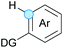
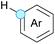
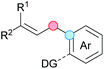
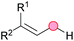Cross-dehydrogenative coupling involving benzylic and allylic C–H bonds
Irene
Bosque
 *,
Rafael
Chinchilla
*,
Rafael
Chinchilla
 ,
Jose C.
Gonzalez-Gomez
,
Jose C.
Gonzalez-Gomez
 ,
David
Guijarro
,
David
Guijarro
 and
Francisco
Alonso
and
Francisco
Alonso
 *
*
Instituto de Síntesis Orgánica and Departamento de Química Orgánica, Facultad de Ciencias, Universidad de Alicante, Apdo. 99, 03080 Alicante, Spain. E-mail: falonso@ua.es; irene.bosque@ua.es
First published on 26th May 2020
Abstract
In recent years, the cross-dehydrogenative coupling (CDC) has demonstrated to be a powerful synthetic tool to form C–C bonds from two C–H bonds. This high atom-economic transformation is an attractive alternative to the classical substitution and coupling approaches for the benzylation and allylation of carbon centers, which rely on the reaction of adequately functionalized starting materials. This review emphasizes the utility of the CDC through the coupling of benzylic and allylic C–H bonds with C(sp)–H, C(sp2)–H and C(sp3)–H bonds.
1. Introduction
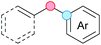
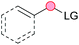
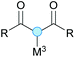
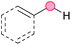
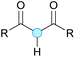
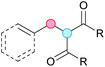
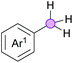
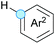
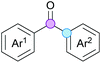
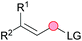
Substitution reactions in the different variants (SN1, SN2, S′N, SNi, AdN-E, SEAr, SNAr, etc.) constitute one of the fundamental pillars in modern organic chemistry.1 Notwithstanding their widespread use for synthetic purposes, proper functionalization of the substrates is required. For instance, benzylation and allylation reactions to form C–C bonds typically involve benzylic and allylic substrates bearing good leaving groups, in combination with carbon nucleophiles (carbanions) derived from terminal alkynes (acetylides), arenes or alkenes (aryl or alkenyl metals) and carbonyl compounds (enolates) [Table 1, (a–c)]. In particular, the benzylation of aromatics has attracted a great deal of attention because the resulting diarylmethanes play an outstanding role in supramolecular chemistry, as well as in the development of target pharmaceuticals to treat manifold diseases; triarylmethanes are relevant to dye chemistry, materials science and bioorganic chemistry.2 Diarylmethanes are commonly prepared through Friedel–Crafts benzylation of aromatics (from benzylic alcohols, acetates or chlorides) under Brønsted or Lewis acid catalysis [Table 1, (d)],3 or through transition-metal catalyzed cross-coupling reactions (i.e., Suzuki–Miyaura, Negishi, Kumada, Stille or Hiyama) [Table 1, (b)];2 these methods are also applicable to allylation reactions. The syntheses of diarylmethanes by benzylic C–H arylation with aryl boronic acids via copper catalysis or with aryl bromides via photoredox and Ni dual catalysis have been recently reported.4 Within the allylation reactions, the Tsuji–Trost reaction is praiseworthy [Table 1, (c)]:5 an intermediate η3-π-allyl palladium complex obtained from allylic esters or carbonates is coupled with carbon nucleophiles, which are the anion of an active methylene compound or Knoevenagel-type carbanions; the decarboxylative allylation can be considered a subset of the Tsuji–Trost reaction, where the nucleophile (e.g., enolate) is generated in situ.6 The transition-metal catalyzed direct allylation of aromatic and vinylic C(sp2)–H bonds with various allylic surrogates (e.g., acetates, carbonates, phosphonates, alcohols, halides, etc.) has been a subject of recent interest;7 the presence of a directing group (DG) is, however, mandatory to attain a regioselective C(sp2)–H activation [Table 1, (f)].On the other hand, the cross-dehydrogenative coupling (CDC) is an efficient synthetic tool to access organic molecules by the formation of C–C (or C–Het) bonds from two C–H (or C–H and Het–H) bonds.8 Within the recent past, the CDC has become one of the most active research areas in organic synthesis.9 In particular, benzylic and allylic C–H bonds can be coupled with C(sp)–H, C(sp2)–H and C(sp3)–H bonds leading to more complex structural motifs in a straightforward and atom-economic manner [Table 1, (a–c)]. For instance, the coupling of benzylic C–H bonds with C(sp2)–H bonds provides a novel entry into the much-demanded diaryl- and triarylmethane compounds. Moreover, diaryl ketones can be formed when the coupling is conducted under oxidative conditions, with this being an advantageous alternative to the Friedel–Crafts aroylation of aromatics with aroyl halides, arenecarboxylic acids or anhydrides under Lewis acid catalysis, where more than one equivalent of catalyst is needed [Table 1, (e)]. The straight coupling of C–H allylic bonds with the acidic α-C–H bond of carbonyl compounds represents an effective alternative to the allylic substitution reactions, including the Tsuji–Trost reactions [Table 1, (c)].
It must be pointed up that, in contrast with the conventional methods implemented to carry out all the above substitution or coupling reactions, which require pre-functionalization of the starting materials, the CDC approach involves only C–H bonds. Additionally, it circumvents the usage of highly reactive organometallic reagents, making the process more compatible with the presence of sensitive functional groups and minimizing waste generation.
Furthermore, the possibility to develop catalytic asymmetric CDC methods makes this an attractive synthetic route to chiral non-racemic compounds.9i However, this is still a challenging and underdeveloped area of research.
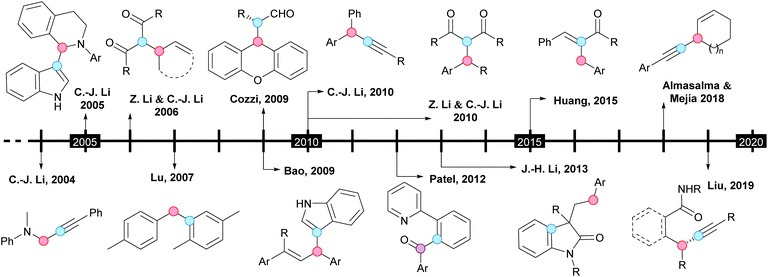
From a historical point of view, the CDC concept was introduced by the group of Li in 2004, when the first efficient copper-catalyzed alkynylation of C(sp3)–H bonds adjacent to a nitrogen atom was reported (Scheme 1).8a Soon after, the same group described the coupling of N-unprotected indoles with 1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinolines, under similar reaction conditions (Scheme 1).8b Indeed, these can be considered two pivotal contributions, where the benzylic C–H bond of 1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinolines was selectively coupled with terminal alkynes or the C3-position of indoles; both processes were catalyzed by copper(I) bromide in the presence of tert-butyl hydroperoxide (TBHP) as an oxidant. Interestingly, when the C3-position of the initial indole was blocked by a methyl group, the C2-coupled product was obtained. With the group of Li having laid the foundations of the CDC, this and other groups have made every endeavor to contribute outstandingly to this field. The pioneering research and subsequent remarkable works are underlined in the timescale depicted in Scheme 1.
In this review, we summarize the formation of C–C bonds by the CDC of benzylic and allylic C–H bonds with C(sp)–H, C(sp2)–H and C(sp3)–H bonds. The CDC coupling of the more activated benzylic and allylic (Het)C–H bonds (Het = N, O and S) has been extensively studied but is out of the scope of this review.9
2. Alkynylation of benzylic C–H bonds
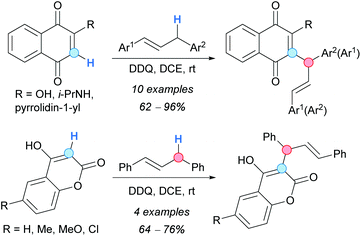
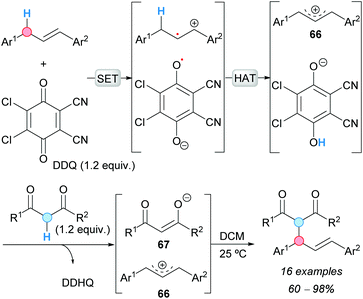
The alkynylation of benzylic C–H bonds was reported for the first time by the group of C.-J. Li in 2010.10 Copper(I) triflate was used to catalyze the CDC of benzylic C–H bonds and terminal alkynes via two consecutive single-electron transfer (SET) processes, using 2,3-dichloro-5,6-dicyano-1,4-benzoquinone (DDQ) as the stoichiometric oxidant, to form the benzylic cation intermediate 1 (Scheme 2a). The reaction of this intermediate with the in situ-generated copper(I) acetylide 2 gave the corresponding alkynyl(diaryl)methanes in moderate-to-good yields. The reaction was found to be sensitive to the nature of the alkyne. Electronic changes in the aromatic ring of the starting diarylmethane changed the effectiveness of the reaction, and conjugation in the starting alkyne was necessary in order to manifest reactivity.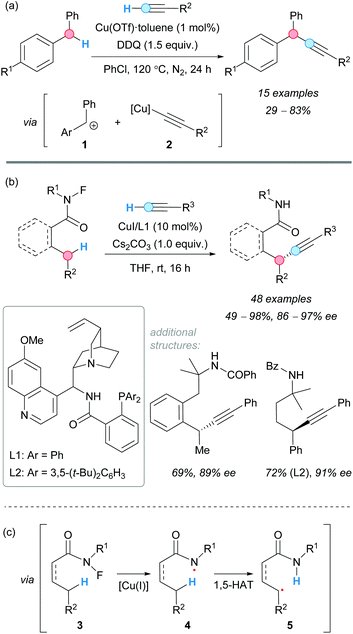 | ||
| Scheme 2 CDC of terminal alkynes and benzylic C–H bonds catalyzed by copper in a (a) racemic and (b) enantioselective version; (c) 1,5-HAT mechanism. | ||
It was not until 2019 when the group of Liu reported an enantioselective version of the Sonogashira-type CDC of benzylic C–H bonds with alkynes utilizing CuI as a catalyst and cinchona-derived ligands (L1 and L2, Scheme 2b).11 The use of an N-fluoroamide moiety in the benzylic substrate 3 was the key to direct the intramolecular 1,5(6)-hydrogen atom transfer (HAT) in the species 4 and to form the benzylic radical 5 (Scheme 2c), followed by enantioselective C–C coupling [through reductive elimination of a Cu(III)-chiral ligand intermediate] and release of the CDC product. It is worth mentioning the excellent selectivities achieved in this reaction, given its complexity. The absence of ligand or the presence of 2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidine 1-oxyl (TEMPO) inhibited the reaction. Good-to-excellent yields were obtained in all cases.
3. Arylation/alkenylation of benzylic C–H bonds
3.1. Benzyl-alkenyl coupling involving toluene derivatives and α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds
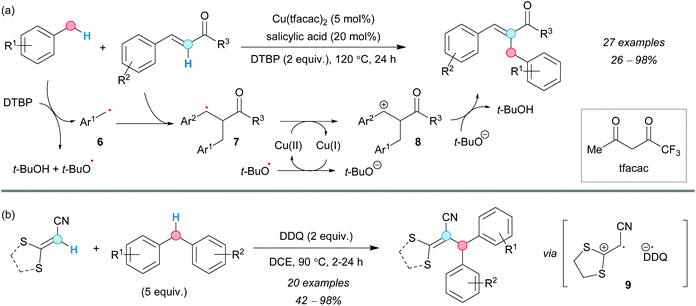
The regioselective synthesis of α-benzylated enones through CDC was first reported by the group of Huang in 2015, using toluene derivatives as coupling partners and thermally activated (>100 °C) di-tert-butyl peroxide (DTBP) in the presence of 5 mol% of a Cu(II) salt and salicylic acid.12 The corresponding tert-butoxyl radical was assumed to be responsible for the formation of the benzylic radical 6 and to act as the terminal oxidant of the reaction via the species 7 and 8. The CDC of (E)-4-arylbut-3-en-2-one derivatives and substituted toluenes was accomplished with different substitution patterns on the aromatic ring of both CDC partners (Scheme 3a). Although electron-donating, as well as electron-withdrawing groups, proved to be effective, the corresponding β-benzylated enones were isolated as by-products in some cases. Interestingly, salicylic acid was reported to enhance the performance of the reaction, perhaps acting as a ligand for copper and tuning its redox potential.Later on, a metal-free method was developed by Zhao, Liu and coworkers to perform the intramolecular CDC reaction between diphenylmethane derivatives and acrylates, using 2 equivalents of DDQ. The reaction was suggested to occur through the formation of the benzylic radical and oxidation of the alkene via charge-transfer (CT) complex formation, followed by SET (9, Scheme 3b).13 The increase of the DDQ loading to 2.5 equivalents also allowed the formation of polysubstituted indenes via a second SET event in a one-pot process.
3.2. Benzyl–aryl(hetaryl) coupling
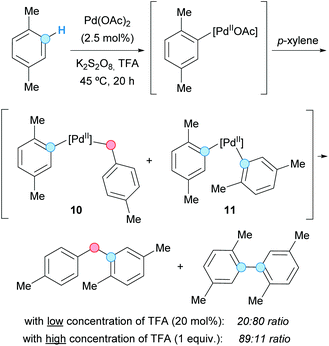
In 2007, the group of Lu presented a benzyl–aryl CDC involving a simple and inactivated substrate such as p-xylene. The process was carried out under palladium(II) acetate catalysis to generate the corresponding diarylmethane or biaryl as the major product, just by tuning the concentration of the present trifluoroacetic acid (TFA), in the absence or presence of potassium persulfate as an oxidant (Scheme 4).14 Thus, the benzylic C–H bond became activated using a higher concentration of TFA, whereas the aryl C–H bond was activated when using a lower one; the actual effect of TFA on the reactivity remains unclear. The reaction mechanism probably involved the formation of a common aryl Pd(II) intermediate, which can be converted into an aryl benzyl Pd(II) intermediate 10 or a diaryl Pd(II) intermediate 11, after reaction with another molecule of p-xylene. Subsequent reductive eliminations would lead to the coupled products. The method was also applied to the coupling of mesitylene and benzene, albeit leading to low product yields.The use of DDQ as a powerful oxidant in CDC processes was exemplified by Pettus and co-workers in the metal-free coupling between the benzylic C–H of a flavan with the aromatic C–H of 1,3,5-tribenzyloxybenzene.15 Apart from this particular case, a transition metal, such as iron, has always been used as catalyst combined with DDQ. Thus, in 2009, the group of Shi employed a combination of iron(II) chloride as a catalyst and DDQ as an oxidant in 1,2-dichloroethane (DCE) as the solvent, which was suitable for the coupling of the C–H bond of substituted benzenes and the benzylic C–H bond of diarylmethanes, leading to triarylmethanes (Scheme 5).16 An electron-donor group (MeO or MeS) must be present at the ortho or para position of the benzene ring relative to the C–H experiencing the coupling. It was assumed that the reaction is initiated by iron-assisted SET oxidation, forming the benzylic radical 12, which would be oxidized to a benzylic cation 13 (Scheme 5). A subsequent Friedel–Crafts-type process, followed by abstraction of the proton by the reduced hydroquinone, would furnish the cross-coupled product with the regeneration of the catalyst.
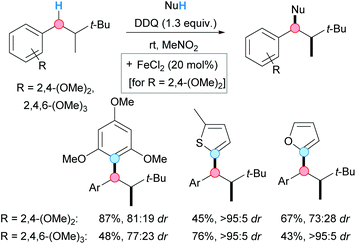
In 2014, the group of Bach reported a diastereoselective DDQ-mediated CDC coupling of di- and trimethoxy-substituted alkylbenzenes with aromatic and heteroaromatic compounds (Scheme 6).17 Alkylbenzenes bearing a stereogenic center at the β-position were used as starting materials. This peculiarity allowed to develop a diastereoselective reaction based on the diastereotopicity of the benzylic hydrogens. From the optimization studies, it was observed the need for FeCl2 as catalyst when using dimethoxy-substituted alkylbenzenes. Although the scope was rather limited, good yields and good-to-excellent diastereoselectivities were achieved when furan, 2-methylthiophene or 1,3,5-trimethoxybenzene were used as nucleophiles.
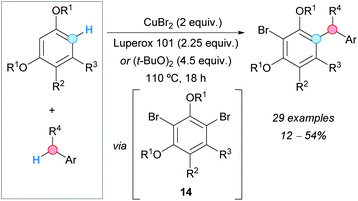
A CDC of alkoxybenzenes and toluene derivatives with concomitant bromination was reported by the group of Greaney, using stoichiometric amounts of copper(II) bromide and dialkyl peroxides as oxidants, such as Luperox® 101 [2,5-bis(tert-butylperoxy)-2,5-dimethylhexane] or DTBP, with moderate yields being obtained in most cases (Scheme 7).18 In one case, the reaction was carried out using copper(II) chloride, although the obtained yield of the related cross-coupled chloride was lower than in the case of using the bromide. The generation of a dibrominated intermediate 14 was proposed by monobromination with copper(II) bromide and subsequent dibromination induced by the generated copper(I) bromide and the peroxide oxidant. Benzylic radicals produced from the para-xylenes would react with the dibrominated intermediate 14, under the action of copper, to generate the new C–C bond. It is interesting to note that an electron-withdrawing group must be present at the meta-position relative to the reacting C–H in the alkoxybenzene, otherwise, the reaction fails. This explains why the bromine in the coupled product remains unreactive. The role of the supposed organocopper intermediates was not established yet.
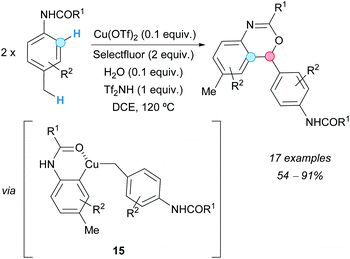
In 2011, Bi, Zhang and coworkers obtained benzoxazine derivatives from N-p-tolylamides via a copper(II) triflate-catalyzed annulation in the presence of Selectfluor {1-chloromethyl-4-fluoro-1,4-diazoniabicyclo[2.2.2]-octane bis(tetrafluoroborate)}, triflimide and water.19 The process consists of an intermolecular CDC reaction of benzylic methyl C–H and aromatic C–H bonds, and subsequent intramolecular C–O bond formation (Scheme 8). Spectroscopic experiments suggested that this transformation could begin with the successive activation of both, the benzylic methyl and the ortho-directed aromatic C–H bonds, by an in situ-generated hydroxo complex catalyst Cu(III)LOH, facilitating an intermolecular C–C bond-coupling and an intramolecular C–O coupling reaction, and giving the final benzoxazine via complex 15.
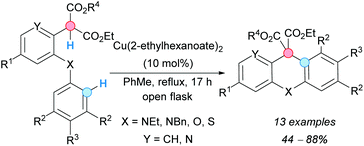
Hurst, Taylor and coworkers obtained acridanes following an approach based on an intramolecular CDC between the benzylic C–H bond and aryl C–H bond of 2-[2-(arylamino)aryl]malonates catalyzed by copper(II) in an open flask (Scheme 9).20 Other related xantenes and thioxantenes could be obtained following the same procedure. The diester moiety resulting from the CDC reaction can be used for further functionalizations.
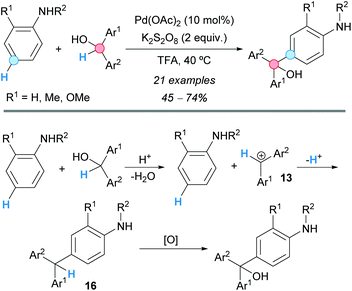
The group of Gu and Tian were able to obtain symmetrically- and unsymmetrically-functionalized triarylmethanols employing a formal CDC reaction of diarylmethanols with aniline derivatives (Scheme 10).21 The reaction proceeds in TFA in the presence of potassium persulfate oxidant and a catalytic amount of palladium(II) acetate. The proposed reaction pathway involves an acid-promoted formation of a dibenzylic cation 13, which undergoes a Friedel–Crafts reaction affording a triarylmethane 16. Subsequent oxidation gives rise to the product.
The group of Shi and Zhao reported a ruthenium catalyst bearing a 1,1′-binaphthyl-2,2′-dihydrogen phosphate (BNDHP) ligand that, under the assistance of ferrocene and DTBP as an oxidant, selectively promoted the meta C–H benzylation of various arenes bearing pyridyl, pyrimidyl and pyrazolyl groups (Scheme 11).22 The site selectivity for the ortho to the meta position could be altered by simply modifying the ligand and the ruthenium precursor.
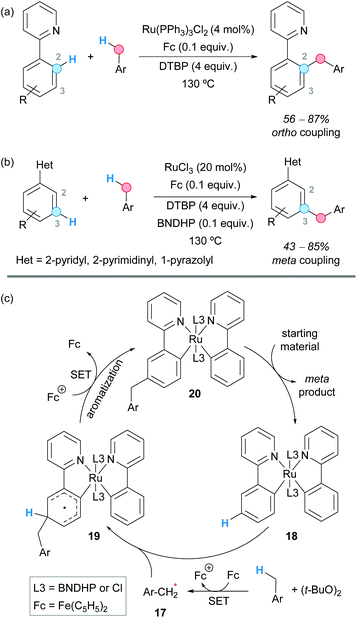 | ||
| Scheme 11 Selective ruthenium-catalyzed ortho- and meta-benzylation of arenes and suggested catalytic cycle in the formation of the meta product. | ||
Thus, when tris(triphenylphosphine)ruthenium(II) dichloride was employed as a ruthenium source, the “normal” pyridyl-directed ortho-compound was preferentially obtained (Scheme 11a), whereas the use of ruthenium trichloride afforded the unusual meta-benzylated product (Scheme 11b). The presence of BNDHP and ferrocene was found to be crucial for the meta-benzylation to occur, and no product was obtained in the presence of a radical scavenger such as TEMPO. Therefore, it was suggested that ferrocene promotes the generation of the benzylic radical 17 in a combination with DTBP. The meta-benzylation reaction was justified by the formation of a ruthenium complex 18 generated from ruthenium trichloride, the pyridyl-containing substrate and BNDHP, in the presence of ferrocene. The benzylic radical 17 formed by H-abstraction of the toluene derivative would couple with this complex, leading to an intermediate 19 that would undergo a SET process promoted by the Fe(III) ion. Deprotonation and aromatization would lead to complex 20 which, after ligand exchange, would afford the coupled product (Scheme 11c).
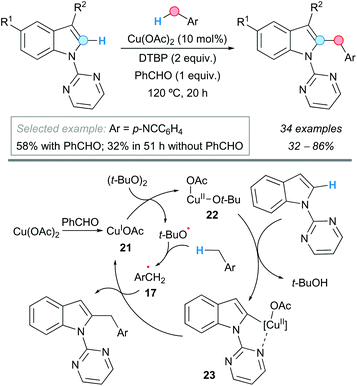
C–H bonds in heteroaromatic compounds, such as those in indoles, can be suitable partners of benzylic C–H bonds in CDC processes. Thus, Zhang, Wen and coworkers reported that N-pyrimidylindoles can be benzylated at the C2-position of the indole ring with substituted toluenes, using copper(II) acetate as a catalyst and DTBP as an oxidant (Scheme 12).23 Even an example of CDC using ethylbenzene and a 3-bromo-substituted indole was included, though resulting in modest yield (37%). The presence of benzaldehyde as an additive in this reaction proved to be beneficial, probably helping to form a Cu(I) catalyst 21 by reduction. This Cu(I) catalyst would be oxidized to the active Cu(II) species 22 and a tert-butoxyl radical. The pyrimidyl group would direct the C–H cupration of the starting indole with the Cu(II) species, affording a metallacycle intermediate 23. The benzylic radical 17, from the reaction between toluene and the tert-butoxyl radical, could interact with the metallacycle forming the final benzylation product and again the Cu(I) species (Scheme 12).
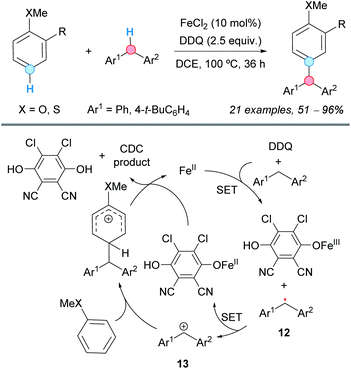
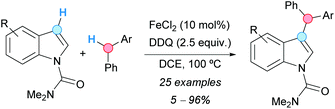
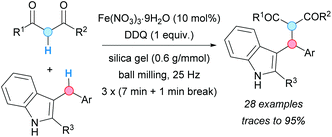
Indoles, N-protected with an N,N-dimethylcarbamoyl moiety, were alkylated at the C3-position with diarylmethanes using a CDC methodology developed by the group of Chen (Scheme 13).24 The reaction involved the use of iron(II) chloride as a catalyst and DDQ as an oxidant in DCE as solvent. The use of other N-protecting groups on the indole system gave no reaction. The isolated yields were moderate to very high when electron-withdrawing groups were present on the indole, but no reaction or very low yields were observed when electron-releasing groups were present. The proposed mechanism involved the formation of a double benzylic cation and its reaction with the indole, similar to the case of the formerly described CDC of methoxy-substituted alkylbenzenes with diarylmethanes (Scheme 5, vide supra).
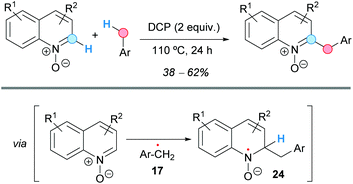
The group of Guo achieved the coupling of the C2-position of quinoline N-oxides with toluene derivatives, in moderate yields, using a CDC methodology that employs dicumyl peroxide (DCP) as an oxidant in the absence of any metal (Scheme 14).25 In addition, other examples of CDC of heterocyclic N-oxides and toluene were explored using these reaction conditions, such as some isoquinoline N-oxides or pyridine N-oxide, all benzylated at the C2-position. The proposed reaction mechanism involves the generation of the benzylic radical 17 by thermal decomposition of the peroxide. Subsequent attack at the more electrophilic C2-position of the quinoline N-oxide would form a radical intermediate 24 that would re-aromatize affording the final benzylated compound.
Isoquinolines experienced CDC at the C1-position with methyl arenes under yttrium(III) triflate catalysis in the presence of DTBP as an oxidant, as reported by the group of Liu, affording C1-benzylated systems (Scheme 15a).26 A suggested mechanism involves the formation of a benzylic radical 17 in the presence of DTBP at 120 °C and its reaction with the isoquinoline, activated by N-coordination with the yttrium catalyst (25). Addition of the benzylic radical at the C1-position and abstraction of hydrogen from intermediate 26, by the tert-butoxyl radical, yields the final benzylated isoquinoline.
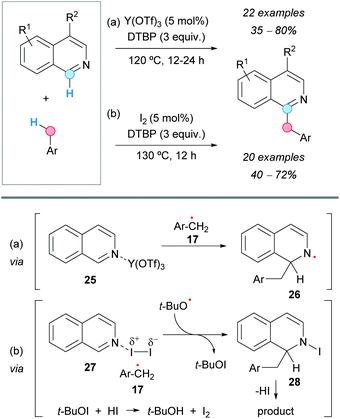 | ||
| Scheme 15 C1-Benzylation of isoquinolines using metal-mediated (a) and metal-free (b) CDC approaches. | ||
A metal-free C1-benzylation of isoquinolines via a CDC between the C1–H bond of isoquinolines and the benzylic C–H bond of methyl arenes was reported by the group of Yang, using iodine as a catalyst and DTBP as an oxidant (Scheme 15b).27 Similar to the previous reaction, the proposed mechanism would involve activation of the isoquinoline by iodine (27) and reaction with the arylmethyl radical 17 generated with DTBP. Elimination of hydrogen iodide from the intermediate 28 would afford the benzylated product. Molecular iodine would be regenerated by the oxidation of the iodide anion by the in situ generated tert-butyl hypoiodite (Scheme 15b).
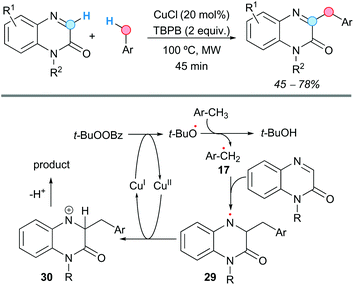
The group of Yuan and Qu demonstrated that quinoxalin-2(1H)-ones can be benzylated at the C3-position with methylarenes, in a rapid CDC process catalyzed by copper(I) chloride, using tert-butyl perbenzoate (TBPB) as an oxidant under microwave irradiation (Scheme 16).28 The reaction afforded moderate-to-good yields of the benzylated products, with many substituents on the aromatic ring and at the N1 being tolerated. However, the reaction failed when strong electron-withdrawing groups (cyano or nitro) were present at the methylarene or at the aromatic ring of the quinoxalinone. The reaction also failed when using an N-unsubstituted quinoxalinone. The proposed mechanism would start with the generation of the tert-butoxyl radical after thermal homolysis of TBPB or a SET process mediated by Cu(I). This radical would generate the benzylic radical 17, which selectively would attack the C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N bond of the quinoxalinone affording the more stable nitrogen radical 29. Single-electron oxidation by Cu(II) would furnish the nitrogen cation 30, which would lead to the final product after proton loss (Scheme 16).
N bond of the quinoxalinone affording the more stable nitrogen radical 29. Single-electron oxidation by Cu(II) would furnish the nitrogen cation 30, which would lead to the final product after proton loss (Scheme 16).
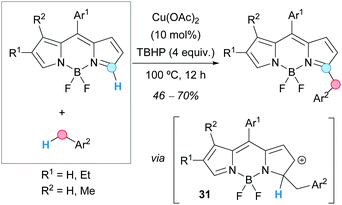
Boron-dipyrromethene (BODIPY) dyes were benzylated at the 5-position of the pyrrole ring by Hao, Jiao, Boens and coworkers, following a CDC-based methodology consisting of the reaction of BODIPYs with toluene derivatives in the presence of TBHP as an oxidant and a catalytic amount of copper(II) acetate (Scheme 17).29 The reaction showed very high regioselectivity, giving rise exclusively to the 5-benzylated product. When the amount of oxidant was increased, the corresponding dibenzylated product was dominant, although in lower yields. The proposed mechanism was very similar to the above-commented copper(II)-catalyzed benzylation of quinoxalinones (Scheme 16), involving the formation of a cationic intermediate 31.
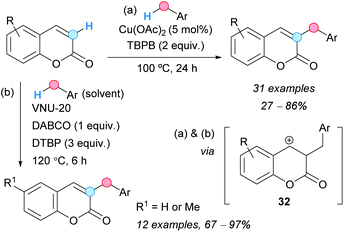
The group of Duan reported the regioselective CDC of coumarins with benzylic C–H bonds. Thus, the C–H at the C3-position of coumarins could be cross-coupled with the benzylic C–H of toluene derivatives using copper(II) acetate as a catalyst and TBPB as an oxidant (Scheme 18a).30 The presence of electron-withdrawing groups on the benzene ring of the coumarin lowered considerably the final yield; the use of ethylbenzene as related coupling partner gave only traces of the final compound. The proposed mechanism is very similar to that proposed for the above benzylation of quinoxalinones (Scheme 16), involving now the generation of a cationic intermediate 32. Following this methodology, other related heterocycles were benzylated, such as some N-methylquinolin-2(1H)-ones, a 4H-chromen-4-one, and even a non-heterocyclic system, such as a naphthalene-1,4-dione, although the reaction failed using an N-methylquinolin-4(1H)-one. Similarly, Tu and Phan and coworkers found that VNU-20, an iron(III)–organic framework, catalyzed the CDC of coumarins and methyl arenes in the presence of DTBP as an oxidant and 1,4-diazabicyclo[2.2.2]octane (DABCO), leading to 3-benzyl-substituted coumarins (Scheme 18b).31 Following this methodology, coumarin and 6-methylcoumarin were cross-coupled with 4-bromotoluene, o-, m- and p-xylene, as well as mesitylene; the final coupled products were obtained in good yields. The catalyst was recovered by filtration and reused up to six times without diminishing its activity.
3.3. Benzylarylation of alkenes to form oxindoles
The Lewis-acid promoted benzylarylation of alkenes to form oxindoles, via CDC, was first reported by J.-H. Li's group in 2013.32 The use of IrCl3 as a catalyst and DTBP as an oxidant facilitated the benzylarylation of N-arylacrylamides to form the desired oxindoles. The method allowed the use of heteroaromatic and secondary or tertiary arylmethane partners, as well as different substituents on the aromatic rings and on the carbon–carbon double bond of the acrylamide. Unfortunately, this strategy was not suitable for unprotected N-arylacrylamides (Scheme 19a).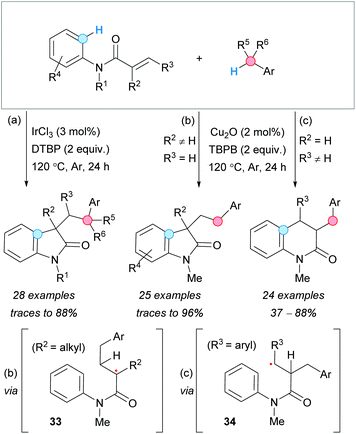 | ||
| Scheme 19 Reaction conditions for the selective construction of oxindoles and dihydroquinolones from acrylamides via CDC reaction. | ||
Parallel to this work, Guo and Duan and coworkers developed a copper(I)–oxide catalyzed procedure using TBPB as an oxidant (Scheme 19b), with the process occurring via radical 33.33 This approach proved to be tolerant to different substituents on the acrylamide and selective to primary arylmethane derivatives, since the use ethylbenzene as CDC partner gave only traces of the product. Interestingly, the kinetic isotopic effect (KIE) experiments using toluene-d8 suggested that the benzylic C–H abstraction is the rate-determining step (RDS). Later on, the same group observed that careful choice of the substituents of the acrylamide carbon–carbon double bond allowed to reverse the regioselectivity of the reaction, forming dihydroquinolones under the same reaction conditions (Scheme 19c).34 Placement of an aryl substituent at the β-position of the acrylamide favored the attack of the benzylic radical to the α-position, leading to 34, with the stabilized radical adjacent to the aryl substituent. Subsequent 6-endo-trig cyclization and oxidation, followed by deprotonation of the aromatic ring, gave the observed dihydroquinolone derivatives.
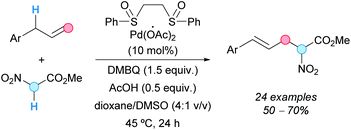
4. Aroylation of aromatics with toluene derivatives35
The Pd-catalyzed CDC coupling of 2-aryl pyridines with toluene derivatives was successfully reported under different oxidative conditions, to obtain 2-(pyridin-2-yl)diaryl ketones in synthetically useful yields. The first example was described by Patel and coworkers in 2012, using 10 mol% Pd(OAc)2, TBHP as the terminal oxidant and toluene derivatives as reactants and solvent (Scheme 20a).36 Importantly, the reaction was inhibited in the presence of TEMPO, suggesting the intermediacy of radicals. It is noteworthy that polymethylated arenes gave selectively monoaroylated products, without affecting the other methyl groups. This seminal contribution prompted other research groups to develop more sustainable methodologies for similar transformations. The reaction temperature, the excess of toluene derivatives, the catalyst loading, the nature and amount of the terminal oxidant, and the recyclability of the catalyst were some of the issues to be addressed in future protocols.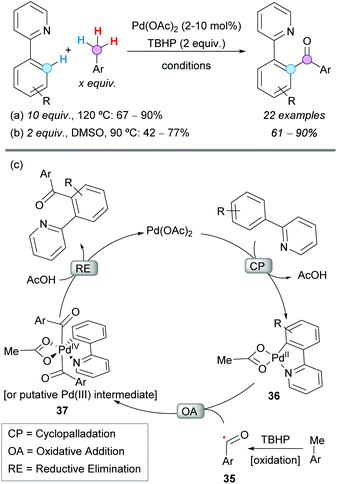 | ||
| Scheme 20 Pd-Catalyzed CDC coupling of 2-aryl pyridines with toluene derivatives and proposed reaction mechanism. | ||
Almost at the same time, Sun and coworkers reported the same transformation under very similar conditions but using only 2 equivalents of the toluene derivative and 2 mol% Pd(OAc)2 in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) as a solvent (Scheme 20b).37 Opposite to what was observed by Patel's group, these authors were able to detect the oxidation of toluene to benzaldehyde with TBHP, even in the absence of Pd(OAc)2. Once again, polymethylated arenes reacted only at one methyl group and this result was attributed to a more difficult second oxidation, due to the electron-withdrawing effect of the initially formed carbonyl group. The reaction showed excellent tolerance to electron-withdrawing and electron-donating groups in the 2-aryl pyridines and toluene derivative substrates. However, 2-(o-tolyl)pyridine and p-nitrotoluene gave only traces of the corresponding product, probably because of the steric hindrance of the former substrate and the difficult methyl oxidation of the electron-poor latter substrate.
Regarding the reaction mechanism, the group of Patel initially proposed the formation of a benzyl intermediate that was further oxidized. However, soon after, it was demonstrated by the group of Sun (and other groups involved in similar transformations) that TBHP can oxidize the toluene derivative to the benzaldehyde, further transformed into the aroyl radical 35 that enters the catalytic cycle. It is, then, generally accepted that the reaction starts with a chelation-directed ortho C–H activation in the 2-phenylpyridine to give the corresponding palladacycle 36 (Scheme 20c).38 Next, the oxidative addition of the in situ formed acyl radical to the palladacycle generates either a Pd(IV)39 or a dimeric Pd(III) intermediate4037 which, after reductive elimination, regenerates the Pd(II) catalyst affording the 2-(pyridyn-2-yl)diaryl ketone product.
The CDC coupling of 2-aryl pyridines with toluene derivatives was also recently reported by Mandapati, Parvathaneni and coworkers, using a Pd(II) complex anchored to a polystyrene (PS) resin (Scheme 21a).41 The catalyst used was very stable and easy to recover and reuse in four consecutive cycles, without affecting its activity or selectivity. The reaction was performed in the absence of solvents, using on-water conditions, very low palladium loading and exhibiting a broad substrate scope. Therefore, this protocol represents a green and economical alternative to other existing methodologies.
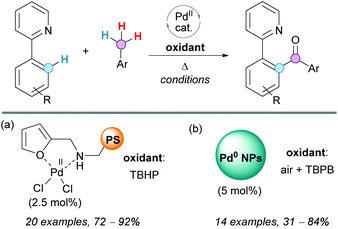 | ||
| Scheme 21 CDC coupling of 2-aryl pyridines with toluene derivatives using (a) a Pd(II) complex anchored to a PS resin or (b) supported palladium nanoparticles (NPs). | ||
Other green replacements for Pd(OAc)2 in this reaction are supported palladium nanoparticles (NPs in Scheme 21b).42 In a recent protocol developed by Zhaorigetu, Bao and coworkers, it was demonstrated that Pd(0) NPs can be used as the catalyst because they are easily oxidized under aerobic conditions to Pd(II). The easy recyclability of this robust catalyst, which maintained its activity after five cycles, is an important advantage of this heterogeneous catalytic system.
The group of Patel also demonstrated that 2-aryloxy pyridine substrates, with an O-linker between the pyridyl and the aryl ring, are suitable substrates for the Pd-catalyzed aroylation with toluene derivatives (Scheme 22a).36 Furthermore, it was shown that ketone oxime ethers can also serve as efficient directing groups for the Pd-catalyzed C–H aroylation reaction (Scheme 22b), affording 1,2-diacyl arenes after oxime hydrolysis, which are versatile building blocks in heterocyclic chemistry.
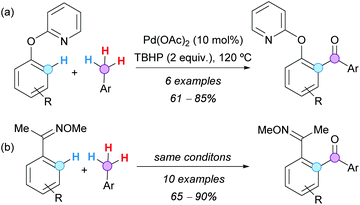 | ||
| Scheme 22 Pd-Catalyzed aroylation of (a) 2-pyridyl benzyl ether derivatives and (b) acetophenone oxime ethers with toluene derivatives. | ||
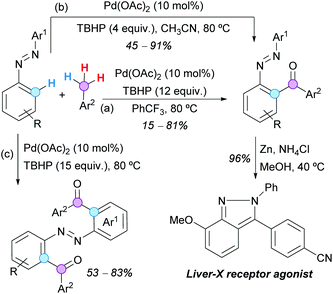
ortho-Acylazoarenes are also readily available by Pd(II)-catalyzed aroylation of azoarenes with aryl methanes, using TBHP (12 equivalents) as the terminal oxidant, as reported by Lu, Zheng and coworkers (Scheme 23a).43 The reductive treatment of one acylated azobenzene with Zn/NH4Cl furnished the corresponding indazole, which is a known liver-X receptor agonist. Similar results were obtained by Wu, Cui and coworkers with only 4 equivalents of TBHP in CH3CN (Scheme 23b), but the diacylated products were obtained by using 15 equivalents of the same oxidant at 80 °C and the toluene derivatives as solvents (Scheme 23c).44
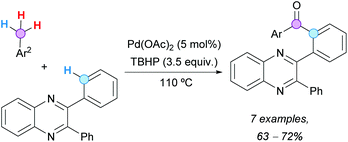
In 2014, Patel's group examined the Pd-catalyzed aroylation of 2,3-diarylquinoxalines (Scheme 24).45 It was found that out of the four available ortho C(sp2)–Hs in the substrate, only one C–H was selectively functionalized. The reaction was accomplished either with aromatic aldehydes or alkylbenzenes as aroyl precursors, observing that the former reacted faster than the latter. In line with their mechanistic experiments, it was proposed that, at least partially, the in situ formation of an aroyl radical was required to follow a reaction pathway similar to that described in Scheme 20c.
A Pd-catalyzed aerobic oxidative C–H aroylation of arenes with toluene derivatives was developed by Jiao and coworkers, using either 2-pyridine (Scheme 25a) or a methylated oxime (Scheme 25b) as directing groups and molecular oxygen as the terminal oxidant. The reaction proceeded under very mild reaction conditions, exhibiting a broad substrate scope.46 It was proposed that substoichiometric N-hydroxyphthalimide (NHPI) facilitated the formation of the aroyl radical 35 (Scheme 25c), which was the active radical reactant in the palladium catalytic cycle. Experiments with 18O2 demonstrated that the oxygen atom of the formed carbonyl group comes from molecular oxygen. Moreover, it was also concluded from kinetic isotopic experiments that the C–H activation should be irreversible and the RDS.
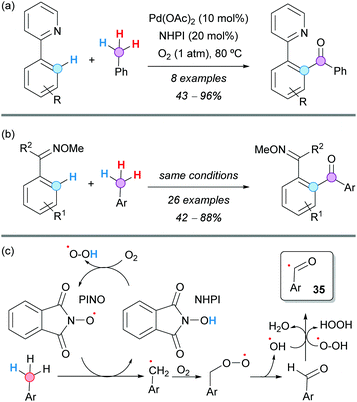 | ||
| Scheme 25 Pd/NHPI-catalyzed aerobic oxidative C–H aroylation of arenes with toluene derivatives using (a) 2-pyridine or (b) oxime as directing groups. | ||
The ortho-acylation of 2-arylbenzoxazoles and 2-arylbenzothiazoles with toluene derivatives was successfully developed by the group of Xuan in 2015, using Pd(OAc)2 as a catalyst and TBHP as a stoichiometric oxidant (Scheme 26a).47 Mechanistically, it was proposed that the aroyl radical is pre-generated and oxidatively added to the in situ formed palladacycle. The reaction conditions were compatible with a wide range of functionalities, except with strong electron-withdrawing groups, such as nitro and acetyl groups on the toluene derivative, most likely because the oxidation of the latter was much more difficult. Notably, using this methodology, the authors prepared a potent bioactive benzothiazole derivative in only four steps from vanillin.
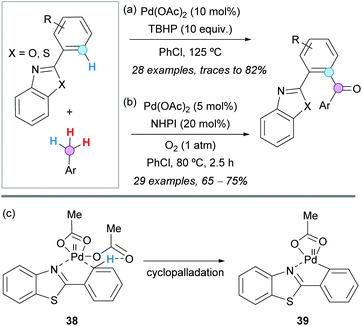 | ||
| Scheme 26 Pd(II)-Catalyzed ortho-acylation of 2-arylbenzoxazoles and 2-arylbenzothiazoles with toluene derivatives. | ||
The same Pd-catalyzed CDC was studied by the group of Chakraborti, but using O2 (balloon) as the stoichiometric oxidant and NHPI as an organocatalyst.48 Under these conditions, a lower Pd(OAc)2 loading was required and the reactions were finished in a shorter time at a lower temperature (Scheme 26b). Importantly, the bis-aroylated products were obtained when the reactions were run for a longer time (ca. 8 h). Kinetic isotope effect studies revealed that C−H bond activation is the RDS, and radical inhibition experiments supported a radical pathway. In addition, it was shown that an external base does not participate in the deprotonation during the C–H activation, and the lack of catalytic efficiency of PdCl2 or Na2PdCl4 was ascribed to the poor basicity of the chloride anion. Accordingly, it was proposed that the chelation-directed C–H bond activation to form the palladacycle 39 is assisted by acetate-mediated deprotonation through a six-membered chair-like transition state 38 (Scheme 26c).
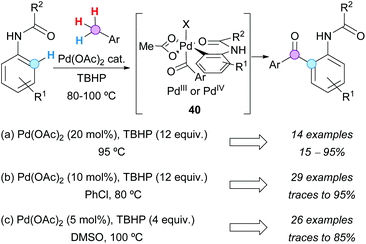
Three different groups independently developed the Pd-catalyzed ortho-aroylation of acetanilides with toluene derivatives at the end of 2012, using Pd(OAc)2 as a catalyst and TBHP as the terminal oxidant. Furthermore, it was proposed in all cases the in situ formation of the aroyl radical, which is added to the six-membered ring palladacycle to obtain a Pd(III) or a Pd(IV) intermediate 40 (Scheme 27). Similar results were obtained by Weng, Zhang and coworkers using 20 mol% catalyst in the toluene derivative as the solvent (Scheme 27a),49 by Kwong's group in chlorobenzene with 10 mol% Pd(OAc)2 (Scheme 27b),50 or even by Yin and Sun in DMSO with only 5 mol% catalyst (Scheme 27c).51
The use of directing groups (DGs) is generally required to facilitate C–H bond activation. It is even more synthetically attractive if the DG can be easily removed or conveniently transformed after the desired modification. In this context, the N-nitroso group has been examined by Luo, Kwong and coworkers as a traceless DG in the Pd-catalyzed CDC of N-nitrosoanilines with toluene derivatives. Eventually, N-alkyl-2-aminobenzophenones were obtained in good yields under mild conditions, with concomitant N–N(O) bond cleavage (Scheme 28a).52 In addition, convenient access to 2-acylindoles was developed by van der Eycken and coworkers via Pd-catalyzed CDC between N-pyrimidyl indoles and toluene derivatives, followed by removal of the directing group.53 The reaction conditions were compatible with a range of functional groups and the pyrimidyl moiety was easily removed by reaction with sodium ethoxide at 100 °C (Scheme 28b). A significant reactivity enhancement was observed using pivalic acid (PivOH) as an additive, while other additives or reaction conditions were less effective. However, the authors did not study the possibility of Pd(OPiv)2 being the catalytically active species.
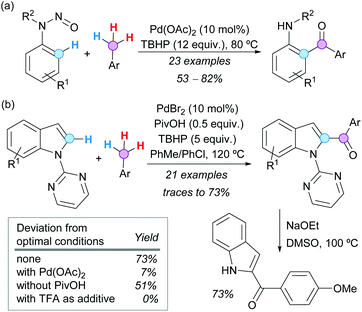 | ||
| Scheme 28 Pd-Catalyzed CDC of (a) N-nitrosoanilines or (b) N-pyrimidyl indoles with toluene derivatives. | ||
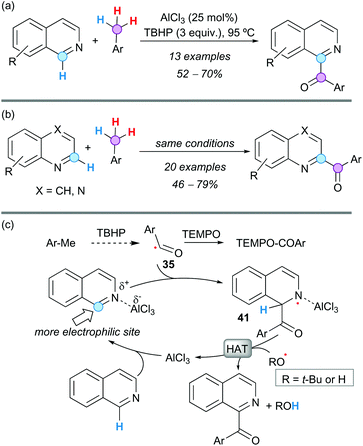
A CDC between electron-deficient N-heterocycles and toluene derivatives was accomplished by Patel and coworkers using AlCl3 as the catalyst and TBHP as a terminal oxidant, in the absence of noble metals.54 The reaction was highly regioselective, affording C1-aroylated isoquinolines in good yields (Scheme 29a) and exclusively C2-aroylated quinolines or quinoxalines (Scheme 29b). Effective inhibition of the reaction with TEMPO supported a radical pathway and kinetic isotopic experiments suggested that the C(sp3)–H bond cleavage was not the RDS. According to these observations and literature precedents, it was proposed that oxidation of the toluene derivative provides the aroyl radical 35. Coordination of AlCl3 to the N-atom of the heterocycle makes the heterocyclic ring further electron-deficient, facilitating the addition of the nucleophilic aroyl radical to the more electrophilic position of the heterocycle, in a Minisci-like addition. Rearomatization of this radical intermediate 41 is possible by HAT, providing the observed product and regenerating the AlCl3 for the next catalytic cycle (Scheme 29c). The loading of AlCl3 was rather high (25 mol%), probably because the product competes with the starting material for the coordination of the catalyst. However, the protocol is still very cost-effective and sustainable because AlCl3 is inexpensive and much less toxic than palladium-based catalysts.
5. Alkylation of benzylic C–H bonds
5.1. Non-enantioselective alkylation of benzylic C–H bonds
Various examples of benzylic alkylation, mainly at the α-position of carbonyl compounds, have been described. The most recurrent partners are malonate derivatives, since the carbonyl α-C–H is specially activated.In 2007, Z. Li, C.-J. Li and coworkers described, for the first time, a Fe(II)–catalyzed protocol at 80 °C that utilized stoichiometric amounts of DTBP as the terminal oxidant (Scheme 30a).55 A tentative mechanism was proposed involving a Fe(II)/Fe(III) cycle and the activation of the propanodione by the Fe(III) species, although no evidence was shown to support it. The scope proved to be broad in the use of several 1,3-propanodione derivatives, albeit only secondary benzylic C–H bonds were suitable for this reaction.
 | ||
| Scheme 30 Cu- and Fe-mediated CDC reactions between 1,3-dicarbonyl compounds and toluene derivatives. | ||
One year later, the group of Powell reported the same reaction in the absence of solvent at 60 °C, using a Cu(II)/phenanthroline catalytic system (Scheme 30b).56 They observed a competitive kinetic isotope effect of 1.6 utilizing a 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 mixture of ethylbenzene and (1,1-D2-ethyl)benzene, which supported the formation of a benzylic radical during the reaction. Later on, Li and coworkers developed a double catalytic Cu(I)/Fe(II) system, involving this time catalytic amounts of NHPI and oxygen as a terminal oxidant (Scheme 30c).57 Higher temperatures were needed in order to obtain good yields. The NHPI/O2/Cu system was assumed to be responsible for the formation of the benzylic radical or the benzhydrol, while the role of iron was to form the iron-enolate intermediate. Under these reaction conditions, less activated derivatives as indane also reacted, albeit in low yields.
1 mixture of ethylbenzene and (1,1-D2-ethyl)benzene, which supported the formation of a benzylic radical during the reaction. Later on, Li and coworkers developed a double catalytic Cu(I)/Fe(II) system, involving this time catalytic amounts of NHPI and oxygen as a terminal oxidant (Scheme 30c).57 Higher temperatures were needed in order to obtain good yields. The NHPI/O2/Cu system was assumed to be responsible for the formation of the benzylic radical or the benzhydrol, while the role of iron was to form the iron-enolate intermediate. Under these reaction conditions, less activated derivatives as indane also reacted, albeit in low yields.
It was not until 2012 when the group of Li developed a Fe(II) protocol suitable for primary benzylic C–H bonds by increasing the temperature and reaction time (Scheme 30d).58 The role of the iron catalyst was investigated using p-xylene in the presence of stoichiometric Fe(dbm)3. The formation of the product in a similar yield indicated the role of Fe(III) as a Lewis acid to activate the dicarbonyl substrate. As expected, Fe(III) was also found to be responsible for the benzylic H abstraction from the toluene derivative.
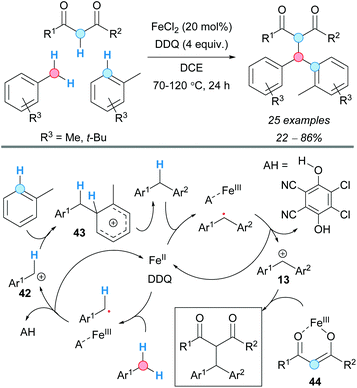
The group of Song developed a double CDC of 1,3-dicarbonyl compounds and arylmethane derivatives (Scheme 31).59 The optimized conditions required the use of a Fe(II) catalyst and stoichiometric DDQ at high temperatures. In general, good yields were obtained for malonate derivatives. However, the presence of amide or ether moieties in the arylmethane inhibited the reactivity of the 1,3-dicarbonyl compound under the reaction conditions. As expected, the more sterically hindered the arene moiety was, the higher the temperature required in order to get the desired product, albeit in low yields. The direct coupling of diethyl malonate with diphenylmethane under the optimized conditions gave the CDC product in 70% yield; that is why the authors proposed a mechanism based on two iron-catalyzed cycles: formation of the diarylmethane derivative and subsequent coupling with the 1,3-dicarbonyl compound.
In the first cycle, DDQ was proposed to perform two SET processes with the toluene derivative, facilitated by Fe(II), to give the benzylic carbocation 42, which was trapped by a second molecule of the toluene derivative; final rearomatization of the formed carbocation 43 gave the diarylmethane compound. The second cycle was proposed to occur similarly, this time being the diarylmethyl carbocation 13 trapped by the iron-enolate intermediate 44 (Scheme 31).
The group of Su described a mechanical activation variant of this type of CDC in 2016 (Scheme 32).60 The mechanical activation of the Fe(III) species allowed to conduct the reaction under solvent-free conditions. Given that radical scavengers as TEMPO inhibited the reaction, a radical mechanism similar to the above described in the second cycle of the double CDC was proposed for the formation of the benzylic carbocation, via two SET events from DDQ. The reaction conditions were also suitable when the 1,3-dicarbonyl compound was replaced by indole derivatives. As expected, coupling at the C-3 position of the corresponding indole was observed in moderate yield. As a control experiment, the reaction was carried out under the optimized conditions in the presence of CH2Cl2 at room temperature and using regular stirring instead of mechanical energy input; only traces of product were obtained.
In 2010, the group of Klussmann developed a metal-free CDC coupling between xanthene or 9,10-dihydroacridine derivatives and carbon nucleophiles, such as ketones or esters (Scheme 33a).61 During control experiments of a metal-catalyzed oxidative coupling, the authors realized that only catalytic amounts of a strong acid were needed to promote the reaction in high yields. Weaker acids gave much lower reaction rates and acetic acid was incapable of promoting the reaction. The authors postulated the autoxidative formation of xanthene hydroperoxide that would react with the carbon nucleophile via acid-catalyzed C–O bond cleavage. The isolation of xanthene peroxide under the reaction conditions, and the formation of the CDC product from xanthene hydroperoxide in the absence of oxygen, supported the proposed mechanism.
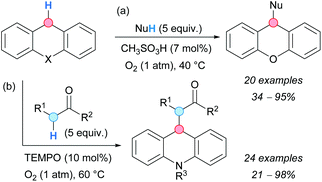 | ||
| Scheme 33 Metal-free catalyzed CDC reactions between xanthene or 9,10-dihydroacridine derivatives and carbon nucleophiles. | ||
Later in 2012, a similar reaction was developed by Jiao and coworkers for 9,10-dihydroacridines but using TEMPO as a mediator (Scheme 33b).62 A variety of carbon nucleophiles were tolerated including nitroalkanes, ketones, esters and nitriles. Unfortunately, diphenylmethane and its derivatives were found to be unreactive under the optimized reaction conditions. KIE experiments suggested that the benzylic C–H bond cleavage is involved in the RDS (kH/kD = 4 for N-methyl-9,10-dideuterioacridine).
The group of Yang designed an oxidative CDC reaction of methylazaarenes and 1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinolines. They used a cooperative copper/Brønsted acid system in the presence of oxygen as the terminal oxidant (Scheme 34a).63 Good yields were obtained for a series of 6-substituted 2-methylquinolines. Later, in 2016, the group of Li and Xie reported an alternative metal-free process using 4-acetamido-2,2,6,6-tetramethylpyridine-1-oxoammonium salt [4N-T(BF4)] as catalyst in stoichiometric amounts, occurring via species 45, which was used in up to 5 cycles without loss of activity (Scheme 34b).64 Interestingly, the optimal solvent for this transformation was found to be water. The possible mechanism involves a hydride abstraction from the N-protected tetrahydroisoquinoline, to form the iminium salt, and its coupling with the enamine unit of the 2-methylquinoline to furnish the CDC product. The iminium salt was isolated, and its combination with 1 equivalent of the quinoline gave the desired product, suggesting its formation during the reaction.
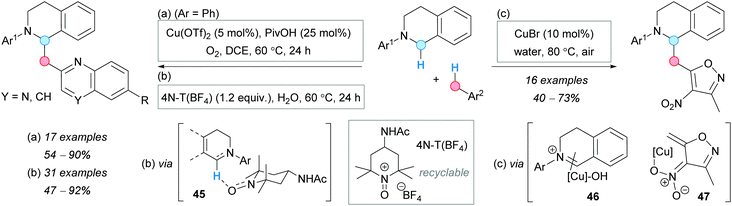 | ||
| Scheme 34 Comparative analysis of methods for the reaction of tetrahydroisoquinolines with azaarenes or 4-nitroisoxazoles. | ||
Similar to the Cu-catalyzed method described above, in 2017, the group of Zhang developed a Cu(I)-mediated CDC using this time 3,5-dimethyl-4-nitroisoxazole as the coupling partner (Scheme 34c).65 Water was also used as the optimal solvent and good substrate scope was reported. According to the copper-catalyzed CDC of tetrahydroisoquinolines, the mechanism of which was clarified by Klussmann and coworkers,66 the authors proposed the tetrahydroisoquinoline oxidation by the Cu(II)/O2 system to give the iminium ion 46, which is trapped by the formed nitronate anion 47.
Recently, the group of Singh developed a metal-free homocoupling of methyl arenes for the synthesis of 1,2-diarylethanes, using persulfate as an oxidant in aqueous acetonitrile medium (Scheme 35).67 The conditions are simple, generating innocuous KHSO4 as stoichiometric residue. The scope was broad for different substitution patterns and substituents except for nitro groups. Interestingly, this solvent combination was found to be crucial for the success of the reaction, since no traces of product were obtained when the reaction was run separately in acetonitrile or water. The presence of TEMPO inhibited the reaction, thereby revealing the generation of the benzylic radical in the process, presumably via HAT from the thermally cleaved sulfate radical anion. This is a much more advantageous approach to 1,2-diarylethanes than the dehalogenative coupling of benzyl halides, which implies the use of stoichiometric amounts of sodium metal (the Wurtz reaction).68
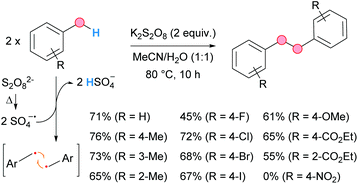 | ||
| Scheme 35 Persulfate-mediated homocoupling of methyl arenes for the generation of bibenzyl derivatives; selected examples. | ||
Following their previous work,69 in 2015, the group of Chatani reported a palladium-catalyzed regioselective CDC between aliphatic amides and toluene derivatives (Scheme 36).70 The chelation-assisted mechanism was found to be essential to attain the excellent enantioselectivities recorded. The simultaneous use of an acid and a base was found to be beneficial for the reaction. Moderate-to-good yields were recorded for toluene and its derivatives. The role of the perfluorinated compound was to generate the benzylic radical 17 and, subsequently, the benzyl iodide 48. A series of deuterium-labeled experiments were carried out in order to elucidate the mechanism of this reaction and the reversibility of each step. As a result, the authors postulated that the formation of the benzyl iodide facilitates its oxidative addition to the palladacycle 49 to give the intermediate 50; subsequent reductive elimination and protonation to release the palladium catalyst gives the final product.
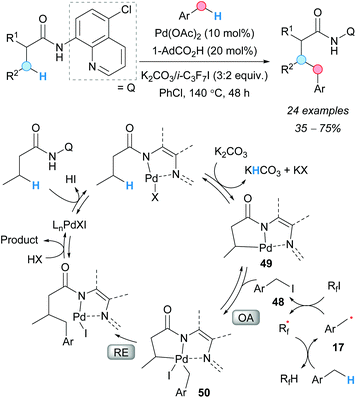 | ||
| Scheme 36 Chelation-assisted Pd(II)-catalyzed CDC of aliphatic amides and toluene derivatives. Proposed reaction mechanism. | ||
5.2. Enantioselective alkylation of benzylic C–H bonds
To develop enantioselective CDC reactions involving benzylic C–H bonds entails special challenges because, in most cases, carbocations and other planar intermediates are formed. To control the attack of the CDC partner to only one face of the intermediate requires a deep knowledge of the system and a great experience in enantioselective reactions. For this reason, comparatively, there are few asymmetric CDC examples in the literature, some of which are discussed in this section.In this regard, in 2009, the group of Cozzi published a seminal contribution describing an enantioselective CDC between aldehydes and benzylic C–H bonds of different nature, such as those in xanthene, flavonoid and indole derivatives (Scheme 37).71 Not only the choice of the organocatalyst but also the nature of its counterion were found to be crucial in order to obtain good enantioselectivities.
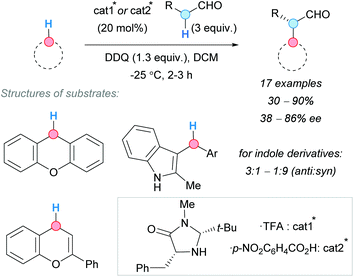 | ||
| Scheme 37 Enantioselective CDC of benzylic C–H bonds of different nature with alkyl aldehydes at low temperature. | ||
An enantioselective version of the CDC of arylmethanes with 1,3-dicarbonyl compounds was developed by the group of Gong in 2010, using a chiral Lewis acid-bonded nucleophile to control the stereochemistry (Scheme 38).72 Up to five different chiral bis(oxazoline) derivatives were screened to finally furnish the products in good-to-excellent enantioselectivities and yields. Only 1 equivalent of DDQ was used, in contrast to the examples described above. 3-Indolyl(aryl)methane derivatives were chosen as coupling partners in this reaction. An oxazoline was selected as the optimal chiral ligand, obtaining the corresponding products in excellent yields and enantioselectivities. Contrary to the previous examples, where high temperatures were needed, the reaction proceeded at 0 °C for 24 h. The absence of the electron spin resonance (ESR) signal characteristic of DDQ, when this was measured in the presence of a 3-benzyl indole, dibenzyl malonate and the copper complex, indicated that cationic rather than radical species were involved in the reaction. In addition, DFT calculations suggested that the reactive intermediate carbocation is, most likely, in its iminium ion form (51), with the charge delocalized over the conjugated system (Scheme 38), rather than a benzylic carbocation, as usually depicted.
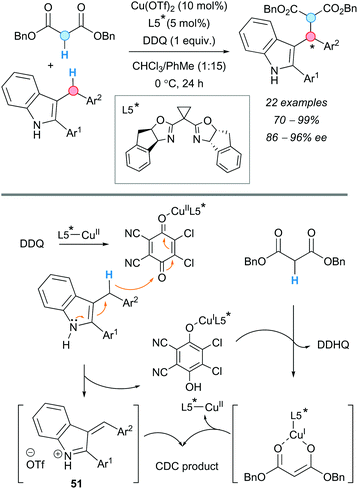 | ||
| Scheme 38 Enantioselective Cu-catalyzed CDC of 3-benzylindoles with 1,3-dicarbonyl compounds and indoles, under solvent-free conditions, and proposed reaction mechanism. | ||
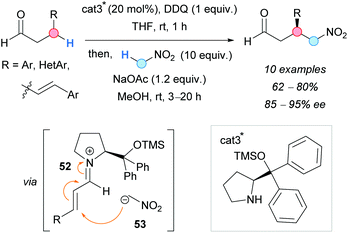
In 2011, the group of Hayashi developed a one-pot enantioselective CDC of β-arylaldehydes and nitromethane (Scheme 39).73 While there are many examples in the literature describing the α-functionalization of aldehydes, a different strategy was applied to achieve β-functionalization. The use of an amine-type catalyst favoured the enamine formation. The presence of aryl groups at the β-position facilitated the DDQ-promoted oxidation of this enamine to the corresponding iminium ion 52. This fact was proved by mixing 3-phenylpropionaldehyde, the organocatalyst and DDQ; cinnamaldehyde was isolated. The subsequent attack of the nitronate 53 to the iminium ion, in the presence of a base, occurred at the β-position, and the final release of the organocatalyst gave the substituted aldehyde with, generally, good yields and excellent enantioselectivities.
In 2013, 1-indanones and 1-tetralones were also successfully used by the group of Feng in the CDC with xanthene, mediated by a Ni(II)/Fe(II) bimetallic catalytic system (Scheme 40).74 The reaction performed well with Fe(II) as the only catalyst, in the presence of an N-proline-derived N,N′-dioxide chiral ligand, giving the racemate in high yield; in contrast, low conversion and excellent enantioselectivity were attained with only Ni(II) as a catalyst. For this reason, the authors decided to combine both catalysts. Careful optimization of the nickel/iron/ligand ratio led to good yields and excellent enantioselectivities for the CDC products. 1-Indanones bearing an ester substituent gave the CDC products in excellent yields using L6*. However, this ligand gave only traces of the desired product when 1-tetralones were used. A modification of the ligand was required in order to promote the reaction, obtaining the corresponding tetralone-derived CDC products in good yields and excellent enantioselectivities.
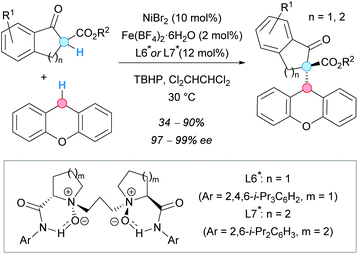 | ||
| Scheme 40 Cooperative bimetallic catalytic system for asymmetric CDC reactions between xanthene and 1-indanone or 1-tetralone derivatives. | ||
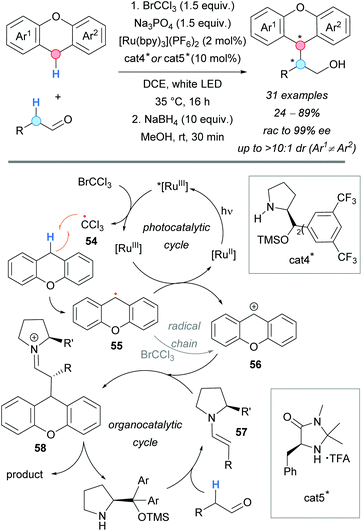
In 2017, visible light was successfully used in the coupling of xanthenes and the α-C–H of alkyl aldehydes by the group of Pericàs (Scheme 41).75 Cooperative photocatalysis and organocatalysis allowed the authors to develop this reaction in an enantioselective version, demonstrating the efficiency of merging these two catalytic strategies. The use of [Ru(bpy)3](PF6)2 as photocatalyst and BrCCl3 as oxidative quencher, observed by Stern–Volmer plot measurements, allowed the access to the highly reactive trichloromethyl radical 54. It was proposed that this species is responsible for the abstraction of the hydrogen atom from the xanthene (RDS, KIE = 4.0), generating the corresponding radical 55, which is further oxidized to the dibenzylic carbocation 56 with regeneration of the photocatalyst. The formation of the C–C bond between the carbocation 56, and the enamine of the aldehyde and the organocatalyst cat4* (57) was found to be the selectivity-determining step, with a computed energy difference between diastereomeric transition states of ΔΔG‡ = 1.7 kcal mol−1. Final hydrolysis of the formed iminium ion 58 and reduction of the aldehyde using NaBH4 would give the CDC alcohol products. Generally, good diastereoselectivities and moderate-to-excellent enantioselectivities were found. Interestingly, the opposite configuration at the α-carbon of the aldehyde was achieved by changing the organocatalyst from cat4* to cat5*, although with moderate diastereo- and enantioselectivities (Scheme 41).
The diastereoselective and asymmetric CDC of carbonyl compounds with other oxygen-containing heterocycles has been recently reported by several research groups.76 In this case, however, the coupling involves the highly activated allylic OC–H of 2H-chromenes and the benzylic OC–H bond of isochromanes.
6. Alkynylation of allylic C–H bonds
The first example of a CDC between an allylic C–H bond and a terminal alkyne was reported by Almasalma and Mejía in 2018 (Scheme 42).77 The process was catalyzed by a copper complex generated from [Cu(MeCN)4]PF6 and terpyridine (L8) as a ligand. An excess of the alkene was used in order to avoid the side dimerization reaction of the alkyne. This approach implied a thermal process using DTBP as an oxidant (conditions A).77a However, very recently, in 2020, the same group developed an improved methodology using a photocatalyzed approach at room temperature in which TBHP was used as the oxidant (conditions B).77b The cross-coupling was successful with cyclic and acyclic allylic substrates, and aromatic and aliphatic terminal alkynes. Concerning the substrate scope, some complementarity was found between the thermal and the photocatalyzed methodologies. The postulated mechanism is depicted in Scheme 42. The initially generated copper(I) catalyst [L8Cu(I)]+ is transformed into complex [L8Cu(II)OR]+ in a thermally or photochemically promoted pathway. The latter copper(II) complex reacts with the allylic radical, 59 generated from the alkene and alkoxyl radicals, giving a copper(III) intermediate 60; the latter undergoes a ligand exchange with the copper acetylide 61 and leads to the final product after reductive elimination, regenerating the catalyst [L8Cu(I)]+.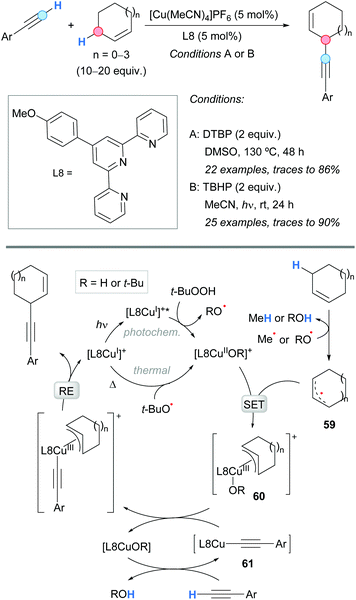 | ||
| Scheme 42 Thermal or photochemical copper-catalyzed alkynylation of allylic C–H bonds and suggested catalytic cycles. | ||
7. Arylation/alkenylation of allylic C–H bonds
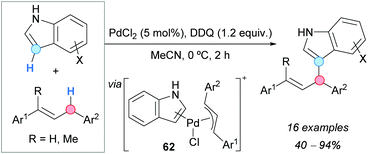
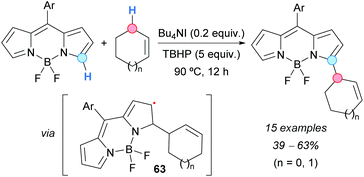
The first direct indolation of 1,3-diarylpropenes at the allylic position was achieved by the group of Bao, using a palladium catalyst and DDQ as an oxidant (Scheme 43).78 Indoles selectively reacted at the 3-position and the formation of the N-allylation product was not observed. Both electron-withdrawing and electron-donating groups were tolerated on the indole. Mixtures of regioisomers were obtained when monosubstituted or asymmetrically disubstituted 1,3-diarylpropenes were used. A mechanistic proposal involves a hydride abstraction from the allylic position of the alkene by DDQ, followed by reaction of the generated allylic cation with PdCl2 and indole to give a π-allylpalladium intermediate 62 (Scheme 43) which, after reductive elimination and deprotonation, would form the final product.The CDC approach has been shown to provide an efficient route to α-functionalized BODIPY dyes, which are difficult to prepare by common synthetic methods. Jiao, Boens and coworkers reported the α-regioselective allylation of BODIPYs by reaction with alkenes (mainly cyclopentene and cyclohexene) using a catalytic amount of Bu4NI and TBHP as an oxidant (Scheme 44).79 Lower yields were obtained with BODIPYs bearing electron-withdrawing groups on the Ar substituent. Under the same reaction conditions, but extending the reaction time to 24 h, products allylated at the α-position of both nitrogen atoms were formed. A mechanism was suggested, starting with the oxidation of iodide to hypoiodite or iodite anions by reaction with TBHP, followed by a hydrogen-atom abstraction from the alkene to generate an allylic radical. The latter then adds to BODIPY at the carbon atom α to nitrogen, leading to radical 63 (Scheme 44) which, after hydrogen abstraction and rearomatization, affords the final product.
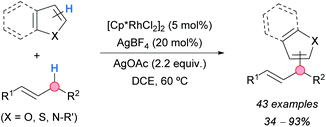
A rhodium-catalyzed CDC of heteroarenes with allylic C–H bonds of alkenes was developed by the group of Glorius (Scheme 45).80 Several 2-substituted thiophenes and furans gave the 5-allylated products in moderate-to-excellent yields, showing a high functional group tolerance. Benzofuran was allylated mainly at the 2-position, whereas benzothiophene reacted at the 2- and 3-positions without any selectivity. N-Substituted pyrrole and indole could be also functionalized selectively at the 3-position. Several alkenes were used as reaction partners. When R1 was an aryl group and R2 an alkyl group, the selective heteroarylation at the carbon atom bonded to R2 was observed. However, with terminal alkenes, such as allylbenzene and 2-allylnaphthalene, the regioselectivity for the branched or the linear products depended on the heteroarene used. When R1 and R2 were alkyl groups, a 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 mixture of regioisomeric products was formed. The synthetic potential of this methodology was demonstrated by the successful allylation of pharmaceutical compounds.
1 mixture of regioisomeric products was formed. The synthetic potential of this methodology was demonstrated by the successful allylation of pharmaceutical compounds.
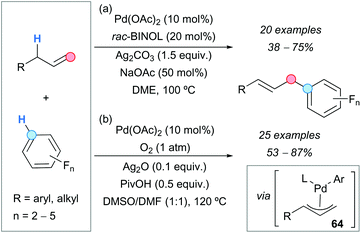
The palladium-catalyzed CDC reaction between terminal alkenes and polyfluorinated arenes led to the synthesis of a variety of linear coupling products in moderate-to-good yields and with very high regioselectivities. Two similar approaches were described which use palladium acetate as a catalyst and differ mainly in the oxidant (Scheme 46). In the first approach, reported by the group of Yang (Scheme 46a),81a silver carbonate was used as an oxidant and racemic 1,1′-bi-2-naphthol (rac-BINOL) as a ligand for palladium, to control the regioselectivity of the process. The formation of Heck-type side products in small amounts was observed in some cases, especially with aliphatic alkenes.
The second approach was reported by the group of Jiang (Scheme 46b)81b and used molecular oxygen as an oxidant, which is convenient from the environmental point of view since it avoids the generation of hazardous waste. Additives such as silver oxide and pivalic acid considerably improved both the yields and selectivities. Small amounts of side products resulting from a Wacker oxidation pathway were detected. Both routes gave good results with aliphatic alkenes and allylarenes bearing electron-withdrawing or electron-donating groups. Concerning the arene partner, reactions with substrates containing 2 to 5 fluorine atoms proceeded successfully. The proposed mechanism involves the generation of a π-allylpalladium complex 64 (Scheme 46), which leads to the final product after reductive elimination.
A metal-free CDC procedure to perform the allylation of 1,4-naphthoquinones and 4-hydroxycoumarins with 1,3-diarylpropenes was reported by Cheng and coworkers (Scheme 47).82 The process was mediated by DDQ and it took place at room temperature. Both 2-substituted-1,4-naphthoquinones and 4-hydroxycoumarins exclusively reacted at the 3-position. A SET process is assumed to occur, given the dramatic drop in the reaction yield observed when TEMPO was used as an additive. Mixtures of α- and γ-isomers were formed with non-symmetric 1,3-diarylpropenes, suggesting that allylic radicals could be involved in the mechanism of the reaction. The corresponding cyclization products, pyranonaphthoquinones and pyranocoumarins, were obtained in moderate-to-good yields when an extra equivalent of DDQ was added after completion of the coupling reaction and stirring was continued for one hour.
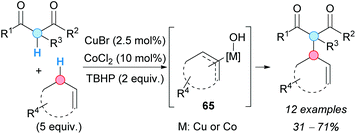
8. Alkylation of allylic C–H bonds
The catalytic allylic alkylation of alkenes with 1,3-dicarbonyl compounds via a CDC reaction was first developed by Li and coworkers.83 After screening different reaction conditions, the authors found a combination of Cu(I) and Co(II) catalysts which, in the presence of an excess of TBHP, furnished the desired products in useful synthetic yields, albeit requiring an excess of the alkene (Scheme 48). Although the role of each metal (cobalt and copper) was not clarified, the mechanistic studies supported the formation of a π-allyl copper or allyl cobalt complex 65 through the allylic H-abstraction.Cheng and Bao reported the CDC between activated methylene compounds and 1,3-diaryl allylic substrates. The reaction was promoted by stoichiometric amounts of DDQ, under metal-free conditions at room temperature, affording the expected products in very good yields (Scheme 49).84 Mechanistically, the formation of a charge-transfer complex (deep green color) between the 1,3-diaryl allylic substrate and DDQ was proposed, followed by HAT to form an allylic cation 66. Deprotonation of the 1,3-dicarbonyl substrate by the phenolate derived from DDQ would produce the corresponding enolate 67, which is finally added to the former allylic cation to give the product.
More recently, a catalytic copper-mediated CDC using stoichiometric DDQ was developed by the group of Huang for the allylation of less activated carbonyl systems, such as ketones or aldehydes (Scheme 50a).85 1,3-Diphenylpropene was selected as a coupling partner, giving the corresponding products in good-to-excellent yields. The proposed mechanism is similar to the one described above, with the copper salt acting as a Lewis acid to promote the enolization of the corresponding aldehyde or ketone, and favouring the nucleophilic attack to the formed allylic cation.
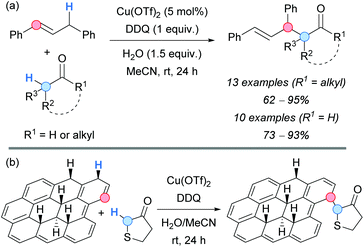 | ||
| Scheme 50 DDQ-promoted Cu-catalyzed CDC between (a) 1,3-diphenylpropene and aldehydes or ketones or between (b) hydrogenated graphene and tetrahydrothiophen-3-one. | ||
Similar reaction conditions were applied in the field of materials science by the group of Pumera, which developed a C–H functionalization of hydrogenated graphene with tetrahydrothiophen-3-one (Scheme 50b).86 Different techniques, such as X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) or Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) were used to confirm the mentioned functionalization.
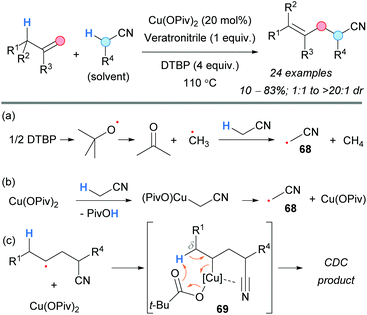
Later on, the group of Dong established a regioselective protocol to convert olefins into nitriles using copper catalysis and DTBP (Scheme 51).87 Generally, good yields and diastereoselectivities were observed. Two different pathways were proposed for the generation of the radical 68: via HAT from the methyl radical (Scheme 51a) or ligand exchange on the copper salt and final copper reduction (Scheme 51b). Intramolecular coordination of the copper center to the triple bond of the nitrile group in the intermediate 69 was proposed in order to account for the observed regioselectivity (Scheme 51c). The formation of radical intermediates was supported by the detection of TEMPO-Me and by a radical-clock experiment.
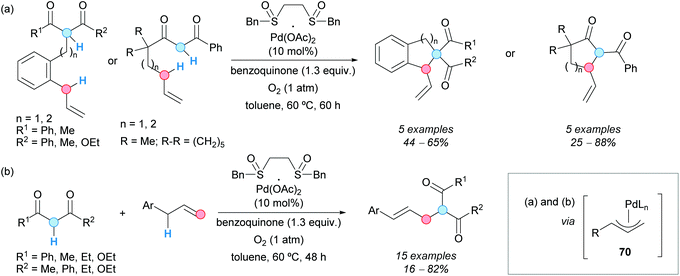
The direct alkylation of allylic C–H bonds was also achieved by the group of Shi via palladium catalysis and was employed in intra/intermolecular processes. Thus, different aromatic and allylic substrates containing 1,3-dicarbonyl moieties experienced an intramolecular annulation, in the presence of 1,2-bis(benzylsulfinyl)ethane/palladium(II) acetate as a catalyst and benzoquinone as an oxidant, to afford indane and tetrahydronaphthalenes or cyclopenta- and cyclohexanones (Scheme 52a).88 The reaction was carried out in toluene as a solvent under an oxygen atmosphere. Under the same reaction conditions, the intermolecular direct allylic alkylation of allylarenes with 1,3-dicarbonyl compounds was achieved (Scheme 52b).88 It was assumed that a π-allylpalladium species 70 was always the key intermediate, formed via an electrophilic allylic C–H bond cleavage by palladium(II) catalysis. Nucleophilic attack by the 1,3-dicarbonylic system, or its enolate, yielded the final product. The formed palladium(0) was re-oxidized by benzoquinone. It is interesting to note that no base was required in any case, the quinone showing a crucial role as a proton acceptor as well as an oxidant.
In addition, the group of White used 1,2-bis(phenylsulfinyl)ethane/palladium(II) acetate catalyst, in combination with DMSO and 2,6-dimethylbenzoquinone (DMBQ)/acetic acid, to achieve an allylic C–H alkylation reaction between a wide range of aromatic and heteroaromatic allylic compounds with activated methylenes, such as methyl nitroacetate; linear (E)-α-nitro-δ-aryl-4-pentenoates were obtained with high stereoselectivities (E/Z selectivities >20![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) and with regioselectivities up to 20
1) and with regioselectivities up to 20![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 (Scheme 53).89 The resulting nitroesters proved to be useful in asymmetric conjugate addition reactions, to give optically enriched α,α-disubstituted amino acid precursors, and in the synthesis of amino esters by selective reduction. As in the case above, π-allylpalladium species should be involved.
1 (Scheme 53).89 The resulting nitroesters proved to be useful in asymmetric conjugate addition reactions, to give optically enriched α,α-disubstituted amino acid precursors, and in the synthesis of amino esters by selective reduction. As in the case above, π-allylpalladium species should be involved.
9. Conclusions and outlook
Concluding this review, we can say that the classical benzylation and allylation reactions of carbon centers have been substantially upgraded with the incorporation of the CDC to the organic chemist toolkit, whereby benzylic and allylic C–H bonds can be straightforwardly coupled with C(sp)–H, C(sp2)–H and C(sp3)–H bonds without any previous installation of functional groups. These reactions are commonly conducted under transition-metal catalysis in the presence of a stoichiometric amount of an oxidant under thermal activation. Among them, the alkynylation of benzylic and allylic C–H bonds, typically under copper catalysis, has been marginally studied in comparison with the arylation or the alkylation counterparts. Copper catalysis also prevails in the arylation and hetarylation of benzylic C–H bonds (not of allylic C–H bonds), with the latter normally occurring at the α-position to nitrogen; other metals, such as palladium, ruthenium or iron have also come into play to a lower extent, whereas the metal-free oxidant-promoted protocols are scarce. The aroylation of aromatics with toluenes, leading to diaryl ketones, has been almost exclusively performed under palladium catalysis by C–H activation in the presence of a directing group. The alkylation of benzylic and allylic C–H bonds usually involves methylene-active carbonyl partners and it is catalyzed by copper, iron or palladium; the sole action of organic or inorganic oxidants has been found to be effective in a few cases.There is no room for doubt about the CDC outperforming the classical routes to accomplish the benzylation or allylation of carbon centers in terms of simplicity, atom economy and functional group compatibility. Furthermore, the fact that toluene derivatives and alkenes are abundant and commercially available starting materials for benzylation and allylation reactions, respectively, opens an array of possibilities for their CDC transformation into more complex molecules with diverse proven or potential applications. In spite of the fact of the clear advantages of the CDC, there are some issues that need attention in order to make the approach more attractive from the sustainable point of view, namely: (a) the relatively high metal loading used for some noble–metal catalysts, (b) the large excess of the oxidant deployed in many cases and the incorporation of molecular oxygen (or air) instead, (c) to replace the chlorinated solvents, often used in the CDC protocols, with green ones or solvent-free conditions, (d) the development of heterogeneous reusable catalytic systems (barely documented for these reactions), (e) the process activation by visible light to the detriment of the thermal, frequently harsh, conditions applied, and (f) the introduction of asymmetric versions for CDC of benzylic and allylic C–H bonds. We are aware that the latter issue is an arduous task, yet underrepresented within the collection of manifold CDCs. That is why efforts must be devoted to search for efficient catalytic asymmetric (preferably enantioselective) methods that successfully combine the inherent advantages of the CDC reactions with achieving high enantiomeric (and/or diastereomeric) product ratios.
Abbreviations
| 4N-T(BF4) | 4-Acetamido-2,2,6,6-tetramethylpyridine-1-oxoammonium salt |
| atm | Atmosphere |
| BINOL | 1,1′-Bi-2-naphthol |
| BNDHP | 1,1′-Binaphthyl-2,2′-dihydrogen phosphate |
| BODIPY | Boron-dipyrromethene |
| bpy | 2,2′-Bipyridine |
| cat | Catalyst |
| CDC | Cross dehydrogenative coupling |
| CP | Cyclopalladation |
| CT | Charge transfer |
| dbm | Dibenzoylmethide |
| DABCO | 1,4-Diazabicyclo[2.2.2]octane |
| DCE | 1,2-Dichloroethane |
| DCM | Dichloromethane |
| DCP | Dicumyl peroxide |
| DDHQ | 2,3-Dichloro-5,6-dicyanohydroquinone |
| DDQ | 2,3-Dichloro-5,6-dicyano-1,4-benzoquinone |
| DG | Directing group |
| DFT | Density functional theory |
| DMBQ | 2,6-Dimethylbenzoquinone |
| DMF | N,N-Dimethylformamide |
| DMSO | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| DTBP | Di-tert-butyl peroxide |
| equiv. | Equivalent |
| ESR | Electron spin resonance |
| Fc | Ferrocene |
| FTIR | Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy |
| HAT | Hydrogen atom transfer |
| HetAr | Hetaryl or heteroaryl |
| KIE | Kinetic isotopic effect |
| LG | Leaving group |
| Luperox® 101 | 2,5-Bis(tert-butylperoxy)-2,5-dimethylhexane |
| M | Metal |
| MOF | Metal–organic framework |
| MW | Microwaves |
| NHPI | N-Hydroxyphthalimide |
| NPs | Nanoparticles |
| OA | Oxidative addition |
| PINO | Phthalimide-N-oxyl |
| PS | Polystyrene |
| rac | Racemate or racemic |
| RDS | Rate-determining step |
| RE | Reductive elimination |
| rt | Room temperature |
| Selectfluor | 1-Chloromethyl-4-fluoro-1,4-diazoniabicyclo[2.2.2]octane bis(tetrafluoroborate) |
| SET | Single electron transfer |
| TBHP | tert-Butyl hydroperoxide |
| TBPB | tert-Butyl perbenzoate |
| TEMPO | 2,2,6,6-Tetramethylpiperidine 1-oxyl |
| TFA | Trifluoroacetic acid |
| tfacac | Trifluoroacetylacetonate |
| TM | Transition metal |
| XPS | X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy |
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest to declare.Acknowledgements
This work was generously supported by the Spanish Ministerio de Ciencia, Innovación y Universidades (MICIU; grant no. CTQ2017-88171-P), the Generalitat Valenciana (GV; grant no. AICO/2017/007) and the Universidad de Alicante (grant no. VIGROB-285/19). I. B. is also grateful to the Spanish MICIU for a Juan de la Cierva-incorporación grant (no. IJCI-2017-33706).References
- M. B. Smith, March's Advanced Organic Chemistry: Reactions, Mechanisms and Structure, John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken (NJ), 7th edn, 2013, ch. 10–13 Search PubMed.
- Review: S. Mondal and G. Panda, Synthetic methodologies of achiral diarylmethanols, diaryl and triarylmethanes (TRAMs) and medicinal properties of diaryl and triarylmethanes-an overview, RSC Adv., 2014, 4, 28317–28358 RSC.
- Review: S. K. Jana, Recent developments of heterogeneous solid catalysts for liquid-phase Friedel–Crafts type benzylation reaction, Catal. Surv. Asia, 2005, 9, 25–34 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) W. Zhang, P. Chen and G. Liu, Copper-catalyzed arylation of benzylic C–H bonds with alkylarenes as the limiting reagents, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2017, 139, 7709–7712 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) X. Cheng, H. Lu and Z. Lu, Enantioselective benzylic C–H arylation via photoredox and nickel dual catalysis, Nat. Commun., 2019, 10, 3549 CrossRef PubMed.
- Reviews: (a) J. T. Mohr and B. H. Stoltz, Enantioselective Tsuji allylations, Chem. – Asian J., 2007, 2, 1476–1491 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) J. Qu and G. Helmchen, Applications of iridium-catalyzed asymmetric allylic substitution reactions in target-oriented synthesis, Acc. Chem. Res., 2017, 50, 2539–2555 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) S. Noreen, A. F. Zahoor, S. Ahmad, I. Shahzadi, A. Irfan and S. Faiz, Novel chiral ligands for palladium-catalyzed asymmetric allylic alkylation/asymmetric Tsuji-Trost reaction: a review, Curr. Org. Chem., 2019, 23, 1168–1213 CrossRef CAS; (d) for Tsuji-Trost-type benzylation reactions, see: J. L. Bras and J. Muzart, Production of Csp3−Csp3 bonds through palladium-catalyzed Tsuji–Trost-type reactions of (hetero)benzylic substrates, Eur. J. Org. Chem., 2016, 2565–2593 CrossRef.
- Review: J. D. Weaver, A. Recio III, A. J. Grenning and J. A. Tunge, Transition metal-catalyzed decarboxylative allylation and benzylation reactions, Chem. Rev., 2011, 111, 1846–1913 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Review: N. K. Mishra, S. Sharma, J. Park, S. Han and I. S. Kim, Recent advances in catalytic C(sp2)–H allylation reactions, ACS Catal., 2017, 7, 2821–2847 CrossRef CAS.
- Pioneering research: (a) Z. Li and C.-J. Li, CuBr-catalyzed efficient alkynylation of sp3 C-H bonds adjacent to a nitrogen atom, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2004, 126, 11810–11811 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) Z. Li and C.-J. Li, CuBr-catalyzed direct indolation of tetrahydroisoquinolines via cross-dehydrogenative coupling between sp3 C–H and sp2 C–H bonds, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2005, 127, 6968–6969 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) Z. Li, D. Scott Bohle and C.-J. Li, Cu-catalyzed cross-dehydrogenative coupling: A versatile strategy for C–C bond formations via the oxidative activation of sp3 C–H bonds, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2006, 103, 8928–8933 CrossRef CAS PubMed; Monograph: (d) From C-H to C-C Bonds: Cross-Dehydrogenative-Coupling, ed C.-J. Li, Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge (UK), 2015 Search PubMed.
- Selected reviews: (a) C.-J. Li, Cross-dehydrogenative coupling (CDC): exploring C–C bond formations beyond functional group transformations, Acc. Chem. Res., 2009, 42, 335–344 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) C. S. Yeung and V. M. Dong, Catalytic dehydrogenative cross-coupling: forming carbon−carbon bonds by oxidizing two carbon−hydrogen bonds, Chem. Rev., 2011, 111, 1215–1292 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) S. A. Girard, T. Knauber and C.-J. Li, The cross-dehydrogenative coupling of Csp3-H bonds: a versatile strategy for C-C bond formations, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2014, 53, 74–100 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (d) M. Itazaki and H. Nakazawa, Iron-catalyzed cross-deshydrogenative-coupling reactions, Top. Organomet. Chem., 2015, 50, 47–82 CrossRef CAS; (e) C.-J. Li, Exploration of new chemical reactivities for sustainable molecular transformations, Chem, 2016, 1, 423–437 CrossRef CAS; (f) B. V. Varun, J. Dhineshkumar, K. R. Bettadapur, Y. Siddaraju, K. Alagiri and K. R. Prabhu, Recent advancements in dehydrogenative cross coupling reactions for C-C bond formation, Tetrahedron Lett., 2017, 58, 803–824 CrossRef CAS; (g) F. Alonso, I. Bosque, R. Chinchilla, J. C. Gonzalez-Gomez and D. Guijarro, Synthesis of propargylamines by cross-dehydrogenative coupling, Curr. Green Chem., 2019, 6, 105–126 CrossRef CAS; (h) C.-Y. Huang, H. Kang, J. Li and C.-J. Li, En route to intermolecular cross-dehydrogenative coupling reactions, J. Org. Chem., 2019, 84, 12705–12721 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (i) S. Ghandi, Catalytic enantioselective cross dehydrogenative coupling of sp3 C–H of heterocycles, Org. Biomol. Chem., 2019, 17, 9683–9692 RSC.
- C. A. Correia and C.-J. Li, Copper-catalyzed cross-dehydrogenative coupling (CDC) of alkynes and benzylic C-H bonds, Adv. Synth. Catal., 2010, 352, 1446–1450 CrossRef CAS.
- Z.-H. Zhang, X.-Y. Dong, X.-Y. Du, Q.-S. Gu, Z.-L. Li and X.-Y. Liu, Copper-catalyzed enantioselective Sonogashira-type oxidative cross-coupling of unactivated C(sp3)−H bonds with alkynes, Nat. Commun., 2019, 10, 5689–5698 CrossRef PubMed.
- G. Qun, X. Chen, L. Yang and H. Huang, Copper-catalyzed α-benzylation of enones via radical-triggered oxidative coupling of two C–H bonds, ACS Catal., 2015, 5, 2882–2885 CrossRef.
- H. Wang, Y.-L. Zhao, L. Li, S.-S. Li and Q. Liu, Metal-free 2,3-dichloro-5,6-dicyano-1,4-benzoquinone (DDQ)-mediated cross-dehydrogenative-coupling (CDC) of benzylic C(sp3)-H bonds and vinylic C(sp2)-H bonds: efficient one-pot synthesis of 1H-indenes, Adv. Synth. Catal., 2014, 356, 3157–3163 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Rong, R. Li and W. Lu, Palladium(II)-catalyzed coupling of p-xylene via regioselective C−H activation in TFA, Organometallics, 2007, 26, 4376–4378 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Selenski and T. R. R. Pettus, (±)-Diinsininone: made nature's way, Tetrahedron, 2006, 62, 5298–5307 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y.-Z. Li, B.-J. Li, X.-Y. Lu, S. Lin and Z.-J. Shi, Cross dehydrogenative arylation (CDA) of a benzylic C-H bond with arenes by iron catalysis, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2009, 48, 3817–3820 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. Nitsch, A. Poethig and T. Bach, Diastereoselective oxidative cross-coupling reactions of chiral alkylbenzenes with arenes and silyl nucleophiles, Synlett, 2014, 2434–2437 CAS.
- T. E. Storr, C. J. Teskey and M. F. Greaney, Cross-dehydrogenative-coupling of alkoxybenzenes with toluenes: copper(II) halide mediated tandem halo/benzylation of arenes, Chem. – Eur. J., 2016, 22, 18169–18178 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. Xiong, Y. Li, X.-H. Bi, Y.-H. Lv and Q. Zhang, Copper-catalyzed dehydrogenative cross-coupling reactions of N-para-tolylamides through successive C-H activation: synthesis of 4H-3,1-benzoxazines, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2011, 50, 7140–7143 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. E. Hurst and R. J. K. Taylor, A Cu-catalysed radical cross-dehydrogenative coupling approach to acridanes and related heterocycles, Eur. J. Org. Chem., 2017, 203–207 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Tian, Y. Sui, Y. Gu and S.-K. Tian, Expedient synthesis of functionalized triarylmethanols through tandem formation of geminal C-C and C-O bonds, Adv. Synth. Catal., 2012, 354, 3475–3479 CrossRef CAS.
- G. Li, D. Li, J. Zhang, D.-Q. Shi and Y. Zhao, Ligand-enabled regioselectivity in the oxidative cross-coupling of arenes with toluenes and cycloalkanes using ruthenium catalysts: tuning the site-selectivity from the ortho to meta positions, ACS Catal., 2017, 7, 4138–4143 CrossRef CAS.
- H.-J. Zhang, F. Su and T.-B. Wen, Copper-catalyzed direct C2-benzylation of indoles with alkylarenes, J. Org. Chem., 2015, 80, 11322–11329 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Guo, Y. Li, Y. Wang, X. Guo, X. Meng and B. Chen, Iron-catalyzed cross dehydrogenative coupling (CDC) of indoles and benzylic C-H bonds, Adv. Synth. Catal., 2015, 357, 950–954 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Wan, K. Qiao, X. N. Sun, Z. C. Di, Z. Fang, Z. J. Li and K. Guo, Benzylation of heterocyclic N-oxides via direct oxidative cross-dehydrogenative coupling with toluene derivatives, New J. Chem., 2016, 40, 10227–10232 RSC.
- M. Wan, H. Lou and L. Liu, C1-Benzyl and benzoyl isoquinoline synthesis through direct oxidative cross-dehydrogenative coupling with methyl arenes, Chem. Commun., 2015, 51, 13953–13956 RSC.
- X. Shi, F. Zhang, W.-K. Luo and L. Yang, Oxidant-triggered C1-benzylation of isoquinoline by iodine-catalyzed cross-dehydrogenative-coupling with methylarenes, Synlett, 2017, 494–498 CAS.
- L. Hu, J. Yuan, J. Fu, T. Zhang, L. Gao, Y. Xiao, P. Mao and L. Qu, Copper-catalyzed direct C-3 benzylation of quinoxalin-2(1H)-ones with methylarenes under microwave irradiation, Eur. J. Org. Chem., 2018, 4113–4120 CrossRef CAS.
- F. Lv, Y. Yu, E. Hao, C. Yu, H. Wang, L. Jiao and N. Boens, Copper-catalyzed α-benzylation of BODIPYs via radical-triggered oxidative cross-coupling of two C–H bonds, Chem. Commun., 2018, 54, 9059–9062 RSC.
- S.-L. Zhou, L.-N. Guo and X.-H. Duan, Copper-catalyzed regioselective cross-dehydrogenative coupling of coumarins with benzylic Csp3−H bonds, Eur. J. Org. Chem., 2014, 8094–8100 CrossRef CAS.
- S. H. Doan, V. H. Nguyen, T. H. Nguyen, P. H. Pham, N. N. Nguyen, A. N. Q. Phan, T. N. Tu and N. T. S. Phan, Cross-dehydrogenative coupling of coumarins with Csp3−H bonds using an iron–organic framework as a productive heterogeneous catalyst, RSC Adv., 2018, 8, 10736–10745 RSC.
- M.-B. Zhou, C.-Y. Wang, R.-J. Song, Y. Lui, W.-T. Wei and J.-H. Li, Oxidative 1,2-difunctionalization of activated alkenes with benzylic C(sp3)–H bonds and aryl C(sp2)–H bonds, Chem. Commun., 2013, 49, 10817–10819 RSC.
- S.-L. Zhou, L.-N. Guo, H. Wang and X.-H. Duan, Copper-catalyzed oxidative benzylarylation of acrylamides by benzylic C-H bond functionalization for the synthesis of oxindoles, Chem. – Eur. J., 2013, 19, 12970–12973 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S.-L. Zhou, L.-N. Guo, H. Wang and X.-H. Duan, Copper-catalyzed tandem oxidative cyclization of cinnamamides with benzyl hydrocarbons through cross-dehydrogenative coupling, Chem. Commun., 2014, 50, 3589–3591 RSC.
- For previous reviews on this topic, see: (a) J.-B. Feng and X.-F. Wu, Transition metal-catalyzed oxidative transformations of methylarenes, Appl. Organomet. Chem., 2015, 29, 63–86 CrossRef CAS; (b) X.-F. Wu, Acylation of (hetero)arenes through C-H activation with aroyl surrogates, Chem. – Eur. J., 2015, 21, 12252–12265 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Guin, S. K. Rout, A. Banerjee, S. Nandi and B. K. Patel, Four tandem C–H activations: a sequential C–C and C–O bond making via a Pd-catalyzed cross dehydrogenative coupling (CDC) approach, Org. Lett., 2012, 14, 5294–5297 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. Xu, B. Xianga and P. Sun, Palladium catalyzed direct ortho C–H acylation of 2-arylpyridines using toluene derivatives as acylation reagents, RSC Adv., 2013, 3, 1679–1682 RSC.
- For previous studies where this chelation-directed C-H activation has been confirmed, see: (a) X. Chen, C. E. Goodhue and J.-Q. Yu, Palladium-catalyzed alkylation of sp2 and sp3 C−H bonds with methylboroxine and alkylboronic acids: two distinct C−H activation pathways, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2006, 128, 12634–12635 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) W.-Y. Yu, W. N. Sit, Z. Zhou and A. S. C. Chan, Palladium-catalyzed decarboxylative arylation of C−H bonds by aryl acylperoxides, Org. Lett., 2009, 11, 3174–3177 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) J. M. Racowski, A. R. Dick and M. S. Sanford, Detailed study of C−O and C−C bond-forming reductive elimination from stable C2N2O2−ligated palladium(IV) complexes, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2009, 131, 10974–10983 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) N. R. Deprez and M. S. Sanford, Synthetic and mechanistic studies of Pd-catalyzed C−H arylation with diaryliodonium salts: evidence for a bimetallic high oxidation state Pd intermediate, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2009, 131, 11234–11241 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) D. C. Powers, M. A. L. Geibel, J. E. M. N. Klein and T. Ritter, Bimetallic palladium catalysis: direct observation of Pd(III)−Pd(III) intermediates, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2009, 131, 17050–17051 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) D. C. Powers and T. Ritter, Bimetallic Pd(III) complexes in palladium-catalysed carbon–heteroatom bond formation, Nat. Chem., 2009, 1, 302–309 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. C. Perumgani, S. P. Parvathaneni, S. Keesara and M. R. Mandapati, Recyclable Pd(II)complex catalyzed oxidative sp2 CH bond acylation of 2-aryl pyridines with toluene derivatives, J. Organomet. Chem., 2016, 822, 189–195 CrossRef CAS.
- Y.-S. Bao, D. Zhang, M. Jia and B. Zhaorigetu, Replacing Pd(OAc)2 with supported palladium nanoparticles in ortho-directed CDC reactions of alkylbenzenes, Green Chem., 2016, 18, 2072–2077 RSC.
- F. Xiong, C. Qian, D. Lin, W. Zeng and X. Lu, Palladium-catalyzed cascade oxidation/sp2 C–H acylation of azoarenes with aryl methanes, Org. Lett., 2013, 15, 5444–5447 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Song, D. Chen, C. Pi, X. Cui and Y. Wu, Palladium(II)-catalyzed direct regioselectively oxidative acylation of azobenzenes with toluene derivatives, J. Org. Chem., 2014, 79, 2955–2962 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. K. Santra, A. Banerjee and B. K. Patel, 2,3-Diarylquinoxaline directed mono ortho-aroylation via cross-dehydrogenative coupling using aromatic aldehydes or alkylbenzenes as aroyl surrogate, Tetrahedron, 2014, 70, 2422–2430 CrossRef CAS.
- Y.-F. Liang, X. Li, X. Wang, Y. Yan, P. Feng and N. Jiao, Aerobic oxidation of PdII to PdIV by active radical reactants: direct C-H nitration and acylation of arenes via oxygenation process with molecular oxygen, ACS Catal., 2015, 5, 1956–1963 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Zheng, W.-B. Song, S.-W. Zhang and L.-J. Xuan, Palladium-catalyzed oxidative ortho-acylation of 2-arylbenzoxazoles and 2-arylbenzothiazoles with toluene derivatives, Tetrahedron, 2015, 71, 1574–1580 CrossRef CAS.
- B. V. Pipaliya and A. K. Chakraborti, Cross-dehydrogenative coupling of heterocyclic scaffolds with unfunctionalized aroyl surrogates by palladium(II) catalyzed C(sp2)-H aroylation through organocatalytic dioxygen activation, J. Org. Chem., 2017, 82, 3767–3780 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Weng, Z. Yu, X. Liu and G. Zhang, Palladium-catalyzed direct oxidative ortho-acylation of anilides with toluene derivatives, Tetrahedron Lett., 2013, 54, 1205–1207 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Wu, P. Y. Choy, F. Mao and F. Y. Kwong, Toluene derivatives as simple coupling precursors for cascade palladium-catalyzed oxidative C–H bond acylation of acetanilides, Chem. Commun., 2013, 49, 689–691 RSC.
- Z. Yin and P. Sun, Palladium-catalyzed direct ortho-acylation through an oxidative coupling of acetanilides with toluene derivatives, J. Org. Chem., 2012, 77, 11339–11344 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Wu, L.-J. Feng, X. Lu, F. Y. Kwong and H.-B. Luo, Palladium-catalyzed oxidative C–H bond acylation of N-nitrosoanilines with toluene derivatives: a traceless approach to synthesize N-alkyl-2-aminobenzophenone, Chem. Commun., 2014, 50, 15352–15354 RSC.
- Y. Zhao, U. K. Sharma, F. Schröder, N. Sharma, G. Song and E. V. Van der Eycken, Direct C-2 acylation of indoles with toluene derivatives via Pd(II)-catalyzed C–H activation, RSC Adv., 2017, 7, 32559–32563 RSC.
- W. Ali, A. Behera, S. Guin and B. K. Patel, Regiospecific benzoylation of electron-deficient N-heterocycles with methylbenzenes via a Minisci-type reaction, J. Org. Chem., 2015, 80, 5625–5632 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. Li;, L. Cao and C.-J. Li, FeCl2-catalyzed selective C-C bond formation by oxidative activation of a benzylic C-H bond, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2007, 46, 6505–6507 CrossRef PubMed.
- N. Borduas and D. A. Powell, Copper-catalyzed oxidative coupling of benzylic C−H bonds with 1,3-dicarbonyl compounds, J. Org. Chem., 2008, 73, 7822–7825 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. A. Correia and C.-J. Li, Catalytic alkylation of benzylic C–H bonds with 1,3-dicarbonyl compounds utilizing oxygen as terminal oxidant, Tetrahedron Lett., 2010, 51, 1172–1175 CrossRef CAS.
- S. G. Pan, J. H. Liu, Y. M. Li and Z. P. Li, Iron-catalyzed benzylation of 1,3-dicarbonyl compounds by simple toluene derivatives, Chin. Sci. Bull., 2012, 57, 2382–2386 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Yang and Q. Song, Fe-catalyzed double cross-dehydrogenative coupling of 1,3-dicarbonyl compounds and arylmethanes, Org. Lett., 2015, 17, 548–551 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J.-B. Yu, Y. Zhang, Z.-J. Jiang and W.-K. Su, Mechanically induced Fe(III) catalysis at room temperature: solvent-free cross-dehydrogenative coupling of 3-benzylic indoles with methylenes/indoles, J. Org. Chem., 2016, 81, 11514–11520 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Á. Pintér, A. Sud, D. Sureshkumar and M. Klussmann, Autoxidative carbon–carbon bond formation from carbon–hydrogen bonds, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2010, 49, 5004–5007 CrossRef PubMed.
- B. Zhang, Y. Cui and N. Jiao, Metal-free TEMPO-catalyzed oxidative C–C bond formation from Csp3−H bonds using molecular oxygen as the oxidant, Chem. Commun., 2012, 48, 4498–4500 RSC.
- F.-F. Wang, C.-P. Luo, G. Deng and L. Yang, C(sp3)–C(sp3) bond formation via copper/Brønsted acid co-catalyzed C(sp3)–H bond oxidative cross-dehydrogenative-coupling (CDC) of azaarenes, Green Chem., 2014, 16, 2428–2431 RSC.
- L. Fang, Z. Li, Z. Jiang, Z. Tan and Y. Xie, A metal-free oxidative cross-dehydrogenative coupling of N-aryl tetrahydroisoquinolines and 2-methylazaarenes using a recyclable oxoammonium salt as oxidant in aqueous media, Eur. J. Org. Chem., 2016, 3559–3567 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Zhang, B.-W. Wei, W.-X. Wang, L.-L. Deng, L.-J. Nie, H.-Q. Luo and X.-L. Fan, Direct vinylogous oxidative cross-dehydrogenative coupling of 4-nitroisoxazoles with N-aryl tetrahydroisoquinolines in water under air conditions, RSC Adv., 2017, 7, 1229–1232 RSC.
- E. Boess, C. Schmitz and M. Klussmann, A comparative mechanistic study of Cu-catalyzed oxidative coupling reactions with N-phenyltetrahydroisoquinoline, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2012, 134, 5317–5325 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. Kumar, T. Guntreddi, R. Singh and K. N. Singh, A practical protocol for the synthesis of bibenzyls via C(sp3)–H activation of methyl arenes under metal-free conditions, Org. Chem. Front., 2017, 4, 147–150 RSC.
- Comprehensive Organic Transformations, ed. R. C. Larock, Wiley–VCH, New York (NY), 2nd edn, 1999, pp. 83–84 Search PubMed.
- Y. Aihara, M. Tobisu, Y. Fukumoto and N. Chatani, Ni(II)-catalyzed oxidative coupling between C(sp2)–H in benzamides and C(sp3)–H in toluene derivatives, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2014, 136, 15509–15512 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. Kubo, Y. Aihara and N. Chatani, Pd(II)-catalyzed chelation-assisted cross dehydrogenative coupling between unactivated C(sp3)–H bonds in aliphatic amides and benzylic C–H bonds in toluene derivatives, Chem. Lett., 2015, 44, 1365–1367 CrossRef CAS.
- F. Benfatti, M. Guiteras Capdevila, L. Zoli, E. Benedetto and P. G. Cozzi, Catalytic stereoselective benzylic C–H functionalizations by oxidative C–H activation and organocatalysis, Chem. Commun., 2009, 5919–5921 RSC.
- C. Guo, J. Song, S.-W. Luo and L.-Z. Gong, Enantioselective oxidative cross-coupling reaction of 3-indolylmethyl C-H bonds with 1,3-dicarbonyls using a chiral Lewis acid-bonded nucleophile to control stereochemistry, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2010, 49, 5558–5562 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Hayashi, T. Itoh and H. Ishikawa, Oxidative and enantioselective cross-coupling of aldehydes and nitromethane catalyzed by diphenylprolinol silyl ether, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2011, 50, 3920–3924 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W. Cao, X. Liu, R. Peng, P. He, L. Lin and X. Feng, Catalytic asymmetric cross-dehydrogenative coupling: activation of C–H bonds by a cooperative bimetallic catalyst system, Chem. Commun., 2013, 49, 3470–3472 RSC.
- E. Larionov, M. M. Mastandrea and M. A. Pericàs, Asymmetric visible-light photoredox cross-dehydrogenative coupling of aldehydes with xanthenes, ACS Catal., 2017, 7, 7008–7013 CrossRef CAS.
- Recent examples: (a) X. Pan, X. Liu, S. Sun, Z. Meng and L. Liu, Catalytic asymmetric cross-dehydrogenative coupling of 2H-chromenes and aldehydes, Chin. J. Chem., 2018, 36, 1187–1190 CrossRef CAS; (b) Z. Zhang, Y.-Q. Tu, X.-M. Zhang, F.-M. Zhang and S.-H. Wang, Copper-catalyzed highly diastereoselective cross-dehydrogenative coupling between 8-hydroxyisochromanes and 1,3-dicarbonyl compounds, Org. Chem. Front., 2019, 6, 2275–2279 RSC.
- (a) A. A. Almasalma and E. Mejía, Copper-catalyzed allylic C−H alkynylation by cross-dehydrogenative coupling, Chem. – Eur. J., 2018, 24, 12269–12273 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) A. A. Almasalma and E. Mejía, Allylic C–H alkynylation via copper-photocatalyzed cross-dehydrogenative coupling, Synthesis, 2020, 529–536 CAS.
- H. Mo and W. Bao, Efficient palladium-catalyzed oxidative indolation of allylic compounds with DDQ via sp3 C-H bond activation and carbon-carbon bond formation under mild conditions, Adv. Synth. Catal., 2009, 351, 2845–2849 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Yu, L. Jiao, J. Wang, H. Wang, C. Yu, E. Hao and N. Boens, Bu4NI/tBuOOH catalyzed, α-regioselective cross-dehydrogenative coupling of BODIPY with allylic alkenes and ethers, Chem. Commun., 2017, 53, 581–584 RSC.
- A. Lerchen, T. Knecht, M. Koy, J. B. Ernst, K. Bergander, C. G. Daniliuc and F. Glorius, Non-directed cross-dehydrogenative (hetero)arylation of allylic C(sp3)−H bonds enabled by C−H activation, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2018, 57, 15248–15252 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) G.-W. Wang, A.-X. Zhou, S.-X. Li and S.-D. Yang, Regio- and stereoselective allylic C–H arylation with electron-deficient arenes by 1,1′-bi-2-naphthol–palladium cooperation, Org. Lett., 2014, 16, 3118–3121 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) H. Jiang, W. Yang, H. Chen, J. Li and W. Wu, Palladium-catalyzed aerobic oxidative allylic C–H arylation of alkenes with polyfluorobenzenes, Chem. Commun., 2014, 50, 7202–7204 RSC.
- D. Cheng, L. Wu, H. Lv, X. Xu and J. Yan, CDC Reaction and subsequent cyclization for the synthesis of 2-hydroxy-3-alkyl-1,4-naphthoquinones and pyranonaphthoquinones, J. Org. Chem., 2017, 82, 1610–1617 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. Li and C.-J. Li, Catalytic allylic alkylation via the cross-dehydrogenative-coupling reaction between allylic sp3 C−H and methylenic sp3 C−H bonds, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2006, 128, 56–57 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. Cheng and W. Bao, Highly efficient metal-free cross-coupling by C-H activation between allylic and active methylenic compounds promoted by DDQ, Adv. Synth. Catal., 2008, 350, 1263–1266 CrossRef CAS.
- X.-F. Huang, M. Salman and Z.-Z. Huang, Copper-catalyzed dehydrogenative cross-coupling reaction between allylic C-H bonds and α-C-H bonds of ketones or aldehydes, Chem. – Eur. J., 2014, 20, 6618–6621 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. K. Chua, Z. Sofer and M. Pumera, Functionalization of hydrogenated graphene: transition-metal-catalyzed cross-coupling reactions of allylic C−H bonds, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2016, 55, 10751–10754 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Wu, J. Riedel and V. M. Dong, Transforming olefins into γ,δ-unsaturated nitriles through copper catalysis, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2017, 56, 11589–11593 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Lin, C.-X. Song, G.-X. Cai, W.-H. Wang and Z.-J. Shi, Intra/intermolecular direct allylic alkylation via Pd(II)-catalyzed allylic C−H activation, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2008, 130, 12901–12903 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. J. Young and M. C. White, Catalytic intermolecular allylic C—H alkylation, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2008, 130, 14090–14091 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
| This journal is © the Partner Organisations 2020 |