid is comparatively less thermodynamically favorable and requires an alkaline reaction medium or additives for the reaction to proceed.119–121
and exothermic, which means it needs to be performed at low reaction temperature. Furthermore, the formation of formic acid is comparatively less thermodynamically favorable and requires an alkaline reaction medium or additives for the reaction to proceed.119–121
Recently, Wu et al.122 and Liu et al.50 reported mechanistic insights into the electrocatalytic, photocatalytic, and thermocatalytic conversion of carbon dioxide into various chemicals using SACs. To scale-up the conversion of CO2 to the industrial level, thermocatalysis is an easier approach, but it involves a high reaction temperature.122 The conversion of CO2 into various value-added chemicals involves, first the formation of CH4, CH3OH, HCOOH, and C2+ fuels or hydrocarbons and then thermocatalytic CH4 reforming into H2 generation (Fig. 6), making it environmentally benign and sustainable process.59
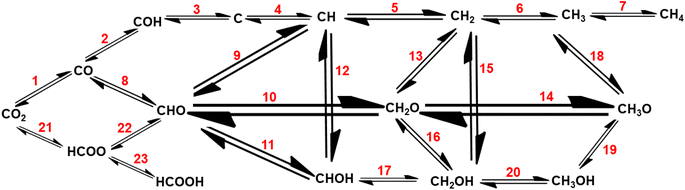 | ||
| Fig. 6 Mechanistic reaction pathways for CO2 hydrogenation to various reduced forms, like methane, methanol, and formic acid. | ||
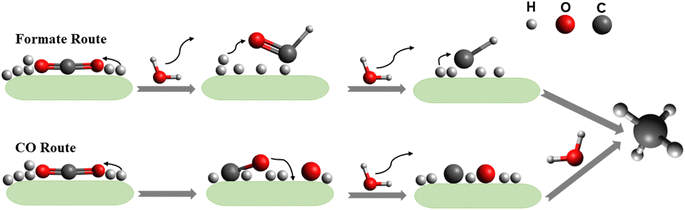
As this review focuses on the thermocatalytic conversion of CO2 into methane using SACs, a discussion on the general mechanism for CO2 conversion to methane (as illustrated in Fig. 7) would be helpful. The typical CO2 hydrogenation can be divided into two major accepted pathways: (1) CO pathway and (2) formate pathway.123
As shown in Fig. 7, in the formate pathway, formate species serve as the primary intermediate products. This is referred to as the CO2 associative pathway of the CO2 hydrogenation reaction. In this pathway, initially chemisorbed CO2 species can transform into bidentate formates (HCOO*) before progressing to formic acid (HCOOH), with CH4 produced as a result. However, in the CO pathway, known as the dissociative pathway of the CO2 hydrogenation reaction, the adsorbed *CO2 species dissociate into *CO and *O. Consequently, the generated *CO species may further dissociate into carbon species (*C). These carbon species (*C) afterward undergo hydrogenation to form CH4 through interaction with dissociated H2 molecules that remain on the metal particles and desorb from the catalyst surface. Meanwhile, *O species can react with hydrogen to generate H2O.76,124,125
3. CO2 methanation using SACs
The conversion of CO2 to methane is captivating as it can replace the traditional fossil fuels and can be utilized for the synthesis of syngas. Methane (CH4) is a beneficial fossil fuel for the environment since it produces more heat and light energy per mass than other hydrocarbons, such as coal and gasoline that have been processed from oil. The hydrogenation of CO2 at lower reaction temperature is a challenging task but is highly desirable. In this regard, various efforts have been made by researchers to enhance the selectivity toward methane rather than CO. For these reactions, the catalysts should be stable and active at high reaction pressure and temperature, and tuning of the catalysts is usually required, in which the interfacial effect between the metal atom and supported material plays a vital role. The use of a support material prevents the metal atoms or particles from agglomeration and preserves the activity of the metal component. However, the interfacial effects between the metal and support are highly affected by the particle size, surface area, porosity, acidity, and basicity of the catalyst, which consequently affects the catalytic activity and selectivity of the material for the conversion reaction. Also, the utilization of supported metal catalysts is a better alternative to deal with the issue of the costly Ru-, Pt-, and Pd-based catalysts. In such metal catalysts, a very small amount (4–6 wt%) of precious metal is doped or dispersed over a low-cost metal support in the SAC. This approach decreases the overall cost of metal catalysts without compromising the catalytic activity.126,127 The atomically dispersed single-atom metals provide the active sites for the reaction and maximize the catalytic performance.128,129 In this context, zeolite-based SACs were synthesized to produce bi-functional materials, which have high catalytic activity as well as good water sorbent capability for CO2 methanation. Wei et al.130 synthesized 13X zeolite as a support material for SACs, where CeOx particles acted as a separator for Ni single atoms. The catalyst was synthesized by the chelation of Ni and Ce ions using citrate and was diffused over 13X zeolite. They observed that the Ce loading played a significant role in tuning of the catalyst's properties, like basicity, reducibility, and activity for the reaction. The balanced basicity and acidity allowed a well-managed interaction of CO2 with the surface of catalyst, so that the selectivity toward methane was not compromised. Among all the synthesized catalysts, 5%Ni2.5%Ce13X showed the highest conversion and selectivity toward methane at 360 °C for 200 h timescale. Furthermore, Fan and coworkers131 synthesized a Ru-supported catalyst on porous hexagonal boron nitride (pBN) and utilized this for CO2 conversion into methane with high conversion and selectivity. The use of a supported material can reduce the overall cost of the catalyst without compromising its activity and thermal stability. In a Ru supported over pBN catalyst, the pBN facilitated the dispersion of Ru and generated defects via B and N coordination, which reduced the valence state of atomic Ru. The Ru-supported pBN catalysts showed superior catalytic activity toward methane with ∼93.5% selectivity, whereas the Ru nanoparticles showed a lower conversion and selectivity during 110 h at 350 °C. Density functional theory (DFT) simulations proved that the increase in the CH4 generation rate was due to both the atomic-scale size and the low valence state of atomic Ru supported on pBN (Fig. 8). When they increased the Ru loading, aggregation occurred, leading to the formation of Ru nanoparticles and a low dispersion of Ru over the pBN support and as a result, the CO2 methanation selectivity decreased.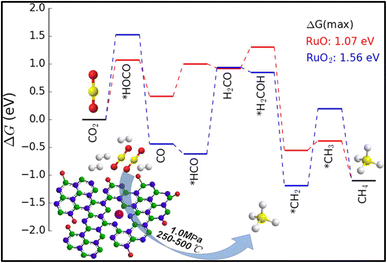 | ||
| Fig. 8 Energy profile diagram for methane formation using Ru/pBN SACs. Adapted with permission from ref. 131. Copyright 2019 American Chemical Society. | ||
Moreover, a comparison between a plasma-decomposed catalyst and a thermally decomposed catalyst was performed for Ni over a ZrO2 catalyst. Also, the interaction between Ni and the ZrO2 support was studied by Jia and coworkers132 for the CO2 methanation reaction, where Ni/ZrO2 with a uniform dispersion of Ni was prepared via a plasma decomposition method and thermal decomposition method. The plasma-decomposed catalyst had a more uniform dispersion of Ni metal over ZrO2 than the thermally synthesized catalyst. Owing to the high dispersion of Ni over the zirconia support, its activity was enhanced, which led to a quicker dissociative adsorption of H2 and H-spillover in the plasma-decomposed catalyst. This H-spillover increased the availability of H atoms for CO2 hydrogenation and generated oxygen vacancies on the surface of the zirconia. The oxygen vacancies ultimately increased the basicity to facilitate the CO2 adsorption and activation capability at the surface of the catalyst. Consequently, a 71.9% conversion with 69.5% selectivity at 300 °C toward methane with a 0.61 s−1 turnover frequency (TOF) was achieved at a low reaction temperature. Compared to the thermally synthesized catalyst, the TOF value was only 0.39 s−1 under the same reaction conditions with a 32.9% conversion and 30.3% selectivity toward methane. DRIFT analysis revealed that the plasma-decomposed catalyst followed the CO hydrogenation pathway at the highly exposed Ni(111) lattice plane and facilitated the decomposition of CO2 and formates into CO, as shown in Fig. 9. The thermally decomposed catalyst had a complex Ni crystal structure and more defects, which play important roles in formate hydrogenation.
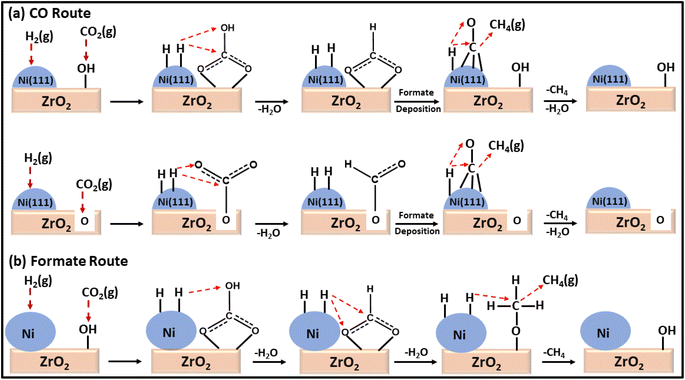 | ||
| Fig. 9 Mechanistic pathways over (a) Ni/ZrO2-plasma and (b) Ni/ZrO2-calcined catalysts for CO2 methanation. | ||
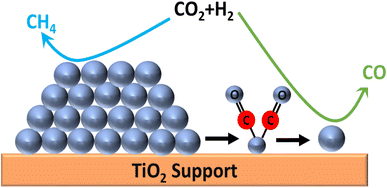
Furthermore, to stabilize Ru and Ni single atoms, Rivera-Cárcamo et al. synthesized CNT- and TiO2-supported SACs and utilized them for CO2 hydrogenation.133 Both the CNT and TiO2 supports were modified to create oxygen vacancies to stabilize the Ru and Ni single atoms. When the supported materials were utilized without creating defects, then nanoparticles and clusters of Ru and Ni were obtained. The doping of Na occurred when synthesizing TiO2-supported SACs, due to the presence of NaBH4. Further, the same authors synthesized Na-doped CNT for comparing the catalytic activity. Among all the synthesized catalysts compared for the CO2 hydrogenation reaction, the Ni-based catalysts all showed less activity than the Ru-based catalysts. Surprisingly, the Na-doped TiO2 catalyst showed enhanced activity and stability compared to the CNT-supported catalyst. However, Ni on the CNT-based SAC showed a higher selectivity toward CO formation, whereas the Ru/CNT-based SACs showed excellent selectivity toward methane formation. The charge transfer between the support and metal was the main reason for the high selectivity of the Ru SACs. They demonstrated that the electron-rich metal surface produced CH4, while the electron-deficient metal surface produced CO more selectively. Recently, an interesting result on a single atom alloy was reported by Tu et al.,134 whereby an Ir/Ni single atom alloy was synthesized via an impregnation method and utilized for CO2 methanation using a homemade mechanical reactor with an attached electromotor for controlling the vibration frequency. In the Ir–Ni catalyst, Ir was atomically dispersed and coordinated with the surface Ni atoms in the form of an Ir–Ni alloy, while the reduced Ir0 species presented an electron-efficient state. This Ir/Ni catalyst displayed superior catalytic performance with a TOF of 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 244 h−1 for methane formation and a 220 h lifetime at 350 °C without deactivation. When compared to the Ir–Ni/Al2O3 catalyst supported by an oxide, the Ir–Ni catalyst demonstrated superior coke-resistant performance. The multiple oxidation states of Ni, i.e., Ni0 and oxidative Ni2+, facilitated CO2 adsorption while the Ir–Ni alloy provided the reaction site for H2 activation and the subsequent hydrogenation reaction.
244 h−1 for methane formation and a 220 h lifetime at 350 °C without deactivation. When compared to the Ir–Ni/Al2O3 catalyst supported by an oxide, the Ir–Ni catalyst demonstrated superior coke-resistant performance. The multiple oxidation states of Ni, i.e., Ni0 and oxidative Ni2+, facilitated CO2 adsorption while the Ir–Ni alloy provided the reaction site for H2 activation and the subsequent hydrogenation reaction.
Moreover, it was reported by Liang et al. and Kwak et al. that the selectivity of the CO2 hydrogenation reaction could be shifted from CO to methane by modifying the catalyst.51,135 Liang et al.135 synthesized a Co single atom supported on SBA-15 via an ALD method, where the CoOx thickness was controlled by the ALD cycle numbers. Based on the ALD cycles, the catalysts were named as 50Co/SBA-15 and 500Co/SBA-15. Co2+ was stabilized by strong Co2+–O–Si bonds when the catalyst was exposed to H2 gas. The catalyst with an ultrastable Co2+ single atom with SBA-15 supported via Co–O–Si bonds exhibited 99% selectivity with a 304.6 mol CO2/mol Co/h TOF toward CO and was stable for up to 500 h at 600 °C. In contrast, the 500Co/SBA-15 catalyst had a weak interaction bond for Co–O–Co, whereby the Co species were partially reduced to metallic Co and this metallic Co further enhanced the product selectivity toward methane. Similarly, in the 300Co/SBA-15 catalyst, the methane selectivity increased with increasing the reduction temperature due to the increased metallic Co at higher reduction temperatures. The experimental and DFT studies revealed that on the single atomic Co2+ catalyst, shifting between the octahedral and tetrahedral fields played an important role and the catalyst exhibited H-assisted CO2 direct dissociation, as shown in Fig. 10. Similarly, Kwak et al.51 reported that a shifting of the catalytic activity could be observed from CO to methane when 3D metal clusters were formed with a higher Ru metal loading in a Ru single atom over an Al2O3 support. The Ru metal loading was varied from 0.1–5% and with increasing the Ru content, and the selectivity toward CO and methane was analyzed. When the metal content was low, i.e., ≤0.5%, the metal was present in the active metal phase with a high dispersion over alumina, and then the CO selectivity was high. As the metal loading of Ru increased from 1% and above, large metal clusters were formed, which led to a decrease in CO formation together with an increase in CH4 formation. The results revealed that the size of the metal clusters decides the production selectivity in the CO2 hydrogenation reaction. Additionally, the Arrhenius plots revealed activation energies of 82 and 62 kJ mol−1 for CO and methane formation, respectively, which confirmed that either the formation of methane followed a different reaction pathway without forming CO as an intermediate or by utilizing different active sites. This result was further confirmed by the difference in onset temperature between CO2 (∼325 °C) and CO (∼450 °C) reduction, i.e., ∼125 °C difference.
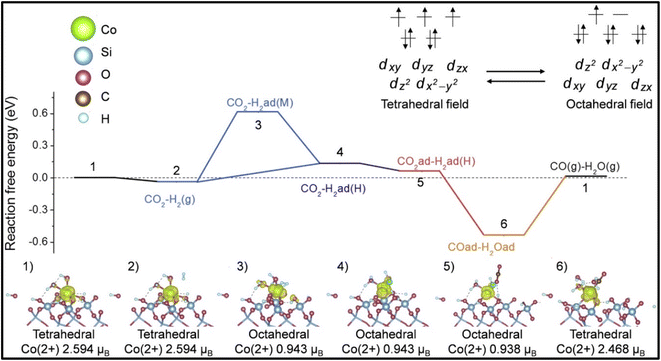 | ||
| Fig. 10 Mechanistic pathway over Co/SBA-15 catalyst for methanation. Adapted with permission from ref. 135. Copyright 2024 Elsevier B.V. | ||
Moreover, dual single-atom catalysts or dual atom catalysts (DACs) have been extensively explored due to their better performance compared to SACs.136 Owing to the presence of heterometal sites, the catalytic activity is enhanced with a few advantages: (1) one metal atom acts as the active site while the other has an electronic regulatory role; (2) both metal centers act as active sites to enhance the catalytic activity due to a synergistic effect;137,138 (3) the scaling relationship limit (SRL) based on SACs is broken by the adsorption effect, in which, providing more sites alters the adsorption structures. Recently, dual metal atom catalysts have been explored for various conversion reactions, like CO2, N2, and O2 gases. Consequently, Zhang et al.139 explored the efficiency of a dual-active-site tandem catalyst (Ru1Ni/CeO2) made of Ru single atoms (Ru1) and Ni nanoparticles. The results showed a substantially greater efficiency in the case of Ru1Ni/CeO2 than that of the Ru1/CeO2 and Ni/CeO2 catalysts. The Ru1Ni/CeO2 catalysts showed a 90% CO2 conversion and ∼99% CH4 selectivity at 325 °C. DFT calculations and the experimental results confirmed the synergistic effect between the Ru1 and Ni sites, which boosted the overall methanation pathway (Fig. 11). As shown in Fig. 11, first the dissociation of CO2 goes on at the Ru single atom, which is further hydrogenated to produce *CHO over the Ni NPs. Afterward, this *CHO is converted into methane over Ni sites of the Ni NPs. Hence, the Ru single atom species help to convert CO2 to CO, whereas the Ni sites promote the reaction further from CO to CH4.
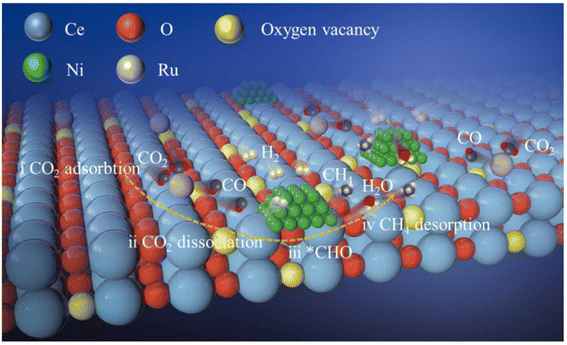 | ||
| Fig. 11 Schematic representation of CO2 methanation using Ru1Ni/CeO2 DACs. Adapted with permission from ref. 139. Copyright 2023 Elsevier B.V. | ||
In another report,140 a Ru1Ni SAA catalyst was synthesized over a SiO2 support and named as Ru1Ni/SiO2. First, Ni phyllosilicate (Ni-ph) was reduced to derive Ni NPs via a hydrothermal preparation method and then the GRR was performed in between ruthenium chloride and the as-synthesized Ni NPs. To compare the catalytic activity, a methanation test was performed, where the Ru1Ni/SiO2 DAC showed higher catalytic activity than Ni/SiO2 and other previously reported Ni-based catalysts. The DAC showed a TOF of 40.00 × 10−3 s−1, which was significantly higher than that of Ni/SiO2, i.e., 4.40 × 10−3 s−1. Based on DFT calculations and the experimental results, the reaction mechanism was proposed and is shown in Fig. 12. It was mentioned that initially, over the Ru and Ni sites of DAC, the adsorption of CO2 occurred. Consequently, this CO2 molecule dissociated into CO*, which further hydrogenated into methane over the Ru single atom. The atomically dispersed Ru species on the Ni surface exhibited a pronounced interaction with nickel atoms, resulting in significant charge transfer from Ru atoms to Ni atoms, facilitating the dissociation of CO2 into CO* for the high catalytic activity and selectivity toward methane formation.
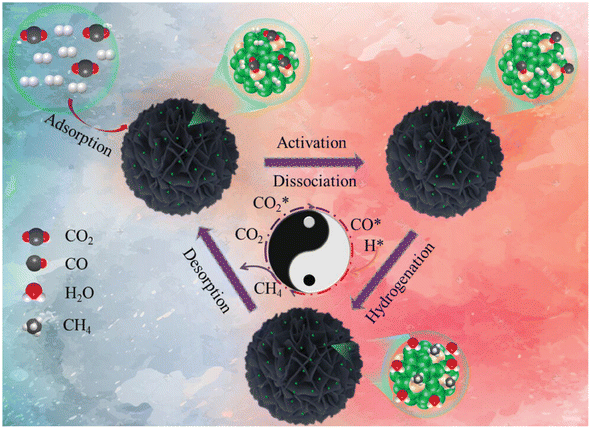 | ||
| Fig. 12 Schematic representation for the production of CH4 over Ru1Ni/SiO2. Adapted with permission from ref. 140. Copyright 2023 Wiley-VCH GmbH. | ||
In addition, Kikkawa et al.141,142 reported a Ni–Pt alloy (iso-Pt) produced on aluminum oxide (Al2O3) via an impregnation method under the pretreatment of hydrogen for reduction. The Ni–Pt alloy over alumina (Ni95Pt5/Al2O3) had isolated Pt atoms surrounded by Ni atoms, and exhibited a relatively high CH4-formation rate owing to a lower activation energy than that of the bulk-Ni (Ni/Al2O3) and bulk-Pt (Pt/Al2O3) catalysts. It was discussed that the iso-Pt species play a dual role: one is for H2 dissociation at low reaction temperature and the other one is tuning the d-electronic state by alloying with Ni atoms. The iso-Pt atoms enhanced the ability of the nearby Ni atoms to encourage more methanation with hydrogen, while weakening the C–O bond of the CO species connected to the Pt atoms. Through the electrical interactions between Ptδ− atoms and the surrounding Niδ+ atoms, isolated Pt atoms were produced on the surface of the Ni95Pt5 solid solution alloy, as shown in Fig. 13. Additionally, they also compared the catalytic activity of Ni95Pt5/Al2O3 with Ni/Al2O3. Moreover, they extended the study into the cooperative effect between the neighboring Ni atoms and isolated Pt atoms in the Pt–Ni alloy using in situ and transient Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) studies and kinetic studies for the production of methane from CO2. They observed that the formation of CO in the bridge form as an intermediate between the iso-Pt and Ni atoms played a significant role in selective methane production. The transient variations in the FT-IR spectra showed that the bridging CO species hydrogenated the CO species connected to the isolated Pt atoms in the direction of CH4. The kinetic studies revealed that after the addition of Pt species in the Ni catalyst, the H2-dissociation step became the rate determining step instead of the hydrogenation of the surface carbon species step. Also, the carbon species on the Ni–Pt alloy were hydrogenated more quickly due to the strong H2-dissociation capacity of the Pt atoms. These results confirmed that the isolated Pt atoms of the Ni–Pt catalyst play a dual role, acting as effective H2 dissociation sites to encourage hydrogenation and as adsorption sites for the on-top CO species to afford a high selectivity toward CH4 (Fig. 14).
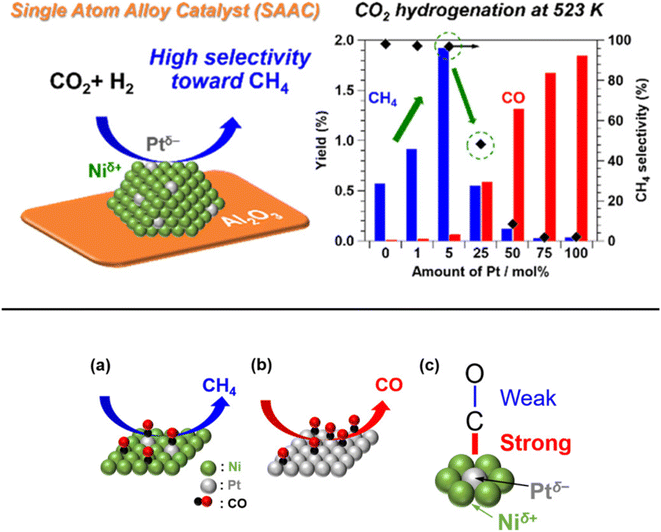 | ||
| Fig. 13 Representation of the adsorbed CO species on the surfaces of the (a) iso-Pt catalyst and (b) bulk-Pt catalyst, and (c) the adsorbed CO model on a single Ptδ− atom encircled by Niδ+ atoms. Adapted with permission from ref. 141. Copyright 2019 American Chemical Society. | ||
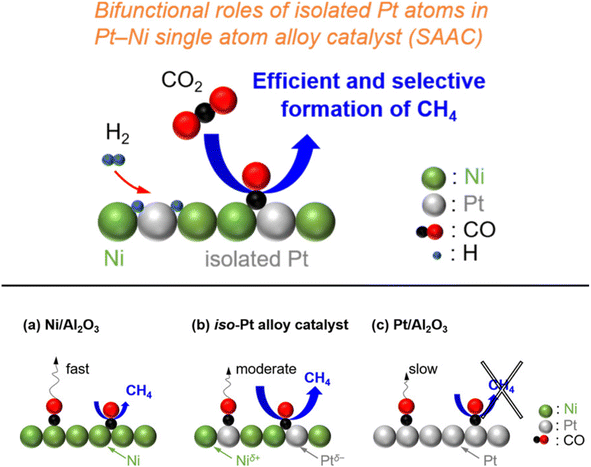 | ||
| Fig. 14 Graphical representation of the adsorbed species and CO2 hydrogenation over (a) Ni/Al2O3, (b) the iso-Pt catalyst, and (c) Pt/Al2O3. Adapted with permission from ref. 142. Copyright 2020 American Chemical Society. | ||
In addition, Kwak et al.143 synthesized Pd + La2O3/MWCNT, a bimetallic catalytic system combining SACs to boost the catalytic activity. Here La2O3 acted as a promoter, while atomically dispersed metallic Pd facilitated the dissociation of H2, and the size of the metal particles determined the selectivity of the product of the CO2 hydrogenation. With this approach, atomically dispersed Pd-based catalysts supported on Al2O3 and Pd over multiwalled carbon nanotube (MWCNT) catalysts were also synthesized. Initially, when their activity for the CO2 hydrogenation reaction was analyzed, the Pd/Al2O3 SACs showed high catalytic activity, while Pd/MWCNT was completely inactive for the hydrogenation of CO2. However, when La2O3 oxide was introduced to the inactive Pd/MWCNT catalyst, then the catalyst showed superior catalytic activity compared to both the Pd/Al2O3 and Pd/MWCNT catalysts. Nonetheless, selectivity and conversion toward methane were only obtained in the case of Pd/Al2O3, as shown in Fig. 15. In this catalyst, large Pd clusters were present over an alumina support, on which the initially generated CO was readily hydrogenated to methane, while the selectivity toward methane increased as the temperature increased due to sintering of the Pd active metal phase.
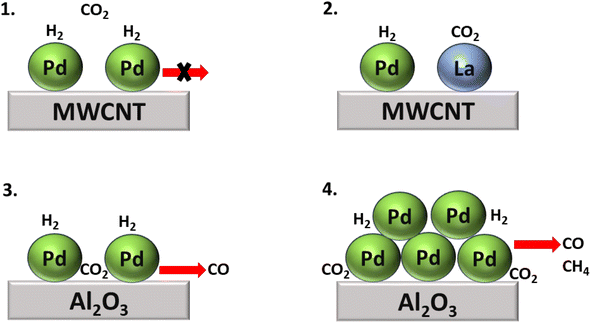 | ||
| Fig. 15 Comparative study of CO2 hydrogenation over (1) Pd/MWCNT, (2) Pd + La2O3/MWCNT, (3) large Pd cluster over Al2O3, and (4) Pd/Al2O3 SACs. | ||
Moreover, Shin et al.144 synthesized an atomically dispersed Pt catalyst over barium zirconate (BaZrO3 = BZ) perovskite with Co nanoparticles and compared the activity with γ-Al2O3-supported catalysts. Generally, the catalyst must transport cooperative hydrogen between the Pt metal support and Co species to produce the desired functionality, so that the dissociation of CO2 occurs on cobalt and that of H2 on the Pt metal. In this regard, they synthesized atomically dispersed Pt on the surface of Co nanoparticles. The catalyst was synthesized by the immobilization of Pt particles over the Co/BZ support with 1 wt% Co and 0.2 wt% Pt loading. They observed more than a 6-fold increase in CH4 formation rate with Pt on the Co/BZ support compared to that with the alumina support at 325 °C. This enhancement in activity in the case of the BZ support was due to the strong interaction between the Co particles and the BZ support, and the dissociation of CO2 and H2 was thus facilitated on the surface of Co and Pt, respectively. Despite this, more than 70% CH4 selectivity was obtained, which remained constant throughout the measured temperature range of 250–350 °C. The selectivity was 80% even at 325 °C, compared to only 43% selectivity with the γ-Al2O3 support. Additionally, when yttria was doped on zirconia (5 and 30 atom%, respectively), a decrease in catalytic activity was observed compared to when yttria was supported by BZ. However, even at low substitution levels, the activity was still higher than that of the γ-Al2O3 support.
In contrast, there are several reports where nanoparticles and nanoclusters have shown higher selectivity toward methane over SACs. However, isolated active sites of SACs suppress the side reactions and generate products with high selectivity. In this regard, the metal particle size must be taken into consideration, as it plays a significant role in the distribution of active sites and consequently in the reactivity and selectivity. The size effect in catalysis is a highly disputed and intricate subject, primarily because the most effective sizes of metal particles can vary significantly across different catalytic setups.60 It often requires careful experimental optimization and theoretical modeling to understand the interplay between the particle size, catalytic activity, and reaction mechanisms. Guo et al.60 studied the effect of the size of the particles in supported SACs for the CO2 hydrogenation reaction to methane in detail. They synthesized a Ru single atom supported on CeO2 nanowire, Ru nanoclusters (1.2 nm), and Ru nanoparticles (4 nm) and utilized these for CO2 hydrogenation to methane. It was observed that with the increase in the size range, the selectivity and activity toward methanation varied. The TOFs for methane selectivity with the Ru/CeO2 SACs, Ru nanoclusters, and Ru nanoparticles were 4.59 × 10−3, 7.41 × 10−3, and 5.30 × 10−4 s−1, respectively at 190 °C. The highest activity and selectivity toward methanation were observed in the case of the Ru nanoclusters. In situ DRIFT analysis revealed that the CO route was the predominant reaction pathway with Ce3+–OH sites and Ru sites near the metal–support interfaces acting as the active sites for CO2 dissociation and carbonyl hydrogenation, respectively. DFT calculations revealed that as the strong metal–support interaction (SMSI) of CeO2 with Ru atom decreased, CO adsorption on the surface of the catalysts increased, whereas weakening of the H-spillover effect enhanced the removal of water. Consequently, the activity and selectivity for methanation were greatly enhanced in the case of the Ru nanoclusters at low reaction temperatures, as shown in Fig. 16. The SMSI and H-spillover play important roles that can affect the activity of the catalysts with the size regimes, which was balanced in the case of the Ru nanocluster supported on CeO2 support.
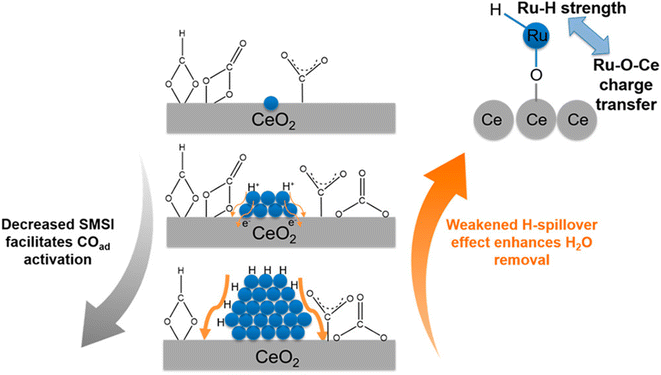 | ||
| Fig. 16 Effect of the competition of SMSI and H-spillover on CO activation. Adapted with permission from ref. 60. Copyright 2018 American Chemical Society. | ||
Furthermore, Matsubu et al.145 compared the catalytic activity of Rh nanoparticles and Rh supported on TiO2 SACs for CO2 hydrogenation reactions. They performed diffuse reflectance infrared Fourier transform spectroscopy (DRIFTS) analysis to quantify the Rh active sites in the synthesized catalysts. There was significant relation observed between the TOF of RWGS with Rhiso (Rh SACs) sites and the TOF for methanation with Rh nanoparticles (RhNP). When the CO2 hydrogenation reaction was performed, the nanoparticles showed selectivity toward CH4 and the SACs showed selectivity toward CO. They demonstrated that all the Rh sites in the Rh nanoparticles were surrounded by other Rh sites, which were more active for H2 dissociation and bound CO very strongly. Consequently, sequential hydrogenation occurred, and methane formation was favored over CO desorption. However, in the case of the SACs, i.e., the isolated Rh sites over the TiO2 support, the CO bonding was weak and the selectivity toward methane decreased. They concluded that the SACs and nanoparticles supported on the same metal oxide, i.e., TiO2, followed uniquely different pathways for CO2 hydrogenation and showed different selectivities, where disintegration of the nanoparticles played a considerable role in controlling the stability (Fig. 17).
Additionally, Jimenez et al.146 compared the catalytic activity of Co/SiO2 single-atom catalysts with Co clusters for the CO2 hydrogenation reaction. They observed that atomically dispersed Co over the SiO2 catalyst where the isolated Co was present in the tetrahedral Co2+ coordination showed the highest conversion toward CO, whereas cobalt clusters (sized 2–30 nm) exhibited selectivity toward CH4 formation under similar reaction conditions. They found that the local coordination environment of the Co metal played an important role to tune the selectivity toward methane. SACs with a distribution of Co0/(Co2++Co0) of 0.122–0.363 exhibited CO2 conversion at a 600 °C reduction temperature, while nanoparticles sized 2–30 nm exhibited CO2 conversion at higher temperature. When the Co0/(Co2++Co0) ratio was 0.363, the catalytic activity and selectivity toward methane were high whereas, then as the ratio decreases, the selectivity and conversion toward methane also decreased. The superior catalytic activity at 0.363 was estimated to be due to a synergistic effect between the metallic Co and Co2+. This result indicated the ensemble effect for transition metals in the subnanometer scale and the effect of the particle size for surface-sensitive reactions. Similarly, Wang et al.147 reported Pt/CeO2 SACs for the CO2 hydrogenation reaction and compared their catalytic activity with nanoclustered Pt catalysts. Atomically dispersed Pt over the CeO2 catalyst had only a 0.05 wt% loading of Pt, whereas the Pt/CeO2 nanoclustered catalyst had a 2 wt% Pt loading. To reduce the total cost of the catalyst, the usage of noble metal should be reduced and, in this context, a significantly lower amount of Pt was utilized in these catalysts. When the reaction was performed for CO2 hydrogenation, the atomically dispersed Pt/CeO2 displayed a 7.2 times higher reaction rate over the nanoclustered Pt/CeO2 catalyst even with a 40 times lower Pt loading. It was revealed that the activation of CO2 occurred on the oxide support while H2 dissociation occurred on the Pt metal. However, the atomically dispersed Pt SACs showed selectivity toward CO formation, whereas the nanoclustered Pt catalyst showed selectivity toward CH4 formation. It was demonstrated that on the dispersed Pt surface, CO binds weakly, which restricts its further hydrogenation to methane and consequently the CO selectivity increases. In both the nanoclusteres and SACs catalysts, the CeO2 present is rich with surface oxygen defects where the adsorption of CO2 occurs. As shown in Fig. 18, CO2 molecules first interact with the oxygen defects of CeO2 and bind with the oxygen of CO2 in a bidentate manner to yield carbonate species. Further, with increasing the reaction temperature, this oxygen is released from the oxygen defects and generates monodentate carbonate species, and consequently at higher reaction temperatures, methane production occurs. Moreover, another mechanism pathway was also proposed where a monodentate system is first generated on the CeO2 surface and reacts with the adsorbed H, which was observed in the in situ DRIFT analysis. Further, the OH− of bicarbonate is replaced with adsorbed H, which generates CO via the cleavage of C–H bonds of the aldehyde group on the single atomic Pt of the atomically dispersed Pt/CeO2 catalyst. This aldehyde further will not be hydrogenated to methane. This might be due to the strong bonding of the OH group with the CeO2 support of the SAC, which reduces the H-spillover, thus hindering CO dissociation and methane formation.
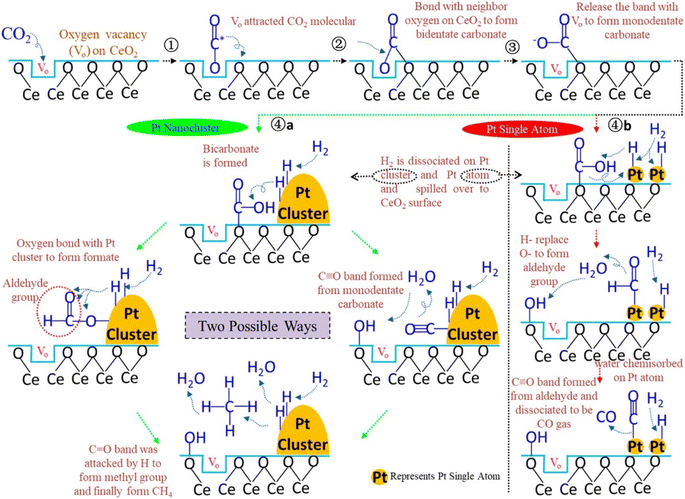 | ||
| Fig. 18 Plausible reaction mechanism over the Pt nanocluster and Pt SACs catalysts. Adapted with permission from ref. 147. Copyright 2018 American Chemical Society. | ||
4. Conclusions and future outlooks
A survey of the available reports on SACs for the hydrogenation of CO2 highlights that the scope grows rapidly toward commercializing natural gas to a promising regime. The invention of SACs on the whole greatly alleviates the obstacle of scaling-up processes that previously used precious metals as catalysts that are highly selective and effective toward CO2 methanation. The most comprehensive progress report on SACs attempted so far is provided with a special emphasis on the hydrogenation of CO2 to methane gas. Based on the survey, the below conclusive points are made and further future directions are suggested:(1) The scope for the methanation of CO2 by SACs is still in its infancy as few systems have yet managed to achieve sufficient selectivity. This is because theoretical studies say that conventional SACs show feasibility toward the hydrogenation of CO2 to formic acid. The bottleneck is the need to formulate SACs based on a clear understanding of the structural features that can control the product selectivity toward methanation during CO2 hydrogenation.
(2) Elaborated data technology is required to unravel the exact structures of SACs and the complex reaction network by theoretical analysis. The state-of-the-art computational details are currently unsatisfactory in this respect.
(3) The understanding of the complex mechanisms underlying catalysis in SAC systems has far to go. It is hard to establish a general reaction mechanism for CO2 conversion by SACs due to the limited understanding of the key reaction intermediates and the complex interactions between different phases of the SACs and reactants, even in the case of SACs with a well-defined structure.
(4) It is essential to reveal the temporal changes in the structural and electronic features of SACs under real-time reaction conditions. Exploiting new characterization tools may allow handling of these issues in the future. Many of the existing analysis tools are not sufficient to fully elucidate the complex processes. For example, the widely used in situ characterization tools, like Operando FT-IR analysis, do not yield information about weak interactions. Instead, Operando techniques, like near ambient pressure X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (NAP-XPS), endorsed by low energy electron diffraction (LEED) and scanning tunneling microscopy (STM) measurements can give more in-depth information about the transient intermediates formed during CO2 methanation.113
(5) The possibilities of providing a proper coordination environment with distinct electronic features for other low-cost metals, like Ni in SACs, which otherwise are not so promising for the methanation of CO2, would also expand the choice of active SAs in SACs to a wider margin in the periodic table.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.Acknowledgements
S. M. M. thanks SERB-DST, New Delhi, India (Project CRG/ 2020/001769), BRNS, Mumbai, India (Project 58/14/17/2020- BRNS/37215), and IIT Indore for financial support. N. C. and N. M. would like to thank UGC, New Delhi for fellowship. K. N. thanks DBT-RA program in Biotechnology and Life Sciences (DBTHRDPMU/DBT-RA/2022-23/EXT/59).References
- W. Li, X. Nie, H. Yang, X. Wang, F. Polo-Garzon, Z. Wu, J. Zhu, J. Wang, Y. Liu, C. Shi, C. Song and X. Guo, Crystallographic Dependence of CO2 Hydrogenation Pathways over HCP-Co and FCC-Co Catalysts, Appl. Catal., B, 2022, 315, 121529, DOI:10.1016/j.apcatb.2022.121529.
- J. Zhong, X. Yang, Z. Wu, B. Liang, Y. Huang and T. Zhang, State of the Art and Perspectives in Heterogeneous Catalysis of CO2 Hydrogenation to Methanol, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2020, 49(5), 1385–1413, 10.1039/C9CS00614A.
- J. Wang, X. Huang, S. Xi, H. Xu and X. Wang, Axial Modification of Cobalt Complexes on Heterogeneous Surface with Enhanced Electron Transfer for Carbon Dioxide Reduction, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2020, 59(43), 19162–19167, DOI:10.1002/anie.202008759.
- S. H. Lee, J. C. Lin, M. Farmand, A. T. Landers, J. T. Feaster, J. E. Avilés Acosta, J. W. Beeman, Y. Ye, J. Yano, A. Mehta, R. C. Davis, T. F. Jaramillo, C. Hahn and W. S. Drisdell, Oxidation State and Surface Reconstruction of Cu under CO2 Reduction Conditions from In Situ X-Ray Characterization, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2021, 143(2), 588–592, DOI:10.1021/jacs.0c10017.
- T.-C. Chou, C.-C. Chang, H.-L. Yu, W.-Y. Yu, C.-L. Dong, J.-J. Velasco-Vélez, C.-H. Chuang, L.-C. Chen, J.-F. Lee, J.-M. Chen and H.-L. Wu, Controlling the Oxidation State of the Cu Electrode and Reaction Intermediates for Electrochemical CO2 Reduction to Ethylene, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2020, 142(6), 2857–2867, DOI:10.1021/jacs.9b11126.
- Z. Zhang, F. Ahmad, W. Zhao, W. Yan, W. Zhang, H. Huang, C. Ma and J. Zeng, Enhanced Electrocatalytic Reduction of CO2 via Chemical Coupling between Indium Oxide and Reduced Graphene Oxide, Nano Lett., 2019, 19(6), 4029–4034, DOI:10.1021/acs.nanolett.9b01393.
- Y. Li, M. Wen, Y. Wang, G. Tian, C. Wang and J. Zhao, Plasmonic Hot Electrons from Oxygen Vacancies for Infrared Light-Driven Catalytic CO2 Reduction on Bi2O3−x, Angew. Chem., 2021, 133(2), 923–929, DOI:10.1002/ange.202010156.
- J. Song, Y. Lu, Y. Lin, Q. Liu, X. Wang and W. Su, A Direct Z-Scheme α-Fe2O3/LaTiO2N Visible-Light Photocatalyst for Enhanced CO2 Reduction Activity, Appl. Catal., B, 2021, 292, 120185, DOI:10.1016/j.apcatb.2021.120185.
- L.-P. Chi, Z.-Z. Niu, X.-L. Zhang, P.-P. Yang, J. Liao, F.-Y. Gao, Z.-Z. Wu, K.-B. Tang and M.-R. Gao, Stabilizing Indium Sulfide for CO2 Electroreduction to Formate at High Rate by Zinc Incorporation, Nat. Commun., 2021, 12(1), 5835, DOI:10.1038/s41467-021-26124-y.
- R. Zeng, K. Lian, B. Su, L. Lu, J. Lin, D. Tang, S. Lin and X. Wang, Versatile Synthesis of Hollow Metal Sulfides via Reverse Cation Exchange Reactions for Photocatalytic CO2 Reduction, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2021, 60(47), 25055–25062, DOI:10.1002/anie.202110670.
- J. Wang, S. Lin, N. Tian, T. Ma, Y. Zhang and H. Huang, Nanostructured Metal Sulfides: Classification, Modification Strategy, and Solar-Driven CO2 Reduction Application, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2021, 31(9), 2008008, DOI:10.1002/adfm.202008008.
- I. Hod, M. D. Sampson, P. Deria, C. P. Kubiak, O. K. Farha and J. T. Hupp, Fe-Porphyrin-Based Metal–Organic Framework Films as High-Surface Concentration, Heterogeneous Catalysts for Electrochemical Reduction of CO2, ACS Catal., 2015, 5(11), 6302–6309, DOI:10.1021/acscatal.5b01767.
- B.-X. Dong, S.-L. Qian, F.-Y. Bu, Y.-C. Wu, L.-G. Feng, Y.-L. Teng, W.-L. Liu and Z.-W. Li, Electrochemical Reduction of CO2 to CO by a Heterogeneous Catalyst of Fe–Porphyrin-Based Metal–Organic Framework, ACS Appl. Energy Mater., 2018, 1(9), 4662–4669, DOI:10.1021/acsaem.8b00797.
- S. N. Ansari, P. Kumar, A. K. Gupta, P. Mathur and S. M. Mobin, Catalytic CO2 Fixation over a Robust Lactam-Functionalized Cu(II) Metal Organic Framework, Inorg. Chem., 2019, 58(15), 9723–9732, DOI:10.1021/acs.inorgchem.9b00684.
- A. Bavykina, N. Kolobov, I. S. Khan, J. A. Bau, A. Ramirez and J. Gascon, Metal–Organic Frameworks in Heterogeneous Catalysis: Recent Progress, New Trends, and Future Perspectives, Chem. Rev., 2020, 120(16), 8468–8535, DOI:10.1021/acs.chemrev.9b00685.
- G. Zhai, Y. Liu, L. Lei, J. Wang, Z. Wang, Z. Zheng, P. Wang, H. Cheng, Y. Dai and B. Huang, Light-Promoted CO2 Conversion from Epoxides to Cyclic Carbonates at Ambient Conditions over a Bi-Based Metal–Organic Framework, ACS Catal., 2021, 11(4), 1988–1994, DOI:10.1021/acscatal.0c05145.
- J. Liang, Y.-Q. Xie, X.-S. Wang, Q. Wang, T.-T. Liu, Y.-B. Huang and R. Cao, An Imidazolium-Functionalized Mesoporous Cationic Metal–Organic Framework for Cooperative CO2 Fixation into Cyclic Carbonate, Chem. Commun., 2018, 54(4), 342–345, 10.1039/C7CC08630J.
- H. Zhong, R. Sa, H. Lv, S. Yang, D. Yuan, X. Wang and R. Wang, Covalent Organic Framework Hosting Metalloporphyrin-Based Carbon Dots for Visible-Light-Driven Selective CO2 Reduction, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2020, 30(35), 2002654, DOI:10.1002/adfm.202002654.
- X. Wang, Z. Fu, L. Zheng, C. Zhao, X. Wang, S. Y. Chong, F. McBride, R. Raval, M. Bilton, L. Liu, X. Wu, L. Chen, R. S. Sprick and A. I. Cooper, Covalent Organic Framework Nanosheets Embedding Single Cobalt Sites for Photocatalytic Reduction of Carbon Dioxide, Chem. Mater., 2020, 32(21), 9107–9114, DOI:10.1021/acs.chemmater.0c01642.
- J. Wu, T. Sharifi, Y. Gao, T. Zhang and P. M. Ajayan, Emerging Carbon-Based Heterogeneous Catalysts for Electrochemical Reduction of Carbon Dioxide into Value-Added Chemicals, Adv. Mater., 2019, 31(13), 1804257, DOI:10.1002/adma.201804257.
- B. Kumar, M. Asadi, D. Pisasale, S. Sinha-Ray, B. A. Rosen, R. Haasch, J. Abiade, A. L. Yarin and A. Salehi-Khojin, Renewable and Metal-Free Carbon Nanofibre Catalysts for Carbon Dioxide Reduction, Nat. Commun., 2013, 4(1), 2819, DOI:10.1038/ncomms3819.
- Y. Yu, R. Jin, J. Easa, W. Lu, M. Yang, X. Liu, Y. Xing and Z. Shi, Highly Active and Stable Copper Catalysts Derived from Copper Silicate Double-Shell Nanofibers with Strong Metal–Support Interactions for the RWGS Reaction, Chem. Commun., 2019, 55(29), 4178–4181, 10.1039/C9CC00297A.
- Y. Liu, S. Li, X. Yu, Y. Chen, X. Tang, T. Hu, L. Shi, M. Pudukudy, S. Shan and Y. Zhi, Cellulose Nanofibers (CNF) Supported (Salen)Cr(III) Composite as an Efficient Heterogeneous Catalyst for CO2 Cycloaddition, Mol. Catal., 2023, 547, 113344, DOI:10.1016/j.mcat.2023.113344.
- J.-C. Lee, J.-Y. Kim, W.-H. Joo, D. Hong, S.-H. Oh, B. Kim, G.-D. Lee, M. Kim, J. Oh and Y.-C. Joo, Thermodynamically Driven Self-Formation of Copper-Embedded Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Nanofiber Catalysts for a Cascade Electroreduction of Carbon Dioxide to Ethylene, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2020, 8(23), 11632–11641, 10.1039/D0TA03322G.
- J. Li, W.-Y. Zan, H. Kang, Z. Dong, X. Zhang, Y. Lin, Y.-W. Mu, F. Zhang, X.-M. Zhang and J. Gu, Graphitic-N Highly Doped Graphene-like Carbon: A Superior Metal-Free Catalyst for Efficient Reduction of CO2, Appl. Catal., B, 2021, 298, 120510, DOI:10.1016/j.apcatb.2021.120510.
- F. Yang, X. Ma, W.-B. Cai, P. Song and W. Xu, Nature of Oxygen-Containing Groups on Carbon for High-Efficiency Electrocatalytic CO2 Reduction Reaction, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2019, 141(51), 20451–20459, DOI:10.1021/jacs.9b11123.
- G. Tuci, A. Rossin, L. Luconi, C. Pham-Huu, S. Cicchi, H. Ba and G. Giambastiani, Pyridine-Decorated Carbon Nanotubes as a Metal-Free Heterogeneous Catalyst for Mild CO 2 Reduction to Methanol with Hydroboranes, Catal. Sci. Technol., 2017, 7(24), 5833–5837, 10.1039/C7CY01772C.
- F. Pan, B. Li, E. Sarnello, Y. Fei, Y. Gang, X. Xiang, Z. Du, P. Zhang, G. Wang, H. T. Nguyen, T. Li, Y. H. Hu, H.-C. Zhou and Y. Li, Atomically Dispersed Iron–Nitrogen Sites on Hierarchically Mesoporous Carbon Nanotube and Graphene Nanoribbon Networks for CO2 Reduction, ACS Nano, 2020, 14(5), 5506–5516, DOI:10.1021/acsnano.9b09658.
- T. Zhang, X. Han, H. Yang, A. Han, E. Hu, Y. Li, X. Yang, L. Wang, J. Liu and B. Liu, Atomically Dispersed Nickel(I) on an Alloy-Encapsulated Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Nanotube Array for High-Performance Electrochemical CO2 Reduction Reaction, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2020, 59(29), 12055–12061, DOI:10.1002/anie.202002984.
- J.-S. M. Lee and A. I. Cooper, Advances in Conjugated Microporous Polymers, Chem. Rev., 2020, 120(4), 2171–2214, DOI:10.1021/acs.chemrev.9b00399.
- N. Choudhary, S. Jiang, H. Pham, G. Kedarnath, A. Datye, J. T. Miller, A. K. Tyagi and M. M. Shaikh, Precisely Designed Cobalt Single Atom on ZrO2 Support for Chemical CO2 Fixation, Appl. Catal., B, 2024, 344, 123627, DOI:10.1016/j.apcatb.2023.123627.
- G. Li, X. Sui, X. Cai, W. Hu, X. Liu, M. Chen and Y. Zhu, Precisely Constructed Silver Active Sites in Gold Nanoclusters for Chemical Fixation of CO2, Angew. Chem., 2021, 133(19), 10667–10670, DOI:10.1002/ange.202100071.
- S.-F. Hung, A. Xu, X. Wang, F. Li, S.-H. Hsu, Y. Li, J. Wicks, E. G. Cervantes, A. S. Rasouli, Y. C. Li, M. Luo, D.-H. Nam, N. Wang, T. Peng, Y. Yan, G. Lee and E. H. Sargent, A Metal-Supported Single-Atom Catalytic Site Enables Carbon Dioxide Hydrogenation, Nat. Commun., 2022, 13(1), 819, DOI:10.1038/s41467-022-28456-9.
- X. Wang, Z. Chen, X. Zhao, T. Yao, W. Chen, R. You, C. Zhao, G. Wu, J. Wang, W. Huang, J. Yang, X. Hong, S. Wei, Y. Wu and Y. Li, Regulation of Coordination Number over Single Co Sites: Triggering the Efficient Electroreduction of CO2, Angew. Chem., 2018, 130(7), 1962–1966, DOI:10.1002/ange.201712451.
- C. Zhao, X. Dai, T. Yao, W. Chen, X. Wang, J. Wang, J. Yang, S. Wei, Y. Wu and Y. Li, Ionic Exchange of Metal–Organic Frameworks to Access Single Nickel Sites for Efficient Electroreduction of CO2, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2017, 139(24), 8078–8081, DOI:10.1021/jacs.7b02736.
- M. Li, H. Wang, W. Luo, P. C. Sherrell, J. Chen and J. Yang, Heterogeneous Single-Atom Catalysts for Electrochemical CO2 Reduction Reaction, Adv. Mater., 2020, 32(34), 2001848, DOI:10.1002/adma.202001848.
- Y. Huang, F. Rehman, M. Tamtaji, X. Li, Y. Huang, T. Zhang and Z. Luo, Mechanistic Understanding and Design of Non-Noble Metal-Based Single-Atom Catalysts Supported on Two-Dimensional Materials for CO2 Electroreduction, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2022, 10(11), 5813–5834, 10.1039/D1TA08337F.
- S. De, A. S. Burange and R. Luque, Conversion of Biomass-Derived Feedstocks into Value-Added Chemicals over Single-Atom Catalysts, Green Chem., 2022, 24(6), 2267–2286, 10.1039/D1GC04285H.
- C. S. Vasconcelos, L. Marchini, S. C. G. Lima, V. G. C. Madriaga, R. S. Ribeiro, V. Rossa, L. E. M. Ferreira, F. C. de Silva, V. F. Ferreira, F. Barboza Passos, R. S. Varma, M. W. Paixão, M. and T. M. Lima, Single-Atom Catalysts for the Upgrading of Biomass-Derived Molecules: An Overview of Their Preparation, Properties and Applications, Green Chem., 2022, 24(7), 2722–2751, 10.1039/D1GC03809E.
- L. Li, X. Chang, X. Lin, Z.-J. Zhao and J. Gong, Theoretical Insights into Single-Atom Catalysts, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2020, 49(22), 8156–8178, 10.1039/D0CS00795A.
- H. Yan, C. Su, J. He and W. Chen, Single-Atom Catalysts and Their Applications in Organic Chemistry, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2018, 6(19), 8793–8814, 10.1039/C8TA01940A.
- J. Ye, J. Yan, Y. Peng, F. Li and J. Sun, Metal-Organic Framework-Based Single-Atom Catalysts for Efficient Electrocatalytic CO2 Reduction Reactions, Catal. Today, 2023, 410, 68–84, DOI:10.1016/j.cattod.2022.09.005.
- H. Wang, Y. Tong and P. Chen, Microenvironment Regulation Strategies of Single-Atom Catalysts for Advanced Electrocatalytic CO2 Reduction to CO, Nano Energy, 2023, 118, 108967, DOI:10.1016/j.nanoen.2023.108967.
- M. Jia, Q. Fan, S. Liu, J. Qiu and Z. Sun, Single-Atom Catalysis for Electrochemical CO2 Reduction, Curr. Opin. Green Sustainable Chem., 2019, 16, 1–6, DOI:10.1016/j.cogsc.2018.11.002.
- C. Xu, A. Vasileff, Y. Zheng and S.-Z. Qiao, Recent Progress of 3d Transition Metal Single-Atom Catalysts for Electrochemical CO2 Reduction, Adv. Mater. Interfaces, 2021, 8(5), 2001904, DOI:10.1002/admi.202001904.
- D. Gao, T. Liu, G. Wang and X. Bao, Structure Sensitivity in Single-Atom Catalysis toward CO2 Electroreduction, ACS Energy Lett., 2021, 6(2), 713–727, DOI:10.1021/acsenergylett.0c02665.
- K. C. Kwon, J. M. Suh, R. S. Varma, M. Shokouhimehr and H. W. Jang, Electrocatalytic Water Splitting and CO2 Reduction: Sustainable Solutions via Single-Atom Catalysts Supported on 2D Materials, Small Methods, 2019, 3(9), 1800492, DOI:10.1002/smtd.201800492.
- S. Vijay, W. Ju, S. Brückner, S.-C. Tsang, P. Strasser and K. Chan, Unified Mechanistic Understanding of CO2 Reduction to CO on Transition Metal and Single Atom Catalysts, Nat. Catal., 2021, 4(12), 1024–1031, DOI:10.1038/s41929-021-00705-y.
- C. Gao, S. Chen, Y. Wang, J. Wang, X. Zheng, J. Zhu, L. Song, W. Zhang and Y. Xiong, Heterogeneous Single-Atom Catalyst for Visible-Light-Driven High-Turnover CO2 Reduction: The Role of Electron Transfer, Adv. Mater., 2018, 30(13), 1704624, DOI:10.1002/adma.201704624.
- L. Liu, M. Li, F. Chen and H. Huang, Recent Advances on Single-Atom Catalysts for CO2 Reduction, Small Struct., 2023, 4(3), 2200188, DOI:10.1002/sstr.202200188.
- J. H. Kwak, L. Kovarik and J. Szanyi, CO2 Reduction on Supported Ru/Al2O3 Catalysts: Cluster Size Dependence of Product Selectivity, ACS Catal., 2013, 3(11), 2449–2455, DOI:10.1021/cs400381f.
- S. ur Rehman, R. Ahmed, J. Liu, J. Wang, M. Sun, Z. Fang, M. A. Aslam, P. C. Morais, C. Wang and H. Bi, Decrease in the Particle Size and Coercivity of Self-Assembled CoNi Nanoparticles Synthesized Under a Repulsive Magnetic Field, Part. Part. Syst. Charact., 2019, 36(6), 1900047, DOI:10.1002/ppsc.201900047.
- A. Goulas, K. Song, Y. R. Johnson, G. P. Chen, J. A. Gokhale, A. C. Grabow, L. Dean and F. Toste, Selectivity Tuning over Monometallic and Bimetallic Dehydrogenation Catalysts: Effects of Support and Particle Size, Catal. Sci. Technol., 2018, 8(1), 314–327, 10.1039/C7CY01306J.
- B. Coq and F. Figueras, Structure–Activity Relationships in Catalysis by Metals: Some Aspects of Particle Size, Bimetallic and Supports Effects, Coord. Chem. Rev., 1998, 178–180, 1753–1783, DOI:10.1016/S0010-8545(98)00058-7.
- A. L. M. da Silva, J. P. den Breejen, L. V. Mattos, J. H. Bitter, K. P. de Jong and F. B. Noronha, Cobalt Particle Size Effects on Catalytic Performance for Ethanol Steam Reforming – Smaller Is Better, J. Catal., 2014, 318, 67–74, DOI:10.1016/j.jcat.2014.07.020.
- J. Quinson, M. Inaba, S. Neumann, A. A. Swane, J. Bucher, S. B. Simonsen, L. Theil Kuhn, J. J. K. Kirkensgaard, K. M. Ø. Jensen, M. Oezaslan, S. Kunz and M. Arenz, Investigating Particle Size Effects in Catalysis by Applying a Size-Controlled and Surfactant-Free Synthesis of Colloidal Nanoparticles in Alkaline Ethylene Glycol: Case Study of the Oxygen Reduction Reaction on Pt, ACS Catal., 2018, 8(7), 6627–6635, DOI:10.1021/acscatal.8b00694.
- X. Shi, Y. Lin, L. Huang, Z. Sun, Y. Yang, X. Zhou, E. Vovk, X. Liu, X. Huang, M. Sun, S. Wei and J. Lu, Copper Catalysts in Semihydrogenation of Acetylene: From Single Atoms to Nanoparticles, ACS Catal., 2020, 10(5), 3495–3504, DOI:10.1021/acscatal.9b05321.
- M. Lei, M. Gao, X. Yang, Y. Zou, A. Alghamdi, Y. Ren and Y. Deng, Size-Controlled Au Nanoparticles Incorporating Mesoporous ZnO for Sensitive Ethanol Sensing, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2021, 13(44), 51933–51944, DOI:10.1021/acsami.1c07322.
- F. Doherty, H. Wang, M. Yang and R. B. Goldsmith, Nanocluster and Single-Atom Catalysts for Thermocatalytic Conversion of CO and CO 2, Catal. Sci. Technol., 2020, 10(17), 5772–5791, 10.1039/D0CY01316A.
- Y. Guo, S. Mei, K. Yuan, D.-J. Wang, H.-C. Liu, C.-H. Yan and Y.-W. Zhang, Low-Temperature CO2 Methanation over CeO2-Supported Ru Single Atoms, Nanoclusters, and Nanoparticles Competitively Tuned by Strong Metal–Support Interactions and H-Spillover Effect, ACS Catal., 2018, 8(7), 6203–6215, DOI:10.1021/acscatal.7b04469.
- L. Liu and A. Corma, Metal Catalysts for Heterogeneous Catalysis: From Single Atoms to Nanoclusters and Nanoparticles, Chem. Rev., 2018, 118(10), 4981–5079, DOI:10.1021/acs.chemrev.7b00776.
- B. Qiao, A. Wang, X. Yang, L. F. Allard, Z. Jiang, Y. Cui, J. Liu, J. Li and T. Zhang, Single-Atom Catalysis of CO Oxidation Using Pt1/FeOx, Nat. Chem., 2011, 3(8), 634–641, DOI:10.1038/nchem.1095.
- S. K. Kaiser, Z. Chen, D. Faust Akl, S. Mitchell and J. Pérez-Ramírez, Single-Atom Catalysts across the Periodic Table, Chem. Rev., 2020, 120(21), 11703–11809, DOI:10.1021/acs.chemrev.0c00576.
- A. Wang, J. Li and T. Zhang, Heterogeneous Single-Atom Catalysis, Nat. Rev. Chem., 2018, 2(6), 65–81, DOI:10.1038/s41570-018-0010-1.
- L. DeRita, J. Resasco, S. Dai, A. Boubnov, H. V. Thang, A. S. Hoffman, I. Ro, G. W. Graham, S. R. Bare, G. Pacchioni, X. Pan and P. Christopher, Structural Evolution of Atomically Dispersed Pt Catalysts Dictates Reactivity, Nat. Mater., 2019, 18(7), 746–751, DOI:10.1038/s41563-019-0349-9.
- K. Asakura, H. Nagahiro, N. Ichikuni and Y. Iwasawa, Structure and Catalytic Combustion Activity of Atomically Dispersed Pt Species at MgO Surface, Appl. Catal., A, 1999, 188(1), 313–324, DOI:10.1016/S0926-860X(99)00247-1.
- Q. Fu, H. Saltsburg and M. Flytzani-Stephanopoulos, Active Nonmetallic Au and Pt Species on Ceria-Based Water-Gas Shift Catalysts, Science, 2003, 301(5635), 935–938, DOI:10.1126/science.1085721.
- X. Zhang, H. Shi and B.-Q. Xu, Catalysis by Gold: Isolated Surface Au3+ Ions Are Active Sites for Selective Hydrogenation of 1,3-Butadiene over Au/ZrO2 Catalysts, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2005, 44(43), 7132–7135, DOI:10.1002/anie.200502101.
- X. Li, X. Yang, J. Zhang, Y. Huang and B. Liu, In Situ/Operando Techniques for Characterization of Single-Atom Catalysts, ACS Catal., 2019, 9(3), 2521–2531, DOI:10.1021/acscatal.8b04937.
- X. Li, W. Bi, L. Zhang, S. Tao, W. Chu, Q. Zhang, Y. Luo, C. Wu and Y. Xie, Single-Atom Pt as Co-Catalyst for Enhanced Photocatalytic H2 Evolution, Adv. Mater., 2016, 28(12), 2427–2431, DOI:10.1002/adma.201505281.
- J. Wang, Z. Huang, W. Liu, C. Chang, H. Tang, Z. Li, W. Chen, C. Jia, T. Yao, S. Wei, Y. Wu and Y. Li, Design of N-Coordinated Dual-Metal Sites: A Stable and Active Pt-Free Catalyst for Acidic Oxygen Reduction Reaction, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2017, 139(48), 17281–17284, DOI:10.1021/jacs.7b10385.
- N. Daelman, M. Capdevila-Cortada and N. López, Dynamic Charge and Oxidation State of Pt/CeO2 Single-Atom Catalysts, Nat. Mater., 2019, 18(11), 1215–1221, DOI:10.1038/s41563-019-0444-y.
- S. K. Kaiser, E. Fako, G. Manzocchi, F. Krumeich, R. Hauert, A. H. Clark, O. V. Safonova, N. López and J. Pérez-Ramírez, Nanostructuring Unlocks High Performance of Platinum Single-Atom Catalysts for Stable Vinyl Chloride Production, Nat. Catal., 2020, 3(4), 376–385, DOI:10.1038/s41929-020-0431-3.
- Z. Qi, Y. Zhou, R. Guan, Y. Fu and J.-B. Baek, Tuning the Coordination Environment of Carbon-Based Single-Atom Catalysts via Doping with Multiple Heteroatoms and Their Applications in Electrocatalysis, Adv. Mater., 2023, 35(38), 2210575, DOI:10.1002/adma.202210575.
- X. Yue, L. Cheng, C. Guan, Y. Liao, Z. Xu, K. K. Ostrikov and Q. Xiang, In-Plane Palladium and Interplanar Copper Dual Single-Atom Catalyst in Bulk-Like Carbon Nitride for Cascade CO2 Photoreduction, Small, 2024, 20(13), 2308767, DOI:10.1002/smll.202308767.
- P. Panagiotopoulou, Hydrogenation of CO2 over Supported Noble Metal Catalysts, Appl. Catal., A, 2017, 542, 63–70, DOI:10.1016/j.apcata.2017.05.026.
- E. Furimsky, CO2 Hydrogenation to Methanol and Methane over Carbon-Supported Catalysts, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2020, 59(35), 15393–15423, DOI:10.1021/acs.iecr.0c02250.
- R. Liu and C. Streb, Polyoxometalate-Single Atom Catalysts (POM-SACs) in Energy Research and Catalysis, Adv. Energy Mater., 2021, 11(25), 2101120, DOI:10.1002/aenm.202101120.
- M. Chung, K. Jin, J. S. Zeng, T. N. Ton and K. Manthiram, Tuning Single-Atom Dopants on Manganese Oxide for Selective Electrocatalytic Cyclooctene Epoxidation, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2022, 144(38), 17416–17422, DOI:10.1021/jacs.2c04711.
- J. Li, S. Zhao, L. Zhang, S. P. Jiang, S.-Z. Yang, S. Wang, H. Sun, B. Johannessen and S. Liu, Cobalt Single Atoms Embedded in Nitrogen-Doped Graphene for Selective Oxidation of Benzyl Alcohol by Activated Peroxymonosulfate, Small, 2021, 17(16), 2004579, DOI:10.1002/smll.202004579.
- Q. Yang, C.-C. Yang, C.-H. Lin and H.-L. Jiang, Metal–Organic-Framework-Derived Hollow N-Doped Porous Carbon with Ultrahigh Concentrations of Single Zn Atoms for Efficient Carbon Dioxide Conversion, Angew. Chem., 2019, 131(11), 3549–3553, DOI:10.1002/ange.201813494.
- Q. Feng, S. Zhao, Q. Xu, W. Chen, S. Tian, Y. Wang, W. Yan, J. Luo, D. Wang and Y. Li, Mesoporous Nitrogen-Doped Carbon-Nanosphere-Supported Isolated Single-Atom Pd Catalyst for Highly Efficient Semihydrogenation of Acetylene, Adv. Mater., 2019, 31(36), 1901024, DOI:10.1002/adma.201901024.
- D. Wang, Z. Yuan, X. Wu, W. Xiong, J. Ding, Z. Zhang and W. Huang, Ni Single Atoms Confined in Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Nanotubes for Active and Selective Hydrogenation of CO2 to CO, ACS Catal., 2023, 13(10), 7132–7138, DOI:10.1021/acscatal.3c00767.
- R. Yun, F. Zhan, N. Li, B. Zhang, W. Ma, L. Hong, T. Sheng, L. Du, B. Zheng and S. Liu, Fe Single Atoms and Fe2O3 Clusters Liberated from N-Doped Polyhedral Carbon for Chemoselective Hydrogenation under Mild Conditions, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2020, 12(30), 34122–34129, DOI:10.1021/acsami.0c09124.
- Y. Zhang, S. Ye, M. Gao, Y. Li, X. Huang, J. Song, H. Cai, Q. Zhang and J. Zhang, N-Doped Graphene Supported Cu Single Atoms: Highly Efficient Recyclable Catalyst for Enhanced C–N Coupling Reactions, ACS Nano, 2022, 16(1), 1142–1149, DOI:10.1021/acsnano.1c08898.
- Y. Li, Z. He, F. Wu, S. Wang, Y. Cheng and S. Jiang, Defect Engineering of High-Loading Single-Atom Catalysts for Electrochemical Carbon Dioxide Reduction, Mater. Rep.: Energy, 2023, 3(2), 100197, DOI:10.1016/j.matre.2023.100197.
- J. Wu, J. Gao, S. Lian, J. Li, K. Sun, S. Zhao, Y. D. Kim, Y. Ren, M. Zhang, Q. Liu, Z. Liu and Z. Peng, Engineering the Oxygen Vacancies Enables Ni Single-Atom Catalyst for Stable and Efficient C-H Activation, Appl. Catal., B, 2022, 314, 121516, DOI:10.1016/j.apcatb.2022.121516.
- Q. Xu, C. Guo, B. Li, Z. Zhang, Y. Qiu, S. Tian, L. Zheng, L. Gu, W. Yan, D. Wang and J. Zhang, Al3+ Dopants Induced Mg2+ Vacancies Stabilizing Single-Atom Cu Catalyst for Efficient Free-Radical Hydrophosphinylation of Alkenes, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2022, 144(10), 4321–4326, DOI:10.1021/jacs.2c01456.
- M. Zhu, P. Tian, X. Cao, J. Chen, T. Pu, B. Shi, J. Xu, J. Moon, Z. Wu and Y.-F. Han, Vacancy Engineering of the Nickel-Based Catalysts for Enhanced CO2 Methanation, Appl. Catal., B, 2021, 282, 119561, DOI:10.1016/j.apcatb.2020.119561.
- H. Yan, Y. Lin, H. Wu, W. Zhang, Z. Sun, H. Cheng, W. Liu, C. Wang, J. Li, X. Huang, T. Yao, J. Yang, S. Wei and J. Lu, Bottom-up Precise Synthesis of Stable Platinum Dimers on Graphene, Nat. Commun., 2017, 8(1), 1070, DOI:10.1038/s41467-017-01259-z.
- J. Wang, Z. Li, Y. Wu and Y. Li, Fabrication of Single-Atom Catalysts with Precise Structure and High Metal Loading, Adv. Mater., 2018, 30(48), 1801649, DOI:10.1002/adma.201801649.
- H. Zhang, G. Liu, L. Shi and J. Ye, Single-Atom Catalysts: Emerging Multifunctional Materials in Heterogeneous Catalysis, Adv. Energy Mater., 2018, 8(1), 1701343, DOI:10.1002/aenm.201701343.
- C. Ling, Y. Ouyang, Q. Li, X. Bai, X. Mao, A. Du and J. Wang, A General Two-Step Strategy–Based High-Throughput Screening of Single Atom Catalysts for Nitrogen Fixation, Small Methods, 2019, 3(9), 1800376, DOI:10.1002/smtd.201800376.
- J. Wu, L. Xiong, B. Zhao, M. Liu and L. Huang, Densely Populated Single Atom Catalysts, Small Methods, 2020, 4(2), 1900540, DOI:10.1002/smtd.201900540.
- J. Lin, A. Wang, B. Qiao, X. Liu, X. Yang, X. Wang, J. Liang, J. Li, J. Liu and T. Zhang, Remarkable Performance of Ir1/FeOx Single-Atom Catalyst in Water Gas Shift Reaction, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2013, 135(41), 15314–15317, DOI:10.1021/ja408574m.
- S. Ding, Y. Guo, M. J. Hülsey, B. Zhang, H. Asakura, L. Liu, Y. Han, M. Gao, J. Hasegawa, B. Qiao, T. Zhang and N. Yan, Electrostatic Stabilization of Single-Atom Catalysts by Ionic Liquids, Chem, 2019, 5(12), 3207–3219, DOI:10.1016/j.chempr.2019.10.007.
- P. E. Imoisili, J. Ren and T.-C. Jen, Single-Atom Catalysts for Lithium Sulfur Batteries via Atomic Layer Deposition Process, Electrochem. Commun., 2022, 135, 107215, DOI:10.1016/j.elecom.2022.107215.
- J. Fonseca and J. Lu, Single-Atom Catalysts Designed and Prepared by the Atomic Layer Deposition Technique, ACS Catal., 2021, 11(12), 7018–7059, DOI:10.1021/acscatal.1c01200.
- Z. Zhang, C. Feng, C. Liu, M. Zuo, L. Qin, X. Yan, Y. Xing, H. Li, R. Si, S. Zhou and J. Zeng, Electrochemical Deposition as a Universal Route for Fabricating Single-Atom Catalysts, Nat. Commun., 2020, 11(1), 1215, DOI:10.1038/s41467-020-14917-6.
- H. Zhang, T. Watanabe, M. Okumura, M. Haruta and N. Toshima, Crown Jewel Catalyst: How Neighboring Atoms Affect the Catalytic Activity of Top Au Atoms?, J. Catal., 2013, 305, 7–18, DOI:10.1016/j.jcat.2013.04.012.
- H. Zhang, T. Watanabe, M. Okumura, M. Haruta and N. Toshima, Catalytically Highly Active Top Gold Atom on Palladium Nanocluster, Nat. Mater., 2012, 11(1), 49–52, DOI:10.1038/nmat3143.
- X. Kong, H. Wu, K. Lu, X. Zhang, Y. Zhu and H. Lei, Galvanic Replacement Reaction: Enabling the Creation of Active Catalytic Structures, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2023, 15(35), 41205–41223, DOI:10.1021/acsami.3c08922.
- J. Mao, J. Yin, J. Pei, D. Wang and Y. Li, Single Atom Alloy: An Emerging Atomic Site Material for Catalytic Applications, Nano Today, 2020, 34, 100917, DOI:10.1016/j.nantod.2020.100917.
- Y. Peng, Z. Geng, S. Zhao, L. Wang, H. Li, X. Wang, X. Zheng, J. Zhu, Z. Li, R. Si and J. Zeng, Pt Single Atoms Embedded in the Surface of Ni Nanocrystals as Highly Active Catalysts for Selective Hydrogenation of Nitro Compounds, Nano Lett., 2018, 18(6), 3785–3791, DOI:10.1021/acs.nanolett.8b01059.
- P. Yin and B. You, Atom Migration-Trapping toward Single-Atom Catalysts for Energy Electrocatalysis, Mater. Today Energy, 2021, 19, 100586, DOI:10.1016/j.mtener.2020.100586.
- D. Yan, J. Chen and H. Jia, Temperature-Induced Structure Reconstruction to Prepare a Thermally Stable Single-Atom Platinum Catalyst, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2020, 59(32), 13562–13567, DOI:10.1002/anie.202004929.
- J. Wang, Z. Li, Y. Wu and Y. Li, Fabrication of Single-Atom Catalysts with Precise Structure and High Metal Loading, Adv. Mater., 2018, 30(48), 1801649, DOI:10.1002/adma.201801649.
- R. Sen, A. Goeppert, S. Kar and G. K. S. Prakash, Hydroxide Based Integrated CO2 Capture from Air and Conversion to Methanol, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2020, 142(10), 4544–4549, DOI:10.1021/jacs.9b12711.
- N. S. Diffenbaugh, D. Singh, J. S. Mankin, D. E. Horton, D. L. Swain, D. Touma, A. Charland, Y. Liu, M. Haugen, M. Tsiang and B. Rajaratnam, Quantifying the Influence of Global Warming on Unprecedented Extreme Climate Events, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2017, 114(19), 4881–4886, DOI:10.1073/pnas.1618082114.
- A. S. Agarwal, E. Rode, N. Sridhar and D. Hill, Conversion of CO2 to Value Added Chemicals: Opportunities and Challenges, in Handbook of Climate Change Mitigation and Adaptation, ed. M. Lackner, B. Sajjadi and W.-Y. Chen, Springer International Publishing, Cham, 2022; pp pp 1585–1623, DOI:10.1007/978-3-030-72579-2_86.
- A. Modak, P. Bhanja, S. Dutta, B. Chowdhury and A. Bhaumik, Catalytic Reduction of CO2 into Fuels and Fine Chemicals, Green Chem., 2020, 22(13), 4002–4033, 10.1039/D0GC01092H.
- M. Kosari, A. M. H. Lim, Y. Shao, B. Li, K. M. Kwok, A. M. Seayad, A. Borgna and H. C. Zeng, Thermocatalytic CO2 Conversion by Siliceous Matter: A Review, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2023, 11(4), 1593–1633, 10.1039/D2TA07613F.
- Z. Zhang, C. Shen, K. Sun, X. Jia, J. Ye and C. Liu, Advances in Studies of the Structural Effects of Supported Ni Catalysts for CO2 Hydrogenation: From Nanoparticle to Single Atom Catalyst, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2022, 10(11), 5792–5812, 10.1039/D1TA09914K.
- C. Costentin, G. Passard, M. Robert and J.-M. Savéant, Ultraefficient Homogeneous Catalyst for the CO2-to-CO Electrochemical Conversion, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2014, 111(42), 14990–14994, DOI:10.1073/pnas.1416697111.
- B. Zhao, B. Yan, Z. Jiang, S. Yao, Z. Liu, Q. Wu, R. Ran, S. D. Senanayake, D. Weng and J. G. Chen, High Selectivity of CO2 Hydrogenation to CO by Controlling the Valence State of Nickel Using Perovskite, Chem. Commun., 2018, 54(53), 7354–7357, 10.1039/C8CC03829E.
- Z. Zhang, X. Hu, Y. Wang, S. Hu, J. Xiang, C. Li, G. Chen, Q. Liu, T. Wei and D. Dong, Regulation the Reaction Intermediates in Methanation Reactions via Modification of Nickel Catalysts with Strong Base, Fuel, 2019, 237, 566–579, DOI:10.1016/j.fuel.2018.10.052.
- C. L. Berre, A. Falqui, A. Casu, T. T. Debela, M. Barreau, C. H. Hendon and P. Serp, Tuning CO2 Hydrogenation Selectivity on Ni/TiO2 Catalysts via Sulfur Addition, Catal. Sci. Technol., 2022, 12(22), 6856–6864, 10.1039/D2CY01280D.
- Y. Wang, L. R. Winter, J. G. Chen and B. Yan, CO2 Hydrogenation over Heterogeneous Catalysts at Atmospheric Pressure: From Electronic Properties to Product Selectivity, Green Chem., 2021, 23(1), 249–267, 10.1039/D0GC03506H.
- Ž. Kovačič, B. Likozar and M. Huš, Photocatalytic CO2 Reduction: A Review of Ab Initio Mechanism, Kinetics, and Multiscale Modeling Simulations, ACS Catal., 2020, 10(24), 14984–15007, DOI:10.1021/acscatal.0c02557.
- Y. Li, B. Li, D. Zhang, L. Cheng and Q. Xiang, Crystalline Carbon Nitride Supported Copper Single Atoms for Photocatalytic CO2 Reduction with Nearly 100% CO Selectivity, ACS Nano, 2020, 14(8), 10552–10561, DOI:10.1021/acsnano.0c04544.
- K. Homlamai, T. Maihom, S. Choomwattana, M. Sawangphruk and J. Limtrakul, Single-Atoms Supported (Fe, Co, Ni, Cu) on Graphitic Carbon Nitride for CO2 Adsorption and Hydrogenation to Formic Acid: First-Principles Insights, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2020, 499, 143928, DOI:10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.143928.
- Q. Wu and C. Wu, Mechanism Insights on Single-Atom Catalysts for CO2 Conversion, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2023, 11(10), 4876–4906, 10.1039/D2TA06949K.
- L. Li, W. Zeng, M. Song, X. Wu, G. Li and C. Hu, Research Progress and Reaction Mechanism of CO2 Methanation over Ni-Based Catalysts at Low Temperature: A Review, Catalysts, 2022, 12(2), 244, DOI:10.3390/catal12020244.
- B. Miao, S. S. K. Ma, X. Wang, H. Su and S. H. Chan, Catalysis Mechanisms of CO2 and CO Methanation, Catal. Sci. Technol., 2016, 6(12), 4048–4058, 10.1039/C6CY00478D.
- A. Quindimil, M. C. Bacariza, J. A. González-Marcos, C. Henriques and J. R. González-Velasco, Enhancing the CO2 Methanation Activity of γ-Al2O3 Supported Mono- and Bi-Metallic Catalysts Prepared by Glycerol Assisted Impregnation, Appl. Catal., B, 2021, 296, 120322, DOI:10.1016/j.apcatb.2021.120322.
- K. L. Zhou, Z. Wang, C. B. Han, X. Ke, C. Wang, Y. Jin, Q. Zhang, J. Liu, H. Wang and H. Yan, Platinum Single-Atom Catalyst Coupled with Transition Metal/Metal Oxide Heterostructure for Accelerating Alkaline Hydrogen Evolution Reaction, Nat. Commun., 2021, 12(1), 3783, DOI:10.1038/s41467-021-24079-8.
- J. Jones, H. Xiong, A. T. DeLaRiva, E. J. Peterson, H. Pham, S. R. Challa, G. Qi, S. Oh, M. H. Wiebenga, X. I. Pereira Hernández, Y. Wang and A. K. Datye, Thermally Stable Single-Atom Platinum-on-Ceria Catalysts via Atom Trapping, Science, 2016, 353(6295), 150–154, DOI:10.1126/science.aaf8800.
- N. Cheng, L. Zhang, K. Doyle-Davis and X. Sun, Single-Atom Catalysts: From Design to Application, Electrochem. Energy Rev., 2019, 2(4), 539–573, DOI:10.1007/s41918-019-00050-6.
- J. Kim, H.-E. Kim and H. Lee, Single-Atom Catalysts of Precious Metals for Electrochemical Reactions, ChemSusChem, 2018, 11(1), 104–113, DOI:10.1002/cssc.201701306.
- L. Wei, H. Grénman, W. Haije, N. Kumar, A. Aho, K. Eränen, L. Wei and W. de Jong, Sub-Nanometer Ceria-Promoted Ni 13X Zeolite Catalyst for CO2 Methanation, Appl. Catal., A, 2021, 612, 118012, DOI:10.1016/j.apcata.2021.118012.
- M. Fan, J. D. Jimenez, S. N. Shirodkar, J. Wu, S. Chen, L. Song, M. M. Royko, J. Zhang, H. Guo, J. Cui, K. Zuo, W. Wang, C. Zhang, F. Yuan, R. Vajtai, J. Qian, J. Yang, B. I. Yakobson, J. M. Tour, J. Lauterbach, D. Sun and P. M. Ajayan, Atomic Ru Immobilized on Porous H-BN through Simple Vacuum Filtration for Highly Active and Selective CO2 Methanation, ACS Catal., 2019, 9(11), 10077–10086, DOI:10.1021/acscatal.9b02197.
- X. Jia, X. Zhang, N. Rui, X. Hu and C. Liu, Structural Effect of Ni/ZrO2 Catalyst on CO2 Methanation with Enhanced Activity, Appl. Catal., B, 2019, 244, 159–169, DOI:10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.11.024.
- C. Rivera-Cárcamo, C. Scarfiello, A. B. García, Y. Tison, H. Martinez, W. Baaziz, O. Ersen, C. Le Berre and P. Serp, Stabilization of Metal Single Atoms on Carbon and TiO2 Supports for CO2 Hydrogenation: The Importance of Regulating Charge Transfer, Adv. Mater. Interfaces, 2021, 8(8), 2001777, DOI:10.1002/admi.202001777.
- R. Tu, Y. Zhang, Y. Xu, J. Yang, L. Zhang, K. Lv, G. Ren, S. Zhai, T. Yu and W. Deng, Single-Atom Alloy Ir/Ni Catalyst Boosts CO 2 Methanation via Mechanochemistry, Nanoscale Horiz., 2023, 8(7), 852–858, 10.1039/D3NH00040K.
- H. Liang, B. Zhang, P. Gao, X. Yu, X. Liu, X. Yang, H. Wu, L. Zhai, S. Zhao, G. Wang, A. P. van Bavel and Y. Qin, Strong Co-O-Si Bonded Ultra-Stable Single-Atom Co/SBA-15 Catalyst for Selective Hydrogenation of CO2 to CO, Chem Catal., 2022, 2(3), 610–621, DOI:10.1016/j.checat.2022.01.020.
- L. Li, K. Yuan and Y. Chen, Breaking the Scaling Relationship Limit: From Single-Atom to Dual-Atom Catalysts, Acc. Mater. Res., 2022, 3(6), 584–596, DOI:10.1021/accountsmr.1c00264.
- N. Choudhary, M. Abdelgaid, G. Mpourmpakis and S. M. Mobin, CuNi Bimetallic Nanocatalyst Enables Sustainable Direct Carboxylation Reactions, Mol. Catal., 2022, 530, 112620, DOI:10.1016/j.mcat.2022.112620.
- N. Choudhary and S. M. Mobin, Conversion of Biomass-Derived Aldehydes Using Environmentally Benign CuNi Nanocatalyst, Asian J. Org. Chem., 2023, 12(2), e202200626, DOI:10.1002/ajoc.202200626.
- T. Zhang, P. Zheng, F. Gu, W. Xu, W. Chen, T. Zhu, Y.-F. Han, G. Xu, Z. Zhong and F. Su, The Dual-Active-Site Tandem Catalyst Containing Ru Single Atoms and Ni Nanoparticles Boosts CO2 Methanation, Appl. Catal., B, 2023, 323, 122190, DOI:10.1016/j.apcatb.2022.122190.
- T. Zhang, P. Zheng, J. Gao, Z. Han, F. Gu, W. Xu, L. Li, T. Zhu, Z. Zhong, G. Xu and F. Su, Single-Atom Ru Alloyed with Ni Nanoparticles Boosts CO2 Methanation, Small, 2024, 20(12), 2308193, DOI:10.1002/smll.202308193.
- S. Kikkawa, K. Teramura, H. Asakura, S. Hosokawa and T. Tanaka, Isolated Platinum Atoms in Ni/γ-Al2O3 for Selective Hydrogenation of CO2 toward CH4, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2019, 123(38), 23446–23454, DOI:10.1021/acs.jpcc.9b03432.
- S. Kikkawa, K. Teramura, H. Asakura, S. Hosokawa and T. Tanaka, Ni–Pt Alloy Nanoparticles with Isolated Pt Atoms and Their Cooperative Neighboring Ni Atoms for Selective Hydrogenation of CO2 Toward CH4 Evolution: In Situ and Transient Fourier Transform Infrared Studies, ACS Appl. Nano Mater., 2020, 3(10), 9633–9644, DOI:10.1021/acsanm.0c01570.
- J. H. Kwak, L. Kovarik and J. Szanyi, Heterogeneous Catalysis on Atomically Dispersed Supported Metals: CO2 Reduction on Multifunctional Pd Catalysts, ACS Catal., 2013, 3(9), 2094–2100, DOI:10.1021/cs4001392.
- H. H. Shin, L. Lu, Z. Yang, C. J. Kiely and S. McIntosh, Cobalt Catalysts Decorated with Platinum Atoms Supported on Barium Zirconate Provide Enhanced Activity and Selectivity for CO2 Methanation, ACS Catal., 2016, 6(5), 2811–2818, DOI:10.1021/acscatal.6b00005.
- J. C. Matsubu, V. N. Yang and P. Christopher, Isolated Metal Active Site Concentration and Stability Control Catalytic CO2 Reduction Selectivity, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2015, 137(8), 3076–3084, DOI:10.1021/ja5128133.
- J. D. Jimenez, C. Wen, M. M. Royko, A. J. Kropf, C. Segre and J. Lauterbach, Influence of Coordination Environment of Anchored Single-Site Cobalt Catalyst on CO2 Hydrogenation, ChemCatChem, 2020, 12(3), 846–854, DOI:10.1002/cctc.201901676.
- Y. Wang, H. Arandiyan, J. Scott, K.-F. Aguey-Zinsou and R. Amal, Single Atom and Nanoclustered Pt Catalysts for Selective CO2 Reduction, ACS Appl. Energy Mater., 2018, 1(12), 6781–6789, DOI:10.1021/acsaem.8b00817.
Footnote |
| † Both authors contributed equally. |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2024 |