Combined three dimensional locomotion and deformation of functional ferrofluidic robots†
Xinjian
Fan
 ab,
Yunfei
Zhang
a,
Zhengnan
Wu
a,
Hui
Xie
ab,
Yunfei
Zhang
a,
Zhengnan
Wu
a,
Hui
Xie
 c,
Lining
Sun
ab,
Tao
Chen
*bd and
Zhan
Yang
c,
Lining
Sun
ab,
Tao
Chen
*bd and
Zhan
Yang
 *ab
*ab
aSchool of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering, Soochow University, No. 8, Jixue Road, Suzhou 215131, China. E-mail: yangzhan@suda.edu.cn
bJiangsu Provincial Key Laboratory of Advanced Robotics, School of Mechanical and Electric Engineering, Soochow University, Suzhou 215123, China
cState Key Laboratory of Robotics and Systems, Harbin Institute of Technology, Yikuang, Harbin 150080, China
dSchool of Future Science and Engineering, Soochow University, No. 1, Jiuyongxi Road, Suzhou 215222, China. E-mail: chent@suda.edu.cn
First published on 9th November 2023
Abstract
Magnetic microrobots possess remarkable potential for targeted applications in the medical field, primarily due to their non-invasive, controllable properties. These unique qualities have garnered increased attention and fascination among researchers. However, these robotic systems do face challenges such as limited deformation capabilities and difficulties navigating confined spaces. Recently, researchers have turned their attention towards magnetic droplet robots, which are notable for their superior deformability, controllability, and potential for a range of applications such as automated virus detection and targeted drug delivery. Despite these advantages, the majority of current research is constrained to two-dimensional deformation and motion, thereby limiting their broader functionality. In response to these limitations, this study proposes innovative strategies for controlling deformation and achieving a three-dimensional (3D) trajectory in ferrofluidic robots. These strategies leverage a custom-designed eight-axis electromagnetic coil and a sliding mode controller. The implementation of these methods exhibits the potential of ferrofluidic robots in diverse applications, including microfluidic pump systems, 3D micromanipulation, and selective vascular occlusion. In essence, this study aims to broaden the capabilities of ferrofluidic robots, thereby enhancing their applicability across a multitude of fields such as medicine, micromanipulation, bioengineering, and more by maximizing the potential of these intricate robotic systems.
1 Introduction
The field of microrobotics has experienced significant progress in recent years, with an increasing focus on the development of magnetically controlled microrobots.1–3 These minuscule robotic systems possess distinctive capabilities that enable them to access confined spaces and execute intricate tasks with minimal disruption to their surrounding environments.4–7 Compared with light field drive and electric field drive,8,9 magnetically controlled microrobots stand out due to their inherent advantages, such as wireless actuation, non-invasive control, reduced size and complexity, and improved adaptability.10–14Despite the promising capabilities of magnetically controlled microrobots, they currently face challenges, including limited deformation and difficulty in achieving motion in restricted environments.15 This is particularly relevant for magnetically controlled soft robots, which are based on elastic materials and designed to navigate complex and delicate environments, such as biological tissues or fluidic systems.16–19 However, their deformation ability is relatively weak, and it remains challenging to generate efficient motion in environments with a cross-sectional area smaller than their own size.20,21 To address this issue, researchers have proposed magnetic droplet robots with more powerful deformation capabilities, such as liquid metal robots and ferrofluidic robots.22–25 The droplet robot has greater deformability and can even achieve extreme deformations such as splitting and fusion, thus acquiring higher flexibility and expanding the functional list of magnetic robots, showcasing superior functionality and flexibility.26 Among them, ferrofluidic robots have drawn widespread attention from researchers due to their superior biocompatibility and controllability. For example, Lin et al. achieved automated virus detection based on the automated control of ferrofluidic robots;27 Fan et al. utilized an electromagnetic array to achieve targeted drug delivery and fragile object micromanipulation of a ferrofluidic robot in a two-dimensional(2D) plane.28 Sun et al. utilized the wetting characteristics of ferrofluidic robots on different materials to achieve efficient artificial cilia and inchworm motion robots.29
However, the current research primarily concentrates on their deformation and motion within two-dimensional spaces,30–34 or rely on a magnetic cilia array, magnetic gripper and so on to achieve the three-dimensional movement of the droplet, which will greatly limit the application of the droplet robot.35,36 This focus results in relatively limited functionality, which in turn restricts their value in a range of potential applications.37–39 Achieving 3D motion and deformation control in droplet robots and equipping them with a diverse set of task execution capabilities remain a critical challenge in the field. Advancements in these areas would enable droplet robots to perform complex tasks, such as navigating through intricate vascular networks or manipulating microscopic objects with high precision.40 Furthermore, improvements in motion control and deformation would facilitate better adaptability to their surroundings, allowing them to overcome obstacles and traverse unstructured environments more effectively. Developing these capabilities can substantially enhance the functionality and versatility of magnetic microrobots.41 For instance, in medicine, improved 3D control could facilitate targeted drug delivery to specific tissues, minimizing side effects and improving the treatment efficacy. In micromanipulation, the ability to perform delicate tasks in 3D spaces could revolutionize fields like microfabrication, enabling the assembly of intricate structures with unparalleled precision.
To surmount the aforesaid limitations, we present deformation control and 3D trajectory control strategies for a ferrofluidic robot. Fig. 1A illustrates the overall structure of the magnetic control system devised in this paper. Fig. 1B depicts the internal components of the ferrofluidic robot, which is composed of Fe3O4 nanoparticles, carriers, and surfactants. Fig. 1C shows the locomotion and deformation control strategy of the ferrofluidic robot by employing the designed magnetic actuation system. By adjusting the external magnetic field direction, we can control the deformation direction of the ferrofluidic robot and accomplish position control based on the magnetic field gradient. Concurrently, considering the heterogeneous distribution of the driving magnetic field intensity and gradient, we propose a sliding mode controller to augment the robustness and anti-interference capabilities of the control process during the 3D motion control of the ferrofluidic robot. This controller exhibits less reliance on control parameters and superior performance in handling nonlinear systems compared to a PID controller.42 Leveraging these capabilities, we exhibit the versatile motion abilities of ferrofluidic robots in complex environments, including accurate tracking of various 2D and 3D trajectories, such as discontinuous lines and curved paths, as well as obstacle avoidance tracking experiments in intricate 3D maps. As illustrated in Fig. 1D–I, building on these capabilities, we further demonstrate the practical applications of ferrofluidic robots in areas such as foreign matter interception, complex path avoidance, microfluidic pump systems, object manipulation, selective vascular occlusion and controllable droplet fusion. In summary, this research article aims to investigate the state-of-the-art in magnetically controlled microrobots, address their current challenges and limitations, and propose innovative solutions for extending their capabilities, particularly in the realm of deformation and 3D motion control. By doing so, we strive to enhance their applicability across a wide range of fields, unlocking new possibilities in fields such as medicine, micromanipulation, bioengineering, and beyond.
2 Results and discussion
2.1 Design and concept of the ferrofluidic robot system
Fig. 2A illustrates the use of an electromagnetic field generation system to produce and manipulate the actuating magnetic field. The magnetic field generates a driving force that actuates the robot, while rotating the magnetic field evenly changes the magnetization direction of the robot. While other forces, such as viscous resistance, gravity, and buoyancy, contribute to the movement of the robot, the primary means of achieving motion control in this system is adjusting the controllable force Fm. Therefore, to generate a controllable magnetic field, we designed and prepared a dedicated electromagnetic coil system. The setup uses eight stationary electromagnetic coils with controllable currents, which are evenly placed at the eight top corners of the cube, with each coil facing downward at a 35.3° angle toward the workspace. Each coil is composed of two groups in parallel, the total number of turns in the inner ring is 800, the total number of turns in the outer ring is 600, the diameter of the selected enamels is 0.4 mm, the total resistance is 4.4 Ω, and the rated voltage is 25 V. Soft magnetism is used in each coil to enhance the magnetic field generated. The workspace cube size is 40 × 40 × 40 mm3, and the coils adopt a mode in which the inner and outer rings are in parallel, reducing the resistance and increasing current. The system includes chutes on the bottom and top plates, as well as supports on the upper and lower bases to adjust the size of the working space. Two power supplies (eTM-6030, TOMMENS) were used, and eight power amplifiers (OPA541, Texas Instruments) were connected to a DAQ card (PCI-6733, National Instruments) with eight channels to receive controlling inputs. To prevent fluctuating temperatures from negatively affecting the magnetic field generation capabilities of the electromagnetic coils, water pipes were wrapped inside and outside the coils, and water pumps were used to dissipate heat for the system. This ensured that the system temperature was maintained at a constant temperature of 24 °C.The workspace consists of a custom-made glass cuboid with dimensions of 24 mm × 24 mm × 50 mm. A mixture of NaCl, glycerol, and water was combined and thoroughly stirred to simulate the fluid environment inside the human body. Besides, two fixed-position cameras were strategically positioned to provide comprehensive visual feedback of the workspace from both overhead and frontal perspectives. The cameras were capable of capturing high-resolution images of 1280 × 768 pixels. The tracking algorithm used was the mean-shift algorithm. The mean-shift algorithm is essentially a centroid shift algorithm. It involves using the mouse to select a box around the robot that you want to track. The program will then calculate the centroid of all the points within the box selection area and move it to the center of that area, creating a new box selection area center. This iterative process helps the program track the movement of the robot step by step, continuously updating the box's position as the robot moves. The ferrofluidic robot, an integral part of the system, exhibits a range of motion that extends across half region within the captured frames. The entire system, designed with optimal precision and efficiency in mind, was managed via the LabVIEW interface on a dedicated desktop computer. A droplet of 0.2 μL of ferrofluid was added to the mixture using a micropipette. For this study, only an oil-based ferrofluid was used, as it has excellent deformability and low hysteresis with changes in the magnetic field, and is immiscible with the body fluids. Fig. 2B presents the Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) image of the ferrofluidic robot, revealing its primary composition of iron oxide nanoparticles. Furthermore, to ensure a more uniform and stable dispersion of these nanoparticles in the carrier liquid, namely hydrocarbons, the ferrofluidic robot was also supplemented with surfactants like silicone oil. These surfactants function as stabilizers, enhancing the robot's stability and preventing it from precipitating even under the influence of strong magnetic fields, thereby maintaining its integrity over extended periods.
2.2 Magnetic control theory of ferrofluidic robots
It is assumed that the magnetically controlled ferrofluidic robot in question is a magnetized entity, characterized by its unique magnetic moment. It is worth noting that the magnetic moment of soft magnetic materials differs from that of permanent magnets, which have a constant size and an unchanging direction. The magnitude and orientation of soft magnetic materials will vary contingent on the applied magnetic field. The magnetization property of the ferrofluid is similar to that of soft magnetism, therefore, the relationship between its magnetization and the external magnetic field must be taken into consideration. Therefore, the force needed to move the robot towards a specific position, along with the torque required to rotate the robot, can be expressed as follows:43| T = SK(M)B | (1) |
 | (2) |
 | (3) |
In this matrix, the Mx, My and Mz stand for the three components of the M axis, respectively. It is important to note that the magnetic torque always points the magnetization direction of the robot towards the external magnetic field. Therefore, we indirectly controlled the magnetization direction of the robot by adjusting the direction of the external magnetic field, rather than directly adjusting its torque. Considering a fixed arrangement of electromagnets, each individual electromagnet can generate a magnetic field throughout the workspace, which can be precomputed. At any particular point P in the workspace, the magnetic field due to the actuation of a specific electromagnet can be depicted by the vector B(P), as displayed in Fig. 2C, whose magnitude is proportional to the current passing through the electromagnet. For hollow electromagnets, each field's contribution is uncoupled, and the total contribution can be computed by linear superposition after calculating the magnetic field generated by energizing a single coil. While an electromagnet with a soft core can produce a more potent field, the total contribution does not superimpose linearly. However, if it is assumed that the soft magnetic core employed is an ideal, hysteresis-free material, and it operates within its linear operating range, the principle of linear superposition remains applicable. Here, the subscript j signifies the contribution due to actuating the jth electromagnet.
 | (4) |
The total flux density at the spatial point P can be computed using a linear superposition of the flux densities produced by all the coils as per eqn (4). The flux density from a single coil can be obtained by multiplying the direction vector  with the current amplitude, as shown in eqn (5):
with the current amplitude, as shown in eqn (5):
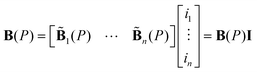 | (5) |
The formula to calculate the magnetic gradient in the x-axis direction, which is obtained by multiplying the flux density gradient vector  with the current amplitude, is shown in eqn (6):
with the current amplitude, is shown in eqn (6):
 | (6) |
By substituting eqn (1) and (3) into eqn (4), we derived eqn (7), which can be used to acquire the desired matrix and its pseudo-inverse matrix. Initially, the flux density and gradient force vector were input, which then yields the magnitude of the current value for each electromagnet as follows:
 | (7) |
Based on the above analysis and theoretical derivation, we can achieve precise motion control of the ferrofluidic robot by designing a closed-loop controller. As shown in Fig. 2D, the position of the robot photographed by the camera is tracked by the shape-adapted mean-shift algorithm,44 and then fed back to the system by the Kalman filtering. Then the system uses the synovial controller for calculations and outputs the final required voltage signal to the coil system through the power amplifier to control the movement of the robot. The system model is imbued with considerable uncertainties. To compensate for these uncertainties and the perturbations they introduce, as well as to minimize the tracking error, we adopted a robust sliding mode controller for the system's control, as depicted in ESI note 2†.
2.3 Modeling of the induced electromagnetic field
The depiction in Fig. 2C demonstrates how the magnetic field around a coil with an iron core is modelled using a magnetic dipole. The resultant magnetic field distribution, propagated by the dipole, is as follows:45 | (8) |
 . We then employ the genetic algorithm to iteratively fine-tune and optimize M and d until the objective function falls within an acceptable range, or until the maximum iteration count is reached. For a detailed execution process of the optimization algorithm, please refer to Fig. S1 and S2.†
. We then employ the genetic algorithm to iteratively fine-tune and optimize M and d until the objective function falls within an acceptable range, or until the maximum iteration count is reached. For a detailed execution process of the optimization algorithm, please refer to Fig. S1 and S2.†
2.4 Theoretical verification of control mechanisms and methods
Subsequently, a theoretical analysis of the control efficacy of the controller with respect to the ferrofluidic robot's motion is embarked upon. The kinematic equation relating to the robot is derived, utilizing the quasi-static force analysis method as a foundation. This derivation serves to construct a computational model, facilitating the evaluation of the robot's motion dynamics under the influence of the predetermined control system. The encompassing force acting on the robot is expressed as follows:| F = ma = Fm + Fg + Fd + Fv | (9) |
In this equation, F is the inertial force on the robot, Fm signifies the magnetic gradient force, Fg = mg denotes gravity, m stands for the robot's mass, Fv = ρVg is the buoyancy of the robot and Fd = 6πηav represents the viscous resistance. Herein, a refers to the acceleration, ρ indicates the density, V specifies the volume, g is the gravitational acceleration, η is the fluid viscosity, a is the radius of the droplet, and v signifies the instantaneous velocity. Following the derivation, the application of the new Euler integral is implemented to simulate the motion of ferrofluidic robots under our proposed control strategies. As depicted in the conceptual graphs of Fig. 3A and E, the proposed simulation algorithm is employed to evaluate the tracking performance of the robot on a 2D circle with a diameter of 6 mm and a 3D polyline with dimensions of 5 mm × 5 mm × 6 mm. Fig. 3B and F display the resulting trajectories, and videos S1 and S2† provide further visual demonstration. The simulated trajectory closely aligns with the preset trajectory, indicating the commendable control effect of the employed methods on the robot's tracking of both 2D and 3D trajectories.
2.5 Assessment of motion velocity and deformability in a ferrofluidic robot
The realization of precise motion speed and deformation control for ferrofluidic robots can facilitate more adaptive management, an attribute of substantial significance for their utilization in complex scenarios. Therefore, we propose to carry out a quantitative analysis to evaluate the control feasibility of velocity and deformation during the locomotion of a ferrofluidic robot. This investigation will contribute to a more comprehensive understanding of the dynamic control capabilities of these robots, thereby expanding their applicability in intricate settings. As shown in Fig. 4A, the velocity of the robot mainly depends on the viscosity of the liquid environment, which is decided by the mass ratio ηm of the glycerin to water (the higher the mass ratio, the more viscous the liquid becomes), and the voltage. If the mass ratio remains the same, then the velocity increases as the voltage increases due to a greater magnetic force. But, if the voltage is constant the velocity will decrease as the mass ratio increases, due to a larger resistance. Additionally, as observed in Fig. 4B, it can be noted that the velocity of the robot is influenced by its diameter. When the diameter of the robot increases, the speed of the robot also increases proportionally. The primary reason for this phenomenon is the larger volume of the robot, which results in a more pronounced magnetic gradient force that is substantial enough to overcome the drag effect caused by the increased volume. Therefore, by modulating parameters such as magnetic field strength and liquid viscosity, we can adjust the motion velocity of a ferrofluidic robot, laying the foundation for realizing its controllable motion.The deformation ability of ferrofluidic robots plays a crucial role in facilitating their movement in confined spaces. Empirical observations demonstrate that when exposed to a magnetic field, ferrofluidic robots exhibit elongation aligned with the magnetic field lines. This phenomenon can be attributed to the inherent tendency of the internal nanoparticles to orient themselves in a head-to-tail fashion. Importantly, the magnitude of this elongation exhibits a directly proportional relationship to the strength of the external magnetic field, highlighting the complex interdependence between the droplet microrobots’ physical properties and the characteristics of the environment in which they function.
Our experimental results provide further evidence for this observation. Specifically, our experiments demonstrate that the microrobot exhibits deformation in response to increasing magnetic field strength, resulting in a corresponding alteration in the ratio of its major axis to its minor axis. The deformability of the microrobot was assessed through the ratio between the major and minor axes of its shape. As illustrated in Fig. 4C, increasing the driving voltage from 1 to 4 V led to an increased deformation of up to 300% from the robot's initial shape. However, further increase in field strength produced diminishing changes in deformation. This gradual saturation of deformation may arise from the gradually dominant role of surface tension that restores the robot's sphericity. Therefore, by selecting a ferrofluidic robot of a suitable size and administering a specific magnetic field, we can fine-tune its elongation characteristics and direction. This approach provides a flexible method to manipulate these robots for specialized tasks and applications. These distinct deformation characteristics of the microrobots can be leveraged for specialized operations such as fluid pumping, controllable pipeline blockade, etc., as substantiated by our subsequent experimental investigations.
2.6 Experimental verification of control mechanisms and methods
Fig. 3C illustrates the experimental results of tracking a circular trajectory by a ferrofluidic robot under the regulation of the proposed control system and its concomitant strategies. To further substantiate the performance of the ferrofluidic robots in tracking varying trajectory types, the outcomes pertaining to their performance on rectangular trajectories are presented. As represented in Fig. S3† and Fig. 3C, the actual trajectories display a noteworthy degree of congruity with the pre-established trajectories, with deviations visible in Fig. S4† and Fig. 3D. The comparative analysis suggests that the circular trajectories exhibit a larger mean error of approximately 0.07 mm, which is approximately twice that of rectangular trajectories. This suggests a suboptimal tracking precision for curvilinear paths, which possess inherent curvature compared to rectangular paths. This can predominantly be attributed to the fact that the arc trajectory requires the robot to continuously change its direction, potentially inciting velocity overshoot during the gradient force transition phase, leading to inertial offset. Nonetheless, the ratios of the mean error to the ferrofluidic robot's diameter, calculated as the average error divided by the robot's diameter, remain below 20%, which is less than one-fifth of the robot's diameter.In addition, magnetic microrobots have surfaced as a potential tool for diverse applications, particularly in targeted therapy. The performance efficiency of these robots largely depends on their accurate control within complex internal environments, such as capillaries and cerebral blood vessels. Therefore, it is pivotal to evaluate the system's 3D trajectory tracking performance to determine its precision in controlling 3D trajectories. Fig. 3E exhibits a ferrofluidic robot tracing a 3D saddle-like trajectory under system control. The dimensions of the 3D trajectory, 7 mm × 7 mm × 5 mm, are specified in Fig. 3G. However, visible discrepancies exist between the robot's actual and predetermined trajectories, with the maximum error and average error being 0.3 and 0.1 mm (Fig. 3H), respectively, which can potentially be ascribed to the robot's inertia during cornering or the additional gradient force exerted on the robot when in proximity to the coil. However, these deviations can be minimized by adjusting certain parameters within the system's sliding mode controller, such as the proportional coefficient k, ms, and the maximum and minimum voltage limit of the driving system. It should be noted that the standardized 3D curve considered here is not an exact replica of the blood vessel channels encountered in real biological experiments, which typically are 3D curves of varying curvatures. To validate the accuracy of the 3D trajectory control, tests involving 3D curves with distinct curvatures, such as involute, saddle shape, and helix were conducted. Fig. S5, S7, and S9† showcase that the actual trajectory closely adheres to the preset trajectory, such as involute, saddle shape, and helix trajectories. The robot's diameter in all instances was 0.8 mm. Additionally, Fig. S6, S8, and S10† validate that regardless of variations in the shape of the target trajectory, the motion control performance of the robot remains consistently high, with the tracking error consistently less than one-third of its own diameter. This reaffirms the effectiveness of the control strategy employed in this work.
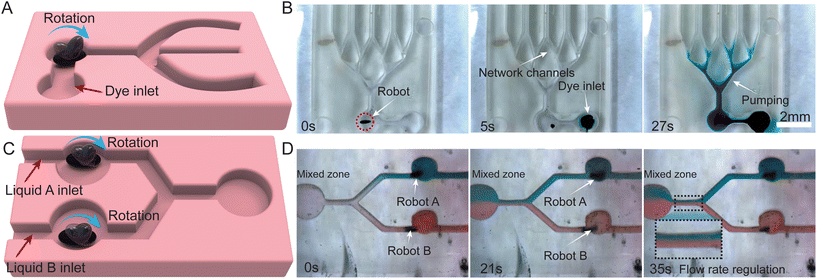
2.7 Deformed ferrofluidic robots as a microfluidic inducer
The diagrams in Fig. 5A and B show in detail the fluid pumping process by a deformed ferrofluidic robot, schematically and experimentally. The rotation of the magnetic fluid in the x–z plane, induced by a controlled rotating magnetic field, enables the translocation of fluid from the inlet point to the outlet point. The pumped fluid was dyed with food-grade coloring for clear visualisation. It was observed that the robot could rapidly and efficiently relocate the fluid, as demonstrated in the figure and further detailed in supplementary Video S3.† Remarkably, the pumping speed was recorded to reach up to 3 mm s−1, outperforming cilia-based methods for microfluidic pumping.46Fig. 5C and D present the conceptual and experimental representations of fluid mixing, respectively. Each channel houses a robot, which is maneuvered by a rotating magnetic field to transport the targeted fluid into a central channel for subsequent mixing. The experimentally recorded footage indicated that the rotation of the ferrofluidic robot induces effective fluid mixing in a Y-shape channel. Moreover, by synchronously adjusting the rotation direction of the ferrofluidic robots, it was possible to freely control the relative flow velocity of the fluid in these two channels. This capability allows for the adjustment of component proportions in the mixed fluid. Considering its microscale size and high-speed pumping operation, the ferrofluidic robot exhibits considerable promise in the realm of microfluid-inducing applications.
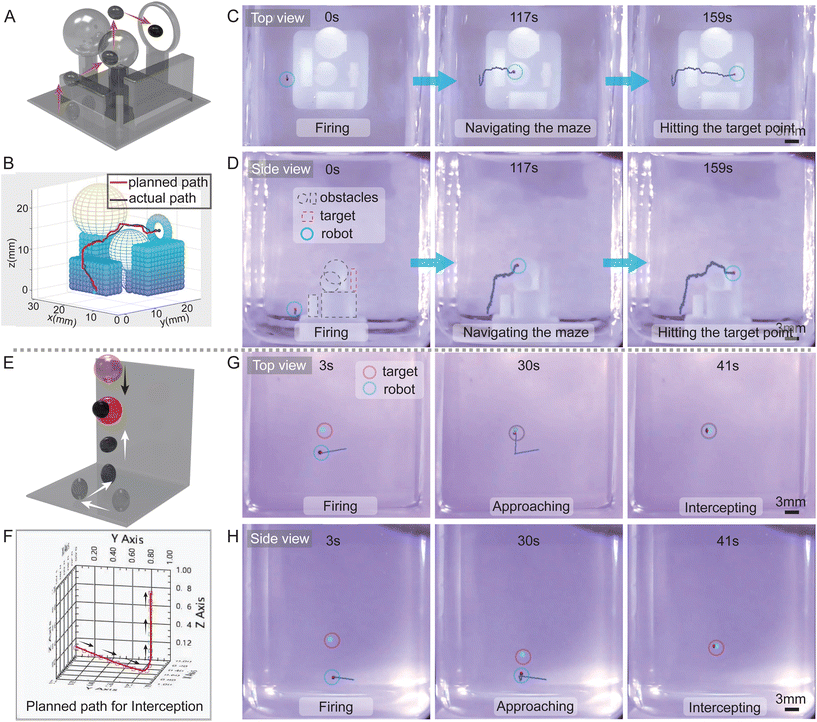
2.8 3D locomotion of ferrofluidic robots for hitting missions
Fig. 6A and B respectively illustrate the conceptual schematic for complex path obstacle avoidance and the process for generating an obstacle-avoidance pathway. Both top and main perspectives of the complex path obstacle avoidance are demonstrated in Fig. 6C and D respectively. A 3D maze, designed using resin-based 3D printing, served as the operational platform. The predetermined trajectory was planned using the LabVIEW software, utilizing the Rapidly-exploring Random Tree (RRT) algorithm for optimal path planning, as expanded in supplementary Video S4.† Subsequently, this planned pathway was integrated into the control system. During the navigational sequence, the robot adeptly maneuvers around the cuboid obstacle, continues along a circular path with a radius slightly exceeding the spherical obstacle, and eventually reaches the central location within the hollow ring. Further detailed observations of this process can be extracted from supplementary Video S4.† Fig. S11† provides a comparison between the actual and generated trajectories, demonstrating the high congruity between the two, with only minor deviations. This emphasizes the precision of the control system and the efficacy of the trajectory planning, underscoring the ferrofluidic robot's precise strike capability against static targets.Fig. 6E and F delineate the conceptual schematic for droplet interception and the interception trajectory generation respectively. Both the interception test and complex path obstacle avoidance maneuvers are regulated by the system, with a camera providing real-time imaging for feedback adjustments. The top and main perspectives of the interception test are depicted in Fig. 6G and H respectively. The initial configuration of the robot and the liquid droplet is presented in the first image, with the concluding interception frame showcased in the third image, providing a visualization of the robot's trajectory. Upon the droplet's initiation of descent from its starting position, the initial coordinates of both the robot and the target droplet are fed into the algorithm to compute the interception trajectory, further detailed in supplementary Video S4.† Subsequently, the controller orchestrates the robot's motion to intercept the falling droplet according to the pre-calculated trajectory. Fig. S12† shows the comparison between the generated interception trajectory and the actual trajectory followed by the robot. Although minor discrepancies are evident at the transitional junction where the x and y plane motion converts into z-axis movement, these do not impinge upon the successful interception of the droplet. The efficacy of this function may prove instrumental in medical applications, for instance, preventing the ingress of impurities into human body fluids, thereby enhancing the safety and precision of therapeutic or diagnostic procedures.
2.9 Applications of ferrofluidic robots based on combined 3D locomotion and deformation
The integration of deformation and locomotion capacities within ferrofluidic robots empowers these entities to carry out more intricate experimental procedures, as demonstrated in Video S5† and Fig. 7A and B. During the procedure, the robot approaches the first oil-based droplet, triggering adsorption and consequent fusion with a secondary droplet of disparate composition. Following thorough mixing, the robot retains its ability to govern the movement of the resultant droplet flexibly. It is noteworthy that the process necessitates the application of an external magnetic field to direct the deformation of the ferrofluidic robot towards the radial direction of the controlled droplet. This precautionary step is undertaken to obviate the possibility of the ferrofluidic robot becoming immobilized due to simultaneous adsorption on opposing sides of the controlled droplet. Adopting this methodology enables the fusion of diverse microscopic droplets in a non-contact, contamination-free manner. The ensuing fluorescence imaging (subfigure in Fig. 7B) substantiates the occurrence of an intense reaction following the mixing of the two droplets, thus evidencing the practicability of ferrofluidic robots within the domain of liquid droplet mixing. This distinctive capacity of ferrofluidic robots promises substantial potential applications in disciplines such as virus detection and control of microscale chemical reactions.47 By enabling precise manipulation and combination of microdroplets, these robots could significantly advance fields requiring high-precision fluid handling, such as lab-on-a-chip technologies or point-of-care diagnostics.The achievement of 3D manipulation of objects within confined and sealed environments bears significant implications for micro-assembly and targeted biomedical applications. Given the inherent wettability of oleophilic materials, ferrofluids can adhere securely to the object being manipulated. This feature, in conjunction with their 3D locomotion ability, facilitates effective oleophilic material transportation. Fig. 7D and E depict the top and front views, respectively, of a ferrofluidic robot during a 3D assembly experiment involving specific cargo. As can be inferred from the image, the robot initially approaches the object and impacts it, achieving adhesion through the process of wetting. Subsequently, under the influence of a specific directional magnetic gradient force, the object is directed to the sidewall of the target area. The force's direction is modulated to synchronize with the cargo, allowing the ferrofluidic robot to navigate the wall and transport the cargo to the intended position within the target area. To effect a controllable separation between the magnetic ferrofluidic robot and the manipulated object, we propose a strategy predicated on the application of a pulsatile high-intensity magnetic field. As demonstrated in Fig. 7C and the accompanying Video S5,† once the ferrofluidic robot reaches the designated area, it undergoes deformation in the direction of separation, thereby reducing its contact area with the cargo. The application of an instantaneous high-intensity magnetic field imparts a significant magnetic force to the robot, resulting in rapid acceleration. Given the involvement of viscous resistance, the cargo is unable to match this acceleration, leading to a relative velocity differential. This, in turn, enables the ferrofluidic robot to overcome the wetting force and disengage from the cargo.
The selective blocking of blood vessels to restrict nutrient delivery has substantial therapeutic potential, particularly in starving diseased tissues.48 Ferrofluid droplets exhibit robust active and passive deformation capabilities, allowing them to conform adaptively to their surrounding environment and efficiently seal specified constrained areas, making them ideally suited for vascular occlusion tasks. Fig. 7G and H (intercepted from Video S5†) show top and front view images, respectively, captured during the vascular occlusion experiment. The associated video and images demonstrate the use of the ferrofluidic robot's 3D mobility to maneuver within a 3D-printed model of the aortic arch and selectively navigate to a predetermined vascular position. Subsequent application of a magnetic field induces the robot to radially expand and deform along the vessel, enabling it to occupy the maximum possible cross-sectional area of the blood vessel and thereby effectuate vascular occlusion, even the cross-section of blood vessels is irregular in shape.
Next, to assess the efficacy of the occlusion, we introduced simulated blood (dyed solution) into the vascular model at a flow rate of 2.5 mm s−1. As can be observed from the accompanying videos and images, the simulated blood is diverted to other branches, with the occluded vessel remaining impassable. Notably, upon withdrawal of the controlling droplet robot from the occluded position, the simulated blood pooled at the base of the vessel is drawn upwards, rising along the occluded vessel. This dynamics effectively corroborates the occlusion effect and robust sealing performance, further validating the feasibility of this approach for vascular occlusion. The potential of robots for use in selective blockage of blood vessels is particularly promising, as they can achieve this task even if the cross-section of the blood vessels is irregular in shape. This highlights the potential of robots for use in medical procedures where precise targeting and control of blood flow is essential, such as in the treatment of tumors and aneurysms.
Fig. 8A showcases a set of Asho tubes, which are a portion of the equipment used in pig lung experiments. We have intercepted this setup, which primarily consists of complex bronchial structures in the shape of a T-frame, featuring an aperture of approximately 3–4 mm. Fig. 8B and C (intercepted from Video S6†) provide the main and top views of a biological experiment designed to remove bronchial impurities. Before commencing the experiment, some of the outermost tissue of fresh pig lungs was removed, and the bronchial tissue in the middle area was cut using scissors. The main bronchus has a T-shaped configuration, with an upper oval hole serving as the entrance for the robot and a lower round hole for the robot's exit. Impurities are carefully placed into the pig's lungs through the entrance using tweezers, and then the pig's lungs are tilted at an angle to allow the impurities to penetrate deeper. After this, the pig's lungs are placed into specific glasses for further experimentation. A solution, consisting of a 3![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 mass ratio of water and glycerin, was poured into a glass to create the experimental environment. The robot, prepared for the task, was then placed into this environment. The entire experimental process is as follows: 1. initially, the robot was controlled by a handle to climb from the bottom of the glass to a position 4 mm above the entrance of the pig lung. 2. The robot was then stretched along the z-axis using a voltage of 5.6 V, enabling it to slowly enter the bronchus with a narrower width. 3. After reaching the inside of the pipe, the voltage was reduced to 2.4 V. The robot tended to take on a spherical shape, increasing the contact area on the plane. Its left and right movements were controlled within the pipeline to facilitate the quicker capture of impurities. 4. Finally, the voltage was increased back to 5.6 V, and the impurities were dragged out from the internal area of the bronchus, successfully achieving the function of removing impurities from small spaces.
1 mass ratio of water and glycerin, was poured into a glass to create the experimental environment. The robot, prepared for the task, was then placed into this environment. The entire experimental process is as follows: 1. initially, the robot was controlled by a handle to climb from the bottom of the glass to a position 4 mm above the entrance of the pig lung. 2. The robot was then stretched along the z-axis using a voltage of 5.6 V, enabling it to slowly enter the bronchus with a narrower width. 3. After reaching the inside of the pipe, the voltage was reduced to 2.4 V. The robot tended to take on a spherical shape, increasing the contact area on the plane. Its left and right movements were controlled within the pipeline to facilitate the quicker capture of impurities. 4. Finally, the voltage was increased back to 5.6 V, and the impurities were dragged out from the internal area of the bronchus, successfully achieving the function of removing impurities from small spaces.
This study demonstrates the ability of robots to selectively occlude blood vessels and remove impurities within a complex organic structure. The intelligent control of the robot's movements and the occlusion method may offer new pathways in medical treatment, especially in precise targeting and control of blood flow in applications like tumor treatment, aneurysms, or any scenarios requiring selective vascular targeting or impurity removal from organs. The experimental design can lead to advancements in the field of medical robotics, potentially revolutionizing specific surgical and therapeutic procedures.
3 Conclusions
In conclusion, this paper provides a comprehensive exploration of the combined 3D locomotion and deformation capabilities of functional ferrofluidic robots. The study demonstrated that these uniquely versatile robots, maneuvered by external magnetic fields, can efficiently navigate through complex 3D paths, including mazes and obstacle courses, with remarkable precision. The research also revealed the ability of the ferrofluidic robots to perform tasks in a controlled and targeted manner, such as fluid pumping and mixing, interception of falling droplets, and carrying and relocating goods. In particular, the ability of the robot to effectively mix distinct micro-droplets presents substantial potential in applications such as virus detection and micro-scale chemical reaction control. Furthermore, the capacity of ferrofluidic robots for selective vascular occlusion has been thoroughly examined. The promising results show that these robots can block target blood vessels in a controlled manner, suggesting potential for impactful advancements in the realm of targeted therapeutic interventions and drug delivery. This study marks a significant stride towards the realization of a new generation of multifunctional microrobots. However, future work is required to optimize the performance of these robots in diverse operational environments and across varied tasks. In addition, the realization of 3D swarm control of ferrofluidic robots by the proposed system will be another potential research direction in the future. It is anticipated that these advances will usher in new opportunities in fields like biomedical engineering, microfluidic technology, and targeted therapy.4 Materials and methods
4.1 Preparation of ferrofluidic robots
The study employs an oil-based ferrofluid, predominantly consisting of magnetic nanoparticles, surfactants, and carrier fluids (Fig. 1B). The fabrication of the microrobots entails the utilization of several instruments, such as pipette guns, permanent magnets, and a glass dropper. To commence the process, the liquid was carefully poured into a glass container, after which the magnetic fluid was precisely extracted using a pipette gun. Subsequently, a permanent magnet was meticulously positioned at the base of the glass to attract the fluid towards the substrate, thus generating ferrofluidic robots with the desired dimensions.4.2 Preparation of droplets in controlled chemical micro-reactions
Droplet A contained a mixture of fluorescent dyes and phenyl oxalate compounds. Droplet B was hydrogen peroxide at roughly 35% concentration. The combination of phenyl oxalate and hydrogen peroxide initiated a chemical reaction in which the esters were oxidized to yield two phenol molecules and one peroxide ester (dioxane butanedione). The peroxide ester then spontaneously broke down into carbon dioxide, releasing energy to excite the dye. The excited dye released energy by emitting photons when returning to the ground state.4.3 Fabrication of 3D structures in experiments
The labyrinthine structures, imitated blood vessels, and enclosed fluidic channels employed in the experiment were all fabricated using a photocurable 3D printer (Anycubic Photon M3 Max). A washable ABS-like resin served as the printing material. The goods transported by the ferrofluidic robot were composed of nylon material that was printed using a 3D printer (Anycubic Mega X).4.4 Preparation of pig lung bronchus in experiment
First, the surface material of the pig lung was carefully removed to reveal the underlying bronchial structures. Among them, a T-shaped bronchial channel with a tube diameter of approximately 3–4 mm was selected for the experiment. Next, the prepared impurities were placed into the inlet of the bronchial channel using tweezers. To facilitate deeper penetration of the impurities, the pig lung was tilted at an angle, allowing them to enter the inner layers of the bronchus. Finally, the pig lung, now containing the impurities, was placed into an experimental glass container. A solution, previously configured with the necessary components, was poured into the glass container to create the desired experimental environment. The setup was now ready for the impurity removal experiment.4.5 Measurement of the magnetic field induced by coils
The magnetic field in the x, y and z directions was detected using a Hall sensor (TLE493D-W2B6, Infineon Technologies Inc.) that measures the strength of magnetic fields. The output from the Hall sensor was obtained through the serial port. The three magnetic field components (Bx, By, and Bz) produced by the coils were measured by attaching the module to motorized translation stages that moved in the x, y and z directions. LabVIEW software was developed for the upper computer to control the sensor's movement to any point within the workspace and save the measured magnetic field data.Author contributions
Zhan Yang, Tao Chen and Xinjian Fan conceived and designed the research. Xinjian Fan and Yunfei Zhang analyzed the experimental and calculated data. Zhengnan Wu prepared the ferrofluidic robot. Yunfei Zhang wrote the simulation and image processing programs. Lining Sun and Hui Xie directed the project. All authors wrote the manuscript.Data availability
All data needed to evaluate the conclusions in the paper are presented in the paper and/or the ESI.† Additional data related to this paper may be requested from the authors.Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.Acknowledgements
This work was partially supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu province (Grant No. BK20210717), the Open Foundation of State Key Laboratory of Robotics and Systems (SKLRS-2023-KF-21), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 62103294, 61925304), the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (Grant No. 7111795721 and 7111785821), and the Postdoctoral Research Support of Jiangsu province (Grant No. 7111751621).References
- M. Sun, X. Fan, X. Meng, J. Song, W. Chen, L. Sun and H. Xie, Magnetic biohybrid micromotors with high maneuverability for efficient drug loading and targeted drug delivery, Nanoscale, 2019, 11(39), 18382–18392 RSC.
- J. Feng and S. K. Cho, Mini and Micro Propulsion for Medical Swimmers, Micromachines, 2014, 5, 97–113 CrossRef.
- Y. Shao, A. Fahmy, M. Li, C. Li, W. Zhao and J. Sienz, Study on magnetic control systems of microrobots, Front. Neurosci., 2021, 15, 736730 CrossRef PubMed.
- D. Quashie, P. Benhal, Z. Chen, Z. Wang, X. Mu, X. Song, T. Jiang, Y. Zhong, U. K. Cheang and J. Ali, Magnetic bio-hybrid micro actuators, Nanoscale, 2022, 14(12), 4364–4379 RSC.
- J. Li, X. Li, T. Luo, R. Wang, C. Liu, S. Chen, D. Li, J. Yue, S. Cheng and D. Sun, Development of a magnetic microrobot for carrying and delivering targeted cells, Sci. Robot., 2018, 3(19), eaat8829 CrossRef PubMed.
- X. Yan, Q. Zhou, M. Vincent, Y. Deng, J. Yu, J. Xu, T. Xu, T. Tang, L. Bian, Y. Wang, K. Kostarelos and L. Zhang, Multifunctional biohybrid magnetite microrobots for imaging-guided therapy, Sci. Robot., 2017, 2(12), eaaq1155 CrossRef PubMed.
- M. Eshaghi, M. Ghasemi and K. Khorshidi, Design, manufacturing and applications of small-scale magnetic soft robots, Extreme Mech. Lett., 2021, 44, 101268 CrossRef.
- Y. Xiao, et al., Moving droplets in 3d using light, Adv. Mater., 2018, 30, 1801821 CrossRef PubMed.
- J.-M. Roux, Y. Fouillet and J.-L. Achard, 3D droplet displacement in microfluidic systems by electrostatic actuation, Sens. Actuators, A, 2007, 134(2), 486–493 CrossRef CAS.
- K. E. Peyer, L. Zhang and B. J. Nelson, Bio-inspired magnetic swimming microrobots for biomedical applications, Nanoscale, 2013, 5(4), 1259–1272 RSC.
- S. Martel, Beyond imaging: Macro- and microscale medical robots actuated by clinical MRI scanners, Sci. Robot., 2017, 2, eaam8119 CrossRef PubMed.
- S. Floyd, E. Diller, C. Pawashe and M. Sitti, Control methodologies for a heterogeneous group of untethered magnetic micro-robots, Int. J. Robot. Res., 2011, 30(13), 1553–1565 CrossRef.
- A. Pena-Francesch, J. Giltinan and M. Sitti, Multifunctional and biodegradable self-propelled protein motors, Nat. Commun., 2019, 10, 3188 CrossRef PubMed.
- B. Yigit, Y. Alapan and M. Sitti, Programmable collective behavior in dynamically self-assembled mobile microrobotic swarms, Adv. Sci., 2019, 6, 1801837 CrossRef PubMed.
- Z. Zheng, H. Wang, S. O. Demir, Q. Huang, T. Fukuda and M. Sitti, Programmable aniso-electrodeposited modular hydrogel microrobots, Sci. Adv., 2020, 8(50), eade6135 CrossRef PubMed.
- D. Rus and M. Tolley, Design, fabrication and control of soft robots, Nature, 2015, 521, 467–475 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. Han, Z. Ma, Y. Zhang, L. Zhu, H. Fan, B. Bai, Q. Chen, G. Yang and H. Sun, Reprogrammable soft robot actuation by synergistic magnetic and light fields, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2022, 32(13), 2110997 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Wang, H. Ugurlu, Y. Yan, M. Li, M. Li, A. M. Wild, E. Yildiz, M. Schneider, D. Sheehan, W. Hu and M. Sitti, Adaptive wireless millirobotic locomotion into distal vasculature, Nat. Commun., 2022, 13(1), 4465 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Kim, H. Yuk, R. Zhao, S. A. Chester and X. Zhao, Printing ferromagnetic domains for untethered fast-transforming soft materials, Nature, 2018, 558(7709), 274–279 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Sun, C. Tian, L. Mao, X. Meng, X. Shen, B. Hao, X. Wang, H. Xie and L. Zhang, Reconfigurable magnetic slime robot: deformation, adaptability, and multifunction, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2022, 32(26), 2112508 CrossRef CAS.
- Z. Ren, R. Zhang, R. H. Soon, Z. Liu, W. Hu, P. R. Onck and M. Sitti, Soft-bodied adaptive multimodal locomotion strategies in fluid-filled confined spaces, Sci. Adv., 2021, 7(27), eabh2022 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Hou, H. Chang, K. Song, C. Lu, P. Zhang, Y. Wang, Q. Wang, W. Rao and J. Liu, Coloration of liquid-metal soft robots: from silver-white to iridescent, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2018, 10(48), 41627–41636 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. Ma, C. Xu, L. Cui, C. o. Zhao and H. Liu, Magnetic printing of liquid metal for perceptive soft actuators with embodied intelligence, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2021, 13(4), 5574–5582 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Zhou, Z. Wu, Y. Zhao, Q. Yang, W. Ling, Y. Li, H. Xu, C. Wang and X. Huang, Droplets as carriers for flexible electronic Devices, Adv. Sci., 2019, 6(24), 1901862 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Li. Hu, H. Wang, X. Wang, X. Liu, J. Guo and J. Liu, Magnetic Liquid Metals Manipulated in the Three-Dimensional Free Space, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2019, 11(8), 8685–8692 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Čejková, T. Banno, M. M. Hanczyc and F. Štěpánek, Droplets as liquid robots, Artif. Life, 2017, 23(4), 528–549 CrossRef PubMed.
- H. Lin, W. Yu, K. A. Sabet, M. Bogumil, Y. Zhao, J. Hambalek, J. S. Lin, S. Chandrasekaran, O. Garner, D. D. Carlo and S. Emaminejad, Ferrobotic swarms enable accessible and adaptable automated viral testing, Nature, 2022, 1–8 Search PubMed.
- X. Fan, X. Dong, A. C. Karacakol, H. Xie and M. Sitti, Reconfigurable multifunctional ferrofluid droplet robots, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2020, 117, 27916 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Sun, B. Hao, S. Yang, X. Wang, C. Majidi and L. Zhang, Exploiting ferrofluidic wetting for miniature soft machines, Nat. Commun., 2022, 13, 7919 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. Chen, Z. Yang, Y. Ji, Y. Dai, L. Feng and F. Arai, Deformable ferrofluid-based millirobot with high motion accuracy and high output force, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2021, 118(13), 134101 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Ahmed, M. Ilami, J. Bant, B. Beigzadeh and H. Marvi, A shapeshifting ferrofluidic robot, Soft Robot., 2021, 8(6), 687–698 CrossRef PubMed.
- W. Q. Zhou, Q. X. Liang and T. N. Chen, 3D Manipulation of Magnetic Liquid Metals, Adv. Intell. Syst., 2020, 1900170 CrossRef.
- J. W. Jeonga, J. B. Leeb and S. K. Chung, et al., Electromagnetic three-dimensional liquid metal manipulation, Lab Chip, 2019, 19, 3261–3267 RSC.
- H. Liu, M. Li, Y. Li, H. Yang, A. Li, T. J. Lu, F. Li and F. Xu, Magnetic steering of liquid metal mobiles, Soft Matter, 2018, 14, 3236–3245 RSC.
- X. Jing, H. Chen, L. Zhang, S. Zhao, Y. Wang, Z. Wang and Y. Zhou, Accurate Magneto-Driven Multi-Dimensional Droplet Manipulation, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2023, 33(9), 2210883 CrossRef CAS.
- A. W. Zhou, C. Y. Xu, P. Kanitthamniyom, C. S. X. Ng, G. J. Lim, W. S. Lew, S. Vasoo, X. S. Zhang, G. Z. Lum and Y. Zhang, Magnetic soft millirobots 3D printed by circulating vat photopolymerization to manipulate droplets containing hazardous agents for in vitro diagnostics, Adv. Mater., 2022, 34, 2200061 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Ramos-Sebastian, S. J. Gwak and S. H. Kim, Multimodal locomotion and active targeted thermal control of magnetic agents for biomedical applications, Adv. Sci., 2022, 9(7), 2103863 CrossRef PubMed.
- M. P. Kummer, J. J. Abbott, B. E. Kratochvil, R. Borer, A. Sengul and B. J. Nelson, OctoMag: An electromagnetic system for 5-DOF wireless micromanipulation, IEEE Trans. Robot., 2010, 26(6), 1006–1017 Search PubMed.
- H. Choi, K. Cha, J. Choi, S. Jeong, S. Jeon, G. Jang, G. Jang, J. Park and S. Park, EMA system with gradient and uniform saddle coils for 3D locomotion of microrobot, Sens. Actuators, A, 2010, 163(1), 410–417 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Ji, C. Gan, Y. Dai, X. Bai, Z. Zhu, L. Song, L. Wang, H. Chen, J. Zhong and L. Feng, Deformable ferrofluid microrobot with omnidirectional self-adaptive mobility, J. Appl. Phys., 2022, 131(6), 064701 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Yu, J. Kim, H. Choi, J. Choi, S. Jeong, K. Cha, J. Park and S. Park, Novel electromagnetic actuation system for three-dimensional locomotion and drilling of intravascular microrobot, Sens. Actuators, A, 2010, 161(1–2), 297–304 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Khalesi, M. Yousefi, H. N. Pishkenari and G. Vossoughi, Robust independent and simultaneous position control of multiple magnetic microrobots by sliding mode controller, Mechatronics, 2022, 84, 102776 CrossRef.
- Z. Yang and L. Zhang, Magnetic actuation systems for miniature robots: A review, Adv. Intell. Syst., 2020, 2(9), 2000082 CrossRef.
- J. Ning, L. Zhang, D. Zhang and C. Wu, Scale and orientation adaptive mean shift tracking, IET Comput. Vis., 2012, 6(1), 52–61 CrossRef.
- J. J. Abbott, E. Diller and A. J. Petruska, Magnetic methods in robotics, Annu. Rev. Control Robot., 2020, 3, 57–90 CrossRef.
- X. Dong, G. Z. Lum, W. Hu, R. Zhang, Z. Ren, P. R. Onck and M. Sitti, Bioinspired cilia arrays with programmable nonreciprocal motion and metachronal coordination, Sci. Adv., 2020, 6(45), eabc9323 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Li, H. Li, Z. Li, Z. Zhao, K. Li, M. Li and Y. Song, Programmable, droplet manipulation by a magnetic-actuated robot, Sci. Adv., 2020, 6(7), eaay5808 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Law, X. Wang, M. Luo, L. Xin, X. Du, W. Dou, T. Wang, G. Shan, Y. Wang, P. Song, X. Huang, J. Yu and Y. Sun, Microrobotic swarms for selective embolization, Sci. Adv., 2022, 8(29), eabm5752 CrossRef PubMed.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available: Section S1. Supplementary figures. Section S2. Supplementary texts. Section S3. Supplementary movies. Fig. S1. Dipole model optimization flow chart. Fig. S2. Genetic algorithm flow chart. Fig. S3. Square experimental locus. Fig. S4. Square track error. Fig. S5. Trajectories of involutes. Fig. S6. Involute track error. Fig. S7. Saddle line track. Fig. S8. Saddle line track error. Fig. S9. Helix trajectory. Fig. S10. Helix trajectory error. Fig. S11. Complex path obstacle avoidance path. Fig. S12. Droplet intercept trajectory. Text S1. Design of a sliding mode controller. Video S1. Simulation and experimental results of the 2D motion control of the ferrofluidic robot. Video S2. Simulation and experimental results of the 3D motion control of the ferrofluidic robot. Video S3. Experimental results show that deformed ferrofluidic robots can be used as microfluidic inducers. Video S4. 3D locomotion of ferrofluidic robots for navigation and hitting missions. Video S5. Applications of ferrofluidic robots based on combined 3D locomotion and deformation. See DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/d3nr02535g |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2023 |