Phenoxazine-based ambipolar luminescent room-temperature liquid crystals capable of being used in bioimaging applications†
Rahul
Ahmed
a,
Anjana
K. N
b,
Vinay S.
Sharma
 c,
Shweta
Thakar
d,
Anitha
B
b,
Paresh Kumar
Behera
a,
Dharmendra
Adak
a,
D. S. Shankar
Rao
e,
Manoj AG
Namboothiry
*b and
Ammathnadu Sudhakar
Achalkumar
*af
c,
Shweta
Thakar
d,
Anitha
B
b,
Paresh Kumar
Behera
a,
Dharmendra
Adak
a,
D. S. Shankar
Rao
e,
Manoj AG
Namboothiry
*b and
Ammathnadu Sudhakar
Achalkumar
*af
aDepartment of Chemistry, Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati, Guwahati, 781039, Assam, India. E-mail: achalkumar@iitg.ac.in
bSchool of Physics, Indian Institute of Science Education and Research Thiruvananthapuram, Maruthamala PO, Vithura, Thiruvananthapuram - 695551, Kerala, India. E-mail: manoj@iisertvm.ac.in
cDepartment of Chemistry, School of Science, Gujarat University, Ahmedabad 38000, India
dDeaprtment of Zoology, School of Sciences, Gujarat University, Ahmedabad 38000, India
eCentre for Nano and Soft Matter Sciences, Arkavathi Campus, Survey No. 7, Shivanapura, Dasanapura Hobli, Bengaluru, 562162, India
fCentre for Sustainable Polymers, Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati, Guwahati, 781039, Assam, India
First published on 11th April 2025
Abstract
A new class of phenoxazine-based luminescent liquid crystal molecules (POs) were synthesized employing the double Knoevenagel condensation of phenoxazine dialdehyde with various alkoxy-substituted phenyl acetonitrile derivatives. This new series of molecules exhibit high solubility and excellent thermal stability. The compound with six peripheral n-alkoxy chains (PO4) stabilizes a room-temperature columnar liquid crystalline phase due to efficient space–filling interactions. The synthesized molecules exhibit high luminescence intensity in both solution and solid states. The liquid crystalline molecule PO4 exhibits positive solvatochromism with HLCT behavior, demonstrating phosphorescence at 77 K. This compound was screened for bioimaging applications due to its excellent fluorescence and high biocompatibility. Among the screened compounds, PO4 was selected due to its lower crystallization tendency and superior fluorescence and it exhibited a uniform stain distribution throughout the nematode, significantly enhancing cellular visualization. The same compound, PO4, was further explored for its potential as a fluorescent probe in bioimaging by staining MCF7 cancer cells, with cellular uptake and localization studies confirming its effectiveness in targeting and visualizing cancer cells with higher fluorescence intensity.
1. Introduction
Phenoxazine, with its fused tricyclic structure and a butterfly-shaped conformation due to the folding of its two benzene rings around the O–N axis, exhibits enhanced electron donating properties, as its ionization potential is 0.7 eV lower than that of carbazole, leading to more stable radical cations.1–3 Contrary to extensive research on carbazole-based emissive molecules, phenoxazine remains underexplored as a building block in the fabrication of organic light emitting diodes (OLEDs),4 organic field effect transistors (OFETs), and bio-imaging materials. The presence of an oxygen atom in the phenoxazine structure slightly diminishes the overall aromaticity of the ring system. In addition, the dipole moment of phenoxazine (μ = 1.93 D, compared to benzene) indicates a non-planar configuration.5 The proton or substituent on the nitrogen atom can position itself between or outside the planes of the two lateral rings. Most phenoxazine derivatives have melting points below 200 °C. They are generally stable, except those substituted at the para position relative to the bridging nitrogen with hydroxy or amino groups, which are susceptible to oxidation. Phenoxazine has become essential in designing thermally activated delayed fluorescence (TADF) active molecules as electron donors.6 Gaining insight into the relationship between the stacking modes of phenoxazine derivatives and their luminescence properties will help researchers design and synthesize organic compounds with phenoxazine substructures, ultimately improving the performance of optoelectronic devices.Recently, luminescent liquid crystals (LLCs) have garnered increasing interest due to their fundamental phenomenological significance and appealing technological applications, including anisotropic LEDs, organic lasers with polarization, light-emitting liquid crystal displays (LCDs), organic memory devices, sensors, and one-dimensional semiconductors. The intrinsic light-emitting properties and unique self-organizing features give LLCs several novel advantages. For instance, LLCs can be used to create various stimuli-responsive luminescent materials because liquid crystals are highly sensitive to external stimuli of mechanical, electrical, thermal, and magnetic origin.7,8
Traditional fluorescent stains have issues like limited tissue penetration, photobleaching, high background noise, stability concerns, cell toxicity, staining anomalies, and reduced specificity that can impact the effectiveness of these dyes in various applications.9 Using phenoxazine as a biological stain offers numerous advantages, including high photostability, strong fluorescence, application versatility, biocompatibility, and potential therapeutic benefits. These compounds exhibit strong fluorescence, enhancing stained structures' visibility under a microscope.10 Their high quantum yields contribute to transparent and bright images of cellular components, facilitating detailed analysis of biological samples. Many phenoxazine derivatives exhibit low cytotoxicity, making them suitable for live cell staining without adversely affecting cellular viability.
Despite the exciting potential of LLCs, preserving light-emitting properties remains a significant challenge because of aggregation-caused quenching (ACQ) of emission in traditional organic luminogens.11–13 Thus, preventing ACQ in liquid crystal materials becomes a key concern while preserving the liquid crystalline self-assembly.14–16 Columnar (Col) phases of discotic liquid crystals (DLCs) that are formed by the one-dimensional (1D) stacking of the disc-like molecules are classified into different types based on the symmetry of the lattice they self-organize.17–22 The long-range order of the discs in the Col phases makes them ‘molecular wires,’ with the insulating mantle of the peripheral alkyl chains.23–26 This enables them to transport the charge along the columns rather than across the columns. DLCs are multifunctional soft materials with diverse applications, including energy generation, storage, photovoltaics, drug delivery, sensing, and adaptive photonic metamaterials. DLCs can self-heal the grain boundaries and other structural defects during their thermal annealing from the isotropic state.27–29 DLCs are typically insulators, but the change in transport can be initiated either by photolysis or by making a charge transfer complex.30–32 Over the years, many research groups, including our own, have shown that Col phases can function as 'molecular wires' for the transport of charge carriers or excitons.33–36
Surprisingly, there is a notable lack of literature on phenoxazine-based LLCs. Motivated by this gap, we have synthesized a novel class of room-temperature LLCs consisting of two alkoxy phenyl groups linked through a cyano-vinylene bond to an N-alkylated phenoxazine, forming a bent-shaped molecule. The non-planar structures of the phenoxazine5 and the cyano phenylvinylene fluorophore groups typically exhibit fluorescence in both solution and solid states.37 Additionally, the photophysical properties of cyano phenylvinylenes are known to be tuned by various external factors, including heat, pressure, solvents, pH, and light.38 Initially, a mono-alkoxy benzyl acetonitrile derivative was reacted with an N-alkylated phenoxazine dialdehyde, resulting in a crystalline material (PO1, with two alkoxy chains). To explore further, the number of peripheral alkoxy chains was increased to four, while varying the substitution positions (PO2 and PO3) still resulted in crystalline materials. Interestingly, the tri-n-alkoxy derivative (PO4, with six alkoxy chains) maintained a stable room-temperature columnar hexagonal phase over a wide thermal range without compromising its luminescence properties in the solid state. The molecular design combines electron donor and acceptor components in a single structure, imparting ambipolar charge transport characteristics in the columnar phase. Additionally, the excellent solubility and stability of these materials facilitated the visualization of nematodes and MCF7 human breast cancer cells under a fluorescence microscope.
2. Results and discussion
2.1. Synthesis and structural characterization
The target POs were prepared following a straightforward synthetic pathway (Scheme 1). In the first step, N-alkylated phenoxazine dialdehyde 2 is prepared using POCl3 and DMF by a well-known Vilsmeier–Hack reaction.39,40 Finally, the PO derivatives were synthesized by a double Knoevenagel condensation reaction of phenyl acetonitrile derivatives (4a,d) and n-alkylated phenoxazine dialdehyde (2) using potassium tert-butoxide as a base and tert-butanol as a solvent at mild temperature.40 The column purification of all the products using a hexane–ethyl acetate mixture yielded a sticky solid with a good yield. All compounds were characterized using standard analytical techniques, including MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry and 1H NMR, 13C NMR, and IR spectroscopy. Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) was carried out to evaluate compounds' thermal stability, revealing a decomposition onset temperature of 249–397 °C for 5 wt% decomposition (Table S1 and Fig. S34, ESI†). | ||
| Scheme 1 Reagents and conditions: (i) POCl3, DMF, 0–80 °C, 24 h, 75%; (ii) KOtBu, tert-BuOH, 2 h, 50 °C, 60–72%. | ||
2.2. Thermal behavior
The mesomorphism was initially explored using polarized optical microscopy (POM) with a controllable hot stage to observe optical textures. This method allowed the visualization of the fluidity (in response to mechanical shear) and birefringent patterns by heating the sample at room temperature and cooling it from the isotropic state. While compounds PO1–PO3 did not show any such changes, they transformed into isotropic liquids. In contrast, compound PO4, which was a sticky gummy solid, showed birefringence coupled with the fluidity upon heating, while cooling the isotropic liquid showed the formation of a mosaic pattern, which is usually observed for Col phases (Fig. 1b and 2a).24 The isotropic point of compound PO4 was first determined using polarized optical microscopy. The DSC thermograms revealed two distinct transitions upon heating: crystal to mesophase and mesophase to isotropic states, which was concurrent with the POM observations (Fig. 2b and Table 1 and Fig. S36, ESI†). Upon cooling the isotropic state, again, two transitions were noticed, i.e. isotropic to mesophase and mesophase to crystal. Notably, the crystal-to-mesophase transition occurred well below room temperature (at approximately 4 °C, ΔH = 15.8 kJ mol−1), confirming the compound's liquid crystalline nature at room temperature. The relatively low clearing point ≈ 53 °C (ΔH = 2.0 kJ mol−1, Fig. 2b) makes this compound particularly suitable for device applications. | ||
| Fig. 1 (a) Structures of POs studied in this work and (b) bargraph representing the mesomorphic behaviors (considered the first cooling scan of DSC). | ||
| Entry | Phase sequencea (kJ mol−1) | T 5 (°C) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Second heating | First cooling | ||
| a Peak onset temperatures in the DSC thermograms obtained during the second heating and first cooling cycles at 5 °C min−1. b Temperature at which 5% decomposition occurs. Cr = Crystalline phase; Colh = Columnar hexagonal phase; I = Isotropic phase. | |||
| PO4 | Cr 4.07 (15.8) Colh 52.7 (2.0) I | I 47.6 (13.8) Colh5.8 (17.6) Cr | 397 |
Furthermore, the powder X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis was conducted to unequivocally assign the symmetry of the columnar phase observed at high and low temperatures. A summarized overview of phase transition temperatures and enthalpy values for all compounds investigated is provided in Table S1 and Fig. S36 (ESI†). The enhanced attractive interactions of the aromatic core complemented with the increased fluidity/nanophase segregation offered by the alkyl chains in compound PO4 were the possible contributing factors that enabled the realization of the liquid crystalline behavior in comparison to other compounds PO1–PO3.
The symmetry of the Col phase exhibited by PO4 was investigated using powder X-ray diffraction studies at 50 °C and room temperature. Both the XRD patterns were almost similar. The XRD pattern of PO4 at 50 °C revealed one distinct Bragg peak in the small-angle region at 30.96 Å, corresponding to the Miller index (10) (Fig. 2c and Table S2, ESI†). Although the single peak cannot confirm any particular mesophase, in the literature there are many references where such single peak is assigned to the columnar phase with a hexagonal lattice,41 with a lattice parameter of a ≈ 35.75 Å. In the wide-angle regime, a d-spacing of 4.71 Å was observed, indicative of the fluid-like packing of alkyl chains. The intracolumnar distance, i.e., the distance between the discs within a column, was 4.19 Å. The lattice parameters remained almost unchanged over the entire mesophase temperature range (28 °C to 50 °C, Table S2, ESI†). The molecular organization within the Col phase was further examined, revealing that approximately two molecules formed a unit cell (Z ≈ 2). A schematic representation (Fig. 2d) illustrates the self-assembly of PO4 molecules into columns, which subsequently organize to form a columnar hexagonal (Colh) lattice. This analysis underscores the unique ability of PO4 to maintain a stable room temperature Colh phase (Fig. S37, ESI†), distinguishing it from other phenoxazine derivatives under similar conditions. Thus, only PO4 bearing six peripheral chains exhibits a LC phase, while others bearing fewer chains did not stabilize any LC phase; in other words, compounds PO1–PO3 do not efficiently fill the space, while the two molecules of PO4 efficiently fill the space to form a disc-like unit, which then self-assembles to form a Colh phase.
2.3. Photophysical properties
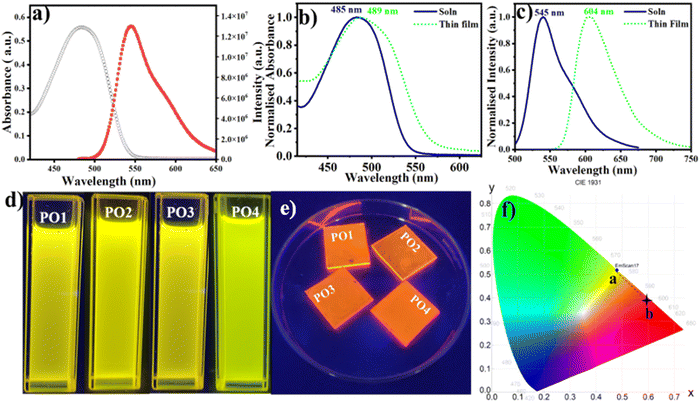
The photophysical properties of the four compounds (PO1, PO2, PO3, and PO4) were studied in both solution and thin film states, with the thin films spin-coated on a quartz substrate. The compounds exhibited good solubility in various solvents of varying polarity like chloroform, THF, cyclohexane, and toluene at a concentration of 1 wt%/vol. Photophysical measurements in solution were conducted using 20 μM chloroform solutions, while 1 wt%/vol toluene solutions were used to prepare the thin films. The absorption spectra of the PO derivatives in micromolar solutions displayed broad absorption bands around 480–485 nm in the more extended wavelength region, indicating effective intramolecular charge transfer (ICT) from the electron-donating phenoxazine moiety to the electron-withdrawing cyano vinylene units. A summary of the results is presented in Table S3 (ESI†) (Fig. 3 and Fig. S38, ESI†). The corresponding emission spectra revealed emission maxima in the 537–545 nm range (Fig. 3 and Fig. S39, ESI†), with significant Stokes shifts ranging from 2082 to 2269 cm−1. These compounds also exhibited high molar extinction coefficients ranging from 15![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 395 to 27
395 to 27![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 880 L mol−1 cm−1 (Table S3, ESI†). The optical energy gap, estimated from the absorption onset, was 2.30 eV.
880 L mol−1 cm−1 (Table S3, ESI†). The optical energy gap, estimated from the absorption onset, was 2.30 eV.
Thin films of the compounds on quartz plates displayed broad, red-shifted absorption and emission bands, with the Stokes shift increasing to 3658–3851 cm−1 in comparison to the solution state (Fig. 3b, c and Fig. S39, S40 and Table S3, ESI†). The compounds emitted bright yellow fluorescence in solution, which shifted to orange-red fluorescence in the solid state, as shown by the CIE coordinates, with a position change from a to b (Fig. 3b–f). This shift in fluorescence emission at longer wavelengths for thin films may be attributed to the non-planarity of the phenoxazine molecule, which reduces nonradiative decay by restricting torsional motion and with further enhancements by appropriate intermolecular arrangements (e.g., J-aggregation).42 The broad absorption bands observed in thin films suggest the formation of excimers (Fig. 3 and Fig. S40 and S41, ESI†), with a slight bathochromic shift indicative of J-type or head-to-tail aggregates. Additionally, a red-shifted λmax peak in the absorption spectra of the POs in the thin film, as shown in Fig. 3b, could be explained by short-distance charge transfer interactions that promote coupling among the π-conjugated aromatic cores, enhancing wave function overlap.43 The fluorescence efficiency of the compounds was assessed by measuring their absolute quantum yields, which ranged from 24% to 43% (Table S3, ESI†). Time-resolved photoluminescence measurements in both solution and thin film states (Fig. S42, S43, and Table S4, ESI†) showed that among all the derivatives, PO4 exhibited the highest lifetime of 2.78 ns in the thin film state (Table S4, ESI†).
The phosphorescence behavior of the PO4 compound was investigated at room temperature (RT) and 77 K in THF, as shown in Fig. 4. Upon irradiation at 485 nm, PO4 displayed dual emission, consisting of fluorescence and phosphorescence at RT. The phosphorescence peak at 654 nm exhibited a typical emission lifetime of 0.067 ms at 77 K (Table S4, ESI†); two prominent phosphorescence peaks were observed at 598 and 645 nm, with a phosphorescence decay lifetime of 2.7 ms. The fine vibrational structure observed in the phosphorescence is likely associated with the locally excited (LE) state. Thus, compound PO4 exhibits weak room-temperature phosphorescence, which increases at 77 K due to the reduced flexibility of the luminescent species, leading to the radiative relaxation processes.44–46 From the time-dependent-density functional theory (TD-DFT) calculations, the S1 and T1 levels of PO4 were 2.32 eV and 1.53 eV, with a ΔEST of 0.79 eV.
 | ||
| Fig. 4 (a) Steady-state PL spectra (blue trace) at RT and 77 K (green trace) (delay 100 μs and 0.1 gating) of PO4 and (b) decay lifetime. | ||
To investigate the HLCT characteristics in the excited state, time-dependent density functional theory (TD-DFT) calculations using the CAM-B3LYP/6-31G(d,p) level of theory were performed to explore the excited-state properties of the first 10 singlet (S0 to S10) and triplet (T1 to T10) states (Table S7, ESI†). The energy difference between the high-lying singlet state S1 and the triplet state T3 was 0.31 eV, while the difference between S2 and T4 was 0.24 eV. These relatively large ΔEST values (S1–T3 and S2–T4) suggest that reverse intersystem crossing (RISC) is unlikely to occur between these states.53,54 Therefore, RISC is expected to proceed from the triplet state closest to the HLCT singlet state via the hot exciton channel. Due to the narrow energy gaps, hot exciton RISC can occur from T7 to S3, with a ΔE(S3–T7) of 0.03 eV (Fig. S44 and Table S7, ESI†).52,55 Analysis of the natural transition orbitals (NTOs) revealed that some excited states are dominated by local excitation (LE), confirming the presence of LE states (e.g., S3, S4, S5, S6, S8, S9, S10, T1, T4, T5, T6, T7 and T8), where the hole and particle are located in the same fragment. Additionally, states where the hole and particle are located in different fragments indicate charge transfer (CT) excited states (e.g., S1, S2, S7, T2, T3, T9, and T10). As a result, the excited states of PO4 exhibited HLCT characteristics, showing a combination of both LE and CT states (Fig. 6 and Table S7, ESI†).55–65 Fluorescent molecules with HLCT characteristics exhibit higher external quantum efficiency (EQE) above the theoretical limit of 5% in OLED devices, highlighting the potential of PO4 as an emissive layer in OLEDs.
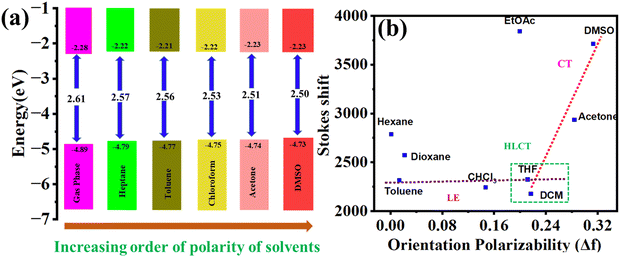
The TD-DFT study of PO4 in the gaseous state and different solvents further supports the bathochromic shift from nonpolar to polar solvents, as shown in Fig. 7a and Table S6 (ESI†). With increasing solvent polarity from heptane to DMSO, the HOMO–LUMO gap decreases from 2.57 eV to 2.50 eV, and the ΔEST value decreases from 0.79 eV to 0.64 eV (Table S6, ESI†).
2.4. Electrochemical properties
The energy and electron transfer processes, as well as the reversibility of redox reactions, are significantly influenced by the electronic energy levels, particularly the frontier molecular orbitals (HOMO and LUMO levels) of organic semiconductors. These characteristics were investigated through cyclic voltammetry (CV) in 0.5 mM solutions of POs in anhydrous dichloromethane, with 0.1 M tetrabutylammonium perchlorate (TBAP) as the supporting electrolyte and at a scan rate of 100 mV s−1. The electrochemical results summarized in Table 2 and Fig. 8 show that compounds PO1, PO2, PO3, and PO4 exhibited an irreversible first reduction at −1.27, −1.37, −1.36, and −1.38 eV, respectively. From these values, the estimated lowest occupied molecular orbital (LUMO) levels of POs were found to be −3.03, −2.92, −2.93, and −2.91 eV, respectively. The corresponding highest occupied molecular orbital (HOMO) levels, derived from their optical band gaps (Eg,opt) of 2.32, 2.31, 2.31, and 2.30 eV, were found to be around −5.35, −5.23, −5.24, and −5.21 eV, respectively (see Table 2 and Fig. 8). Overall, these results indicate that the number of alkoxy chains has minimal effect on the electrochemical properties of these compounds.| Electrochemical data | Data from DFT calculations | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entry |
E
1st![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) red red
|
E LUMO | E HOMO | ΔEg, (opt)dg | E LUMO | E HOMO | ΔEσdh |
| a 0.5 mM dichloromethane solution. b Experimental conditions: Ag/AgNO3 reference electrode, glassy carbon working electrode, platinum wire counter electrode, TBAP (0.1 M) as a supporting electrolyte, room temperature. c In volts (V). d In electron volts. e Estimated from the formula by using ELUMO = −(4.8 − E1/2, Fc/Fc+ + Ered, onset) eV. f Estimated from the formula EHOMO = (ELUMO − Eg,opt) eV. g Calculated from the red edge of the absorption band of each compound. E1/2,Fc/Fc+ = 0.50. h Obtained from DFT calculations by employing the combination of the Becke3-Lee–Yang–Parr (B3LYP) hybrid functional and the 6-31G(d,p) basis set using the Gaussian 09 package. | |||||||
| PO1 | −1.27 | −3.03 | −5.35 | 2.32 | −2.03 | −4.99 | 2.96 |
| PO2 | −1.37 | −2.92 | −5.23 | 2.31 | −2.06 | −4.98 | 2.92 |
| PO3 | −1.36 | −2.93 | −5.24 | 2.31 | −1.98 | −4.90 | 2.92 |
| PO4 | −1.38 | −2.91 | −5.21 | 2.30 | −2.02 | −4.93 | 2.91 |
 | ||
| Fig. 8 (a) Cyclic voltammogram of POs and (b) the energy band level diagram showing experimental HOMO and LUMO energy levels of POs. | ||
2.5. Density functional theory studies
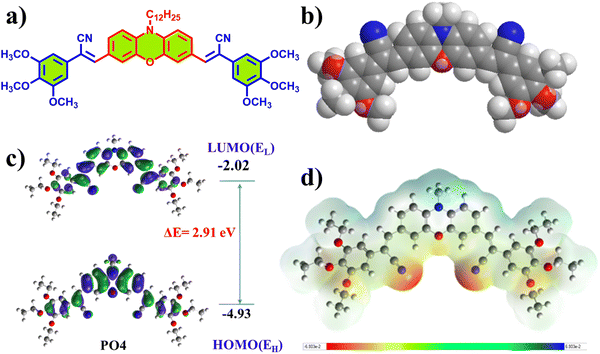
To investigate the geometry, electronic structure, molecular conformation, and frontier molecular orbitals (FMOs: HOMO and LUMO) of POs, we conducted density functional theory (DFT) calculations using the B3LYP/6-31G(d,p) method. Analysis of the HOMO and LUMO distributions revealed that the energy levels are mainly localized around the central aromatic ring and the phenyl acetonitrile group, as shown in Fig. 9 and Fig. S48 (ESI†). For PO1, the calculated HOMO and LUMO energy levels were −4.99 eV and −2.03 eV, respectively, yielding a HOMO–LUMO gap of 2.96 eV. In contrast, the introduction of a tri-n-alkoxy chain in the phenyl acetonitrile unit of PO4 lowered the HOMO energy by 0.04 eV, slightly reducing the HOMO–LUMO gap. However, in PO2 and PO3, the band gap remained nearly the same as in PO4. These theoretical results are consistent with the experimental data, confirming a slight decrease in the band gap with the increase in peripheral side chains. The optimized molecular diameters of the POs were approximately 53 Å, as shown in Fig. S47a (ESI†). The 3D molecular electrostatic potential (MEP) maps reveal electron density concentration around the oxygen atom and CN units of the POs, while the central core remains electron-poor (Fig. 9d). The theoretical band gaps for the POs ranged from 2.96 to 2.91 eV, slightly larger than the optical band gaps, but showed the same trend as presented in Table 2.2.7. Charge carrier mobility studies
The charge-carrier mobilities of the liquid crystal PO4 were determined by measuring its current density–voltage (J–V) characteristics in a device configuration where the material was sandwiched between two electrodes. The space-charge-limited currents (SCLC) were analyzed using the Mott–Gurney equation (eqn (1)): | (1) |
Two distinct SCLC cells were fabricated to investigate the ambipolar charge transport properties of the material: one for hole mobility and the other for electron mobility. Hole-only devices (HODs) consisted of an ITO/PEDOT: PSS bottom layer and a MoO3/Ag top layer, while electron-only devices (EODs) employed an ITO/ZnO bottom layer and a PDINN/Ag top layer. The liquid crystal layer thickness in both single-carrier devices was approximately 100 nm, and the dielectric constant, calculated from capacitance–frequency measurements, was 3.95 nF (Fig. S49, ESI†). The SCLC data and the corresponding fits according to eqn (1) are shown in Fig. 10a and b, with the device structure depicted in the inset. The charge-carrier mobility, calculated using eqn (1), is 1.92 × 10−4 cm2 V−1 s−1 for the hole-only device and 1.19 × 10−4 cm2 V−1 s−1 for the electron-only device, confirming the ambipolar nature of the material. The charge carrier mobilities are comparable with the values of other organic semiconductors with similar structures (Table S9, ESI†).
 | ||
| Fig. 10 J–V characteristics of the hole-only device (a) and electron-only device (b) in the dark (inset: device structures). | ||
3. Bioimaging studies
Fluorescent compounds continue to drive significant advancements in the field of bioimaging. Compound PO4 exhibited exceptional fluorescence properties and a high quantum yield, highlighting its potential as an effective agent for nematode cell imaging studies. Its low crystallization tendency and robust fluorescence characteristics made it well-suited for such applications. Nematodes are commonly used as model organisms in scientific research due to their simple anatomy, well-understood biology, and adaptability across various experimental setups. Their unsegmented, cylindrical body, short lifecycle, and straightforward anatomical structure make them ideal for studying biological processes and disease mechanisms. Furthermore, their ease of cultivation and minimal maintenance contribute to their widespread laboratory use. Numerous studies have established nematodes as a reliable model for toxicological evaluations, particularly in assessing the effects of chemical probes.66,67A solution of compound PO4 was prepared in THF solvent and introduced into nematodes for imaging (Fig. 11). Although the compound exhibited aggregation-caused quenching (ACQ) in aqueous media, it showed excellent imaging results when dissolved in THF due to its enhanced fluorescence, particularly when viewed under green and blue filters using a fluorescence microscope. The compound stained the entire body of the nematode, allowing for detailed visualization of its anatomical and cellular structures. This uniform staining highlights its potential as a reliable tool for advanced imaging in biological research. Notably, no crystallization was observed at room temperature, ensuring the compound's even dispersion within the nematodes. This consistent distribution allowed for thorough and effective staining of the entire organism, providing precise and reliable insights into the nematode's anatomy and internal structures.
 | ||
| Fig. 11 Exposure of nematodes to compound PO4 in THF (10 μM) under different filters ((a) and (d) white light, (b) and (e) blue filter, and (c) and (f) green filter). | ||
The fluorescence observed in the nematodes indicated that the compound could permeate the organism effectively. Notably, no visible damage was detected, demonstrating the biocompatibility of the phenoxazine-based fluorescent luminophore for biological applications. To further evaluate its effectiveness, the luminophore solution was diluted to 10 μM and introduced into multiple nematodes (Fig. 12). Fluorescence microscopy revealed that all the nematodes absorbed the solution, resulting in uniform staining of their internal and external surfaces. Observations were made using simple light microscopy and blue and green fluorescence filters. At lower concentrations, the luminophore showed reduced crystallization tendencies and moderate fluorescence permeability, suggesting that imaging selectivity could be finely tuned by adjusting the compound concentration. In the early stages, the motility of the nematodes was tracked, demonstrating the utility of this method for real-time monitoring of their movement. This approach allows for direct visualization of locomotion of nematodes, offering valuable insights into their dynamics, responses to external stimuli, and environmental interactions. These capabilities are beneficial for studying nematode biology and have potential applications in parasitology, toxicology, and ecological research. The findings also highlight the broader applicability of phenoxazine-based luminophores for cellular imaging beyond nematodes. In addition, freely moving nematodes during imaging suggest the absence of acute toxic effects, further supporting the non-toxic nature of PO4 in a living system. No signs of cellular damage were observed in our biological studies, providing initial evidence of biocompatibility.
 | ||
| Fig. 12 Exposure of multiple nematodes to a solution of compound PO4 in THF (10 μM) was observed under different filters (a)–(f). | ||
Light-emitting compounds in imaging have become a cornerstone in cancer diagnostics and treatment, greatly enhancing the contrast between well-perfused and poorly perfused regions within cancer cells. Inspired by the promising performance of the phenoxazine-functionalized compound PO4 in nematode cell imaging, we are excited to explore its potential in advancing bioimaging applications, particularly for targeting the MCF7 human breast cancer cell line. Using fluorescence microscopy, we captured detailed images of PO4-stained cancer cells, enabling a thorough examination of cellular morphology and histology. This high-resolution technique reveals even the most minor clusters of cells, which traditional imaging methods might miss, and holds promise for adapting to a wide range of cancers, potentially integrating with other imaging modalities to enhance diagnostic precision.68 Investigating changes in cell morphology is vital in cancer research, as these alterations can profoundly impact cell growth, gene expression, and overall behavior. Our observations of PO4-stained cells show a remarkable improvement in cellular visibility compared to unstained cells, with even minor, previously indiscernible cells detected through fluorescence imaging. These compounds enable efficient and precise staining of cancer cells with minimal spectral overlap, significantly reducing background interference and enhancing imaging clarity.69 Recent strides in cancer research have highlighted the value of single-cell analysis, providing a clear, temporal, and spatial understanding of apoptosis—the process of programmed cell death.70 This approach allows researchers to individually track the events leading to cell death, revealing insights often hidden in bulk-cell analysis. Studying a single cell also eliminates distractions from neighboring cells, offering a focused investigation of the unique or pathological features specific to cancer cells.71
The uptake of compound PO4 into MCF7 cells was examined using fluorescence microscopy with various RGB filters. The results revealed that the probe efficiently penetrated the plasma membrane, resulting in distinct and compelling staining of the cancer cells, highlighting its potential for bioimaging applications. In cancer research assays, DMSO is commonly used as a solvent to facilitate the uptake of staining compounds, and this approach was also applied to compound PO4. Intense fluorescence staining was observed under different filters, suggesting a strong affinity due to π–π stacking interactions from the compound's rigid aromatic structure, which enhances its specificity and binding efficiency in cellular environments.72 When the stained cells were viewed through a green filter, they emitted bright red fluorescence (Fig. 13c and f), which became even more intense at higher resolutions. At lower resolutions, even smaller cells were visible.
In contrast, blue filters produced green images (Fig. 13b and e) with relatively lower fluorescence intensity, providing more apparent cell outlines and transparent visualization. Higher magnification imaging was employed to capture clear, localized fluorescence signals, allowing for accurate visualization of intracellular changes that might not be evident at lower magnifications. This strategy minimizes the risk of misinterpretation and enhances data reliability. Both lower and higher magnifications were used to ensure an unbiased and precise analysis of PO4-stained cells. Additionally, regions with a dense cell population were prioritized (Fig. 13d–f) to optimize imaging conditions, reduce background noise in high-magnification images, and improve clarity and fluorescence specificity. Combining these techniques achieved more detailed morphological observations essential for diagnostic purposes. Notably, the intense staining did not cause any visible changes in cell morphology, indicating that the compound does not induce membrane disruption or cell death. Furthermore, it produced rapid effects without requiring intricate procedures during staining, making it a user-friendly technique. These findings suggest that the compound selectively interacts with cellular structures while enhancing imaging clarity. The compound maintained its functional state throughout the staining process, with no solidification or precipitation occurring at room temperature. This stability is attributed to functionalizing a central hydrophobic aromatic phenoxazine core with terminally substituted aliphatic alkyl groups, reducing the compound's crystallinity. This structural design promotes efficient cell membrane penetration while maintaining interactions with intracellular targets and active sites. The results highlight the compound's potential as a reliable fluorescent probe for imaging breast cancer cells. It provides vigorous fluorescence intensity without compromising cell integrity, reduces background noise, and ensures consistent and uniform staining.73 To accurately quantify fluorescence intensity, as raw intensity measurements could underestimate staining in flattened cells compared to rounded ones, we calculated corrected total cell fluorescence (CTCF) using ImageJ 1.54f software. This analysis confirmed that the green and blue filters consistently produced the most potent signals (Fig. S50, ESI†).
In the literature, reports written by Ma et al. and Palanisamy et al. demonstrated that phenoxazine-based probes had shown detection limits ranging from 0.11 μM to 0.60 μM for bioimaging in live cells and zebrafish.4b,c In contrast, PO4 exhibited exceptional fluorescence imaging capabilities at an ultra-low concentration of 0.0004 μM, orders of magnitude lower than previously reported probes. This remarkable sensitivity highlights PO4's superior imaging potential, even without direct quantitative fluorescence intensity comparisons. In our study, PO4 demonstrated high quantum yields (24–43%) and significant Stokes shifts (2082–2269 cm−1 in solution and 3658–3851 cm−1 in thin films), contributing to enhanced imaging contrast. Additionally, PO4 exhibited excellent photostability, retaining its fluorescence intensity during extended imaging sessions without significant photobleaching or signal loss. Unlike conventional fluorescent stains, which often suffer from high background noise and stability concerns, PO4 showed strong fluorescence in both solution and solid states, facilitating uniform and high contrast staining in MCF7 cancer cells and nematodes. Furthermore, the hybridized localized and charge-transfer (HLCT) behavior in PO4 enhances emission efficiency, balancing brightness and stability. Techniques such as Förster resonance energy transfer (FRET) could be employed to study molecular interactions. At the same time, super-resolution microscopy (e.g., STORM and PALM) could provide nanoscale imaging of cancer structures.74 Additionally, approaches like multiphoton microscopy (MPM) and fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy (FLIM) offer deep tissue penetration and metabolic insights, respectively, which could further expand the applicability of PO molecules in biomedical imaging.75 Future studies can explore these integrations to maximize the diagnostic and analytical potential of PO molecules in future cancer research.
4. Conclusions
In conclusion, we have developed and characterized a new series of phenoxazine (PO) derivatives. One of these derivatives stabilizes a room-temperature columnar hexagonal phase while retaining its luminescence properties in the solid state. All the compounds showed high absorption coefficients and significant Stokes shifts. In solution, they emitted in the yellow region, but in the solid state, their fluorescence shifted to the orange-red region due to J-aggregation. Notably, the PO4 derivative exhibited phosphorescence at 77 K and displayed positive solvatochromism with hybrid localized and charge-transfer (HLCT) characteristics. PO4 demonstrated ambipolar behavior, with hole and electron mobilities of 1.92 × 10−4 cm2 V−1 s−1 and 1.19 × 10−4 cm2 V−1 s−1, respectively. Additionally, PO4 showed excellent permeability in nematodes, efficiently crossing cellular membranes and distributing uniformly across tissues. Imaging studies at room temperature revealed its remarkable permeability, high intensity, and resistance to crystallization interference. Overall, the distinctive structural and photophysical properties of PO4 position it as a reliable and efficient fluorescent probe for imaging MCF7 cancer cells. Its intense fluorescence, minimal background interference, and compatibility with standard imaging techniques make it a promising tool for advancing cancer diagnostics and research.Data availability
The data supporting this article have been included as part of the ESI.†Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest to declare.Acknowledgements
ASA extends his sincere gratitude to the Science and Engineering Board (SERB) and BRNS-DAE for their generous funding of this project under grant no. CRG/2018/000362 and 2012/34/31/BRNS/1039, respectively. We also appreciate the Ministry of Human Resource Development for establishing the Centre of Excellence in FAST (F. No. 5-7/2014-TS-VII).References
- Y. Zhu, A. P. Kulkarni, P. T. Wu and S. A. Jenekhe, New Ambipolar Organic Semiconductors. 1. Synthesis, Single-Crystal Structures, Redox Properties, and Photophysics of Phenoxazine-Based Donor-Acceptor Molecules, Chem. Mater., 2008, 20, 4200–4211 CrossRef CAS.
- H. A. Sharji, R. Ilmi and M. S. Khan, Recent Progress in Phenoxazine-Based Thermally Activated Delayed Fluorescent Compounds and Their Full-Color Organic Light-Emitting Diodes, Top. Curr. Chem., 2024, 5, 382 Search PubMed.
- A. N. Oleksy, J. Sołoducho and J. Cabaj, Phenoxazine Based Units- Synthesis, Photophysics and Electrochemistry, J. Fluoresc., 2011, 21, 169–178 CrossRef.
- (a) A. P. Kulkarni, Y. Zhu, A. Babel, P.-T. Wu and S. A. Jenekhe, New Ambipolar Organic Semiconductors, Chem. Mater., 2008, 20, 4200–4211 CrossRef; Effects of Electron Acceptor Strength on Intramolecular Charge Transfer Photophysics, Highly Efficient Electroluminescence, and Field-Effect Charge Transport of Phenoxazine-Based Donor-Acceptor Materials, Chem. Mater., 2008, 20, 4212–4223 Search PubMed; (b) P. Ravichandirana, A. B. Czubarab, M. Masłykc, A. P. Bellad, P. M. Johnsond, S. A. Subramaniyane, K. S. Shime and D. J. Yooa, A phenoxazine-based fluorescent chemosensor for dual channel detection of Cd2+ and CN− ions and its application to bio-imaging in live cells and zebrafish, Dyes Pigm., 2020, 172, 107828 CrossRef; (c) W. Ma, X. Zhao, Q. Niu, T. Hu and J. Chen, A new phenoxazine-based turn-on fluorescent probe for monitoring hypochlorite in food/urine/water/beverage samples and bioimaging in zebrafish, Microchem. J., 2023, 193, 109107 CrossRef CAS.
- M. A. Sridhar, M. Ramegowda, N. K. Lokanath, J. Shashidhara Prasad, G. B. Ere Gowda and K. N. Thimmaiah, Structural Studies of Some Phenoxazine Derivatives, Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst., 1999, 326, 189–214 CrossRef CAS.
- L. X. Guo, Y. B. Xing, M. Wang, Y. Sun, X. Q. Zhang, B. P. Lin and H. Yang, Luminescent liquid crystals bearing an aggregation-induced emission active tetraphenylthiophene fluorophore, J. Mater. Chem. C, 2019, 7, 4828–4837 RSC.
- Y. Wang, J. Shi, J. Chen, W. Zhu and E. Baranoff, Recent progress in luminescent liquid crystal materials: design, properties and application for linearly polarised emission, J. Mater. Chem. C, 2015, 3, 7993–8005 RSC.
- Y. Iida, Y. Shimomura, M. Tokita and G. I. Konishi, Push-pull biphenyl and tolane derivatives as novel luminescent liquid crystals: synthesis and properties, Liq. Cryst., 2024, 51, 2032–2045 CrossRef CAS.
- V. Boyd, O. M. Cholewa and K. K. Papas, Limitations in the Use of Fluorescein Diacetate/Propidium Iodide (FDA/PI) and Cell Permeable Nucleic Acid Stains for Viability Measurements of Isolated Islets of Langerhans, Curr. Trends Biotechnol. Pharm., 2008, 2, 66–84 Search PubMed.
- S. Shukla, J. Dwivedi, N. Yaduvanshi and S. Jain, Medicinal and Biological Significance of Phenoxazine Derivatives, Mini-Rev. Med. Chem., 2021, 21, 1541–1555 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Chen, Z. Peng, Y. Tao, Z. Wang, P. Lu and Y. Wang, Polymorphism-dependent emissions of two phenoxazine derivatives, Dyes Pigm., 2019, 161, 44–50 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Zhang, S. Jiang, G. Lin, H. Guo and F. Yang, Novel fluorescent columnar liquid crystal based on tetraphenylethylene- rufigallol-tetraphenylethylene triads, J. Mol. Struct., 2022, 1252, 132210 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Arivazhagan, P. Malakar, R. Jagan, E. Prasad and S. Ghosh, Dimesitylboryl-functionalised cyanostilbene derivatives of phenothiazine: distinctive polymorphism-dependent emission and mechanofluorochromism, CrystEngComm, 2018, 20, 3162–3166 RSC.
- L. X. Guo, Y. B. Xing, M. Wang, Y. Sun, X. Q. Zhang, B. P. Lin and H. Yang, Luminescent liquid crystals bearing an aggregation-induced emission active tetraphenylthiophene fluorophore, J. Mater. Chem. C, 2019, 7, 4828–4837 RSC.
- D. Verma, G. P. Maurya, S. Jawla, V. Haridas and A. Sinha, Designing Luminescent Liquid Crystals Using an AIE-Active Pseudopeptide Chiral Dopant: Circular Dichroism, Circularly Polarized Luminescence, and Photoluminescence Studies, ACS Appl. Opt. Mater., 2024, 2, 11 Search PubMed.
- Q. Yang, J. Zhu, Z. Li, X. S. Chen, Y. X. Jiang, Z. W. Luo, P. Wang and H. L. Xie, Luminescent Liquid Crystals Based on Carbonized Polymer Dots and Their Polarized Luminescence Application, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2021, 13, 26522–26532 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Wöhrle, I. Wurzbach, J. Kirres, A. Kostidou, N. Kapernaum, J. Litterscheidt, J. C. Haenle, P. Staffeld, A. Baro, F. Giesselmann and S. Laschat, Chem. Rev., 2016, 116, 1139–1241 CrossRef PubMed.
- H. K. Bisoyi and Q. Li, Stimuli directed alignment of self-organized one-dimensional semiconducting columnar liquid crystal nanostructures for organic electronics, Prog. Mater. Sci., 2019, 104, 1 CrossRef CAS.
- H. K. Bisoyi and Q. Li, Liquid Crystals: Versatile Self-Organized Smart Soft Materials, Chem. Rev., 2022, 122, 4887–4926 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Termine and A. Golemme, Charge Mobility in Discotic Liquid Crystals, Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2021, 22, 877 CrossRef CAS.
- A. E. Murschell and T. C. Sutherland, Anthraquinone-Based Discotic Liquid Crystals, Langmuir, 2010, 26(15), 12859–12866 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Zhou, S. W. Kang, S. Kumar, R. R. Kulkarni, S. Z. D. Cheng and Q. Li, Self-Assembly of Porphyrin and Fullerene Supramolecular Complex into Highly Ordered Nanostructure by Simple Thermal Annealing, Chem. Mater., 2008, 20, 3551–3553 CrossRef CAS.
- R. De and S. Kumar Pal, Self-assembled discotics as molecular semiconductors, Chem. Commun., 2023, 59, 3050–3066 RSC.
- S. Kumar, Chemistry of Discotic Liquid Crystals From Monomers to Polymers, CRC press, 2011 Search PubMed.
- S. Kumar, Self-organization of disc-like molecules: chemical aspects, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2006, 35, 83–109 RSC.
- P. K. Behera, M. R. Nagar, R. K. Gupta, S. Pradhan, D. S. S. Rao, S. K. Prasad, L. The, A. Choudhury, J. H. Jou and A. S. Achalkumar, Highly stable deep red-to-NIR OLEDs with an external quantum efficiency of 4.9% from room temperature nanostructured columnar fluids based on hetero atom bay-annulated perylene bisimides, J. Mater. Chem. C, 2022, 10, 18351 RSC.
- S. K. Pal, S. Setia, B. S. Avinash and S. Kumarb, Triphenylene-based discotic liquid crystals: recent advances, Liq. Cryst., 2013, 40(12), 1769–1816 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Eccher, G. C. Faria, H. Bock, H. V. Seggern and I. H. Bechtold, Order Induced Charge Carrier Mobility Enhancement in Columnar Liquid Crystal Diodes, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2013, 5, 11935–11943 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Kumar and S. Kumar, Liquid crystals in photovoltaics: a new generation of organic photovoltaics, Polym. J., 2017, 49, 85–111 CrossRef CAS.
- P. K. Behera, F. R. Chen, I. Mondal, S. Lenka, P. Gautam, N. Khatiwoda, I. Siddiqui, V. E. Krishnaprasad, R. Ahmed, D. S. Shankar Rao, S. P. Senanayak, J. H. Jou and A. S. Achalkumar, Superior electron mobility, red electroluminescence with high quantum efficiency from printable room temperature columnar liquid crystalline perylene bisimide, Chem. Eng. J., 2024, 488, 150762 CrossRef CAS.
- J. De, I. Bala, S. P. Gupta, U. K. Pandey and S. K. Pal, High Hole Mobility and Efficient Ambipolar Charge Transport in Heterocoronene-Based Ordered Columnar Discotics, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2019, 141, 18799–18805 Search PubMed.
- J. Xu, Room-Temperature Columnar Liquid Crystals from Twisted and Macrocyclic 9,9′-Bifluorenylidene Mesogen with Ambipolar Carrier Transport Properties, ACS Mater. Au, 2023, 3, 450–455 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. D. Nguyen, J. Labella, J. L. Martın, C. L. Folcia, J. Ortega, T. Torres, T. Sierra and J. L. Sessler, Columnar liquid crystals based on antiaromatic expanded porphyrins, Chem. Commun., 2024, 60, 3401–3404 RSC.
- P. K. Behera, K. Yadav, D. S. S. Rao, U. K. Pandey and A. S. Achalkumar, Self-assembled anti-naphthalene-3,4:9,10-bis(benzimidazole)s: stabilizing room temperature columnar phase with ambipolar conductivity, ACS Appl. Electron. Mater., 2023, 5, 5417–5421 Search PubMed.
- J. Hanna, A. Ohno and H. Iino, Charge carrier transport in liquid crystals, Thin Solid Films, 2014, 554, 58–63 CrossRef CAS.
- P. K. Behera, K. Yadav, D. S. Shankar Rao, U. K. Pandey and A. A. Sudhakar, Ambipolar columnar self-assembled organic semiconductors based on heteroatom bay-annulated perylene bisimides, Chem. – Asian J., 2023, 18, 202300086 CrossRef.
- M. M. Abadı, S. Varghese, B. Milian-Medina, J. Gierschner, R. Gimenez and M. B. Ros, Bent-core liquid crystalline cyanostilbenes: fluorescence switching and thermochromism, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2015, 17, 11715–11724 RSC.
- A. M. Al-Soliemy, Novel asymmetrical phenothiazine for fluorescent detection of cyanide anions, J. Mol. Struct., 2019, 1179, 525–531 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Wei, X. Zhang, L. Wang, Y. Liu, T. Bing, X. Liua and D. Shangguan, Interaction of bisbenzimidazole-substituted carbazole derivatives with G-quadruplexes and living cells, RSC Adv., 2015, 5, 75911–75917 Search PubMed.
- J. W. Park, S. Nagano, S. J. Yoon, T. Dohi, J. Seo, T. Seki and S. Y. Park, High Contrast Fluorescence Patterning in Cyanostilbene- Based Crystalline Thin Films: Crystallization-Induced Mass Flow Via a Photo-Triggered Phase Transition, Adv. Mater., 2014, 26, 1354–1359 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) K. Ohta, Linear algebraic proof and examples of composite lattice-based liquid crystalline phases, Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst., 2017, 658, 13–31 CrossRef CAS; (b) K. Ohta, Physics and Chemistry of Molecular Assemblies, World Scientific, 2020 Search PubMed.
- J. H. Kim, T. Schembri, D. Bialas, M. Stolte and F. Würthner, F. Slip-stacked J-aggregate materials for organic solar cells and photodetectors, Adv. Mater., 2022, 34, 2104678 CrossRef CAS.
- N. J. Hestand and F. C. Spano, Expanded theory of H- and J-molecular aggregates: the effects of vibronic coupling and intermolecular charge transfer, Chem. Rev., 2018, 118, 7069 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Mukherjee and P. Thilagar, Recent advances in purely organic phosphorescent materials, Chem. Commun., 2015, 51, 10988–11003 RSC.
- M. Baroncini, G. Bergamini and P. Ceroni, Rigidification or interaction-induced phosphorescence of organic molecules, Chem. Commun., 2017, 53, 2081–2093 RSC.
- J. Ren, Y. Tian, Y. Wang, J. Yang, M. Fang and Z. Li, The influence of p–p stacking on the room temperature phosphorescence of phenothiazine 5,5-dioxide derivatives, J. Mater. Chem. C, 2022, 10, 13741 RSC.
- P. S. Singh, P. M. Badani and R. M. Kamble, Impact of the donor substituent on the optoelectrochemical properties of 6H-indolo[2,3-b] quinoxaline amine derivatives, New J. Chem., 2019, 43, 19379–19396 RSC.
- X. Tang, Q. Bai, Q. Peng, Y. Gao, J. Li, Y. Liu, L. Yao, P. Lu, B. Yang and Y. Ma, Efficient Deep Blue Electroluminescence with an External Quantum Efficiency of 6.8% and CIEy < 0.08 Based on a Phenanthroimidazole−Sulfone Hybrid Donor−Acceptor Molecule, Chem. Mater., 2015, 27, 7050–7057 CrossRef CAS.
- W. Li, Y. Pan, L. Yao, H. Liu, S. Zhang, C. Wang, F. Shen, P. Lu, B. Yang and Y. Ma, A Hybridized Local and Charge-Transfer Excited State for Highly Efficient Fluorescent OLEDs: Molecular Design, Spectral Character, and Full Exciton Utilization, Adv. Opt. Mater., 2014, 2, 892–901 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Hou, H. Wang, Y. Miao, H. Xu, Z. Guo, Z. Chen, X. Liao, L. Li, J. Li and K. Guo, Highly Efficient Deep-Blue Electroluminescence from a A−π−D−π−A Structure Based Fluoresence Material with Exciton Utilizing Efficiency above 25%, ACS Appl. Energy Mater., 2018, 1, 3243–3254 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Zhang, M. Qile, J. Sun, M. Xu, K. Wang, F. Cao, W. Li, Q. Song, B. Zou and C. Zhang, Ratiometric pressure sensors based on cyano-substituted oligo(p-phenylene vinylene) derivatives in the hybridized local and charge-transfer excited state, J. Mater. Chem. C, 2016, 4, 9954–9960 RSC.
- L. Xianhao, M. Sun, L. Xu, R. Wang, H. Zhou, Y. Pan, S. Zhang, Q. Sun, S. Xue and W. Yang, Highly efficient non-doped blue fluorescent OLEDs with low-efficiency roll-off based on hybridized local and charge transfer excited state emitters, Chem. Sci., 2020, 11, 5058–5065 Search PubMed.
- X. Chen, D. Ma, T. Liu, Z. Chen, Z. Yang, J. Zhao, Z. Yang, Y. Zhang and Z. Ch, Hybridized Local, and Charge-Transfer Excited-State Fluorophores through the Regulation of the Donor-Acceptor Torsional Angle for Highly Efficient Organic Light-Emitting Diodes, CCS Chem, 2022, 4, 1284–1294 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Xu, Y. Yuan, X. Cai, C. Zhang, F. Hu, J. Liang, G. Zhang, D. Zhang and B. Liu, Tuning the singlet-triplet energy gap: a unique approach to efficient photosensitizers with aggregation-induced emission (AIE) characteristics, Chem. Sci., 2015, 6, 5824 RSC.
- (a) Y. Pan, J. Huang, W. Li, Y. Gao, Z. Wang, D. Yu, B. Yang and Y. Ma, Theoretical investigation of high-efficiency organic electroluminescent material: HLCT state and hot exciton process, RSC Adv., 2017, 7, 19576 Search PubMed; (b) M. I. Alam, M. R. Nagar, D. Barman, P. K. Iyer, J. H. Jou and S. Vaidyanathan, Tailoring structural rigidity utilizing a lock/unlock donor strategy for highly efficient solution-processed blue and green HLCT OLEDs, J. Mater. Chem. C, 2024, 12, 13585 Search PubMed.
- X. Wang, C. Ma, M. Xie, L. Chu, Y. Zhou, Q. Sun, W. Yang and S. Xue, Efficient and ultra-high luminance orange-red organic light emitting diode (OLED) based on a triphenylamine-benzothiadiazole-phenoxazine hybrid molecule with hybrid local and charge-transfer (HLCT) characteristic, Dyes Pigm., 2024, 229, 112274 CrossRef CAS.
- I. Bala, N. Singh, R. A. K. Yadav, J. De, S. P. Gupta, D. P. Singh, D. K. Dubey, J. H. Jou, R. Douali and S. K. Pal, Room temperature perylene-based columnar liquid crystals as solid-state fluorescent emitters in solution-processable organic light-emitting diodes, J. Mater. Chem. C, 2022, 8, 12485–12494 RSC.
- I. Bala, R. A. K. Yadav, M. Devi, J. De, N. Singh, K. Kailasam, J. Jayakumar, J. H. Jou, C. H. Cheng and S. K. Pal, High-performing D–π–A–π–D benzothiadiazole-based hybrid local and charge-transfer emitters in solution-processed OLEDs, J. Mater. Chem. C, 2020, 8, 17009–17015 RSC.
- T. Jairam and W. P. Hong, Recent progress in imidazole based efficient near ultraviolet/blue hybridized local charge transfer (HLCT) characteristic fluorophores for organic light-emitting diodes, J. Mater. Chem. C, 2022, 10, 16173–16217 RSC.
- H. Zhang, J. Zeng, W. Luo, H. Wu and C. Zeng, Synergistic tuning of the optical and electrical performance of AIEgens with a hybridized local and charge-transfer excited state, J. Mater. Chem. C, 2019, 7, 6359–6368 RSC.
- C. Wang, X. Li, Y. Pan and S. Zhang, Highly efficient non-doped green organic light-emitting diodes with combination of high photoluminescence and high exciton utilization, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2016, 8, 3041–3049 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Zhang, W. Li, L. Yao, Y. Pan, F. Shen, R. Xiao, B. Yang and Y. Ma, Enhanced proportion of radiative excitons in non-doped electro-fluorescence generated from an imidazole derivative with an orthogonal donor-acceptor structure, Chem. Commun., 2013, 49, 11302–11304 Search PubMed.
- W. P. Hong and J. Tagare, Recent Progress in Imidazole Based Efficient near Ultraviolet/Blue Hybridized Local Charge Transfer (HLCT) Characteristics Fluorophores for Organic Light-Emitting Diodes, J. Mater. Chem. C, 2022, 10, 16173–16217 RSC.
- X. Tang, Q. Bai, Q. Peng, Y. Gao, J. Li, Y. Liu, L. Yao, P. Lu, B. Yang and Y. Ma, Efficient deep blue electroluminescence with an external quantum efficiency of 6.8% and CIE y< 0.08 based on a phenanthroimidazole–sulfone hybrid donor-acceptor molecule, Chem. Mater., 2015, 27, 7050–7057 Search PubMed.
- P. K. Behera, S. Lenka, F. R. Chen, M. Roy, I. Mondal, D. S. Rao, S. P. Senanayak, J. H. Jou and A. S. Achalkumar, Revelation of room temperature liquid crystallinity and yellow-orange electroluminescence (EQE> 7%) in a columnar self-assembled N-annulated perylene bisimide, Chem. Eng. J., 2024, 497, 154719 CrossRef.
- A. Hägerbäumer, S. Höss, P. Heininger and W. Traunspurger, Experimental studies with nematodes in ecotoxicology: an overview, J. Nematol., 2015, 47, 11 Search PubMed.
- P. R. Hunt, The C. elegans model in toxicity testing, J. Appl. Toxicol., 2017, 37, 50–59 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Zhang, Y. T. Sun, S. Gan, A. Ren, S. Milaneh, D. J. Xiang and W. L. Wang, Recent progress of organic fluorescent molecules for bioimaging applications: cancer-relevant biomarkers, J. Mater. Chem. C., 2023, 11, 16859–16889 Search PubMed.
- A. S. Stender, K. Marchuk, C. Liu, S. Sander, M. W. Meyer, E. A. Smith and N. Fang, Single cell optical imaging and spectroscopy, Chem. Rev., 2013, 113, 2469–2527 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Murschhauser, P. J. F. Röttgermann, D. Woschee, M. F. Ober, Y. Yan, K. A. Dawson and J. O. Radler, A high-throughput microscopy method for single-cell analysis of event-time correlations in nanoparticle-induced cell death, Commun. Bio., 2019, 2, 35 CrossRef PubMed.
- A. Saini, V. Sharma, P. Mathur and M. M. Shaikh, The development of fluorescence turn-on probe for Al(III) sensing and live cell nucleus-nucleoli staining, Sci. Rep., 2016, 6, 34807 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Sadhu and A. K. Mitra, Synthetic, biological and optoelectronic properties of phenoxazine and its derivatives: a state-of-the-art review, Mol. Divers., 2024, 28, 965–1007 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Y. Zhu, H. W. Yao, Y. J. Fu, X. F. Guo and H. Wang, Effect of substituents on Stokes shift of BODIPY and its application in designing bioimaging probes, Anal. Chim. Acta, 2019, 1048, 194–203 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Valdez, M. Robertson and Z. Qiang, Fluorescence resonance energy transfer measurements in polymer science: A review, Macromol. Rapid Commun., 2022, 43, 2200421 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. P. Provenzano, K. W. Eliceiri and P. J. Keely, Multiphoton microscopy and fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy (FLIM) to monitor metastasis and the tumour microenvironment, Clin. Exp. Metastasis, 2009, 26, 357–370 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available. See DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/d5tb00207a |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2025 |