Improved lithium–sulfur batteries with a conductive coating on the separator to prevent the accumulation of inactive S-related species at the cathode–separator interface†
Abstract
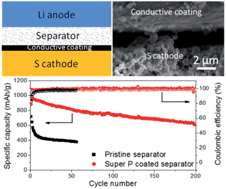
Lithium–sulfur (Li–S) batteries are highly attractive for future generations of portable electronics and electric vehicles due to their high energy density and potentially low cost. In the past decades, various novel electrodes and electrolytes have been tested to improve Li–S battery performance. However, these designs on electrodes and electrolytes have not fully addressed the problem of low cycling stability of Li–S batteries. Here, we show the role of the separator in the capacity decay of the Li–S battery, namely that it can accommodate a large amount of polysulfides inside which then precipitates as a thick layer of inactive S-related species. Using a thin conductive coating on the separator to prevent the formation of the inactive S-related species layer, we show that the specific capacity and cycling stability of the Li–S battery are both improved significantly compared to the battery with a pristine separator. Combining this separator design with a monodisperse sulfur nanoparticle cathode, we show Li–S batteries with a life of over 500 cycles with an initial specific capacity of 1350 mA h g−1 at C/2 and a cycle decay as low as 0.09% per cycle.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...