Substitution effects on the antiradical activity of hydralazine: a DFT analysis†
Abstract
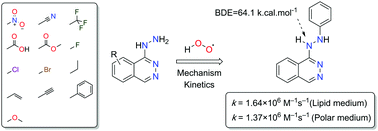
The present study aims to elucidate the substitution effects on the antiradical activity of the commercial vasodilator drug hydralazine (HZ). Thirteen typical substituents used in medicinal chemistry were screened in silico at all the possible positions of hydralazine. It was found that the presence of substituents at positions 4, 5, 6, and 7 had minor contributions to the bond dissociation enthalpy (BDE) values of the N9–H bond, whereas that for the ionization potential (IP) values changed depended on the nature of the substituents. Based on thermodynamic and kinetic calculations of the antiradical mechanisms as well as the reactions with the HOO˙ radical, we have identified compound 10-Ph-HZ as the best antioxidant in this family of compounds. The rate constants of the reaction of 10-Ph-HZ with HOO˙ in lipid and polar environments were found to be 1.64 × 106 and 1.37 × 106 M−1 s−1, respectively. These values are approximately 28 times higher than those of unsubstituted HZ, and the activities in the lipid and polar environments are 10.5 and 16.4 times higher, respectively, than those of Trolox. These results suggest that 10-Ph-HZ is a promising artificial antioxidant in both lipid and polar environments.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...