Themed collection Sodium-ion batteries – Topic Highlight

A comprehensive review of cathode materials for Na–air batteries
In recent years, rechargeable sodium–air batteries have attracted extensive attention and developed rapidly for electrochemical energy storage applications due to low costs, abundance of precursor resources, and high energy density.

Energy Adv., 2023,2, 465-502
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2YA00340F
Headway towards contemporary 2D MXene-based hybrid electrodes for alkali-ion batteries
This review provides a comparative study of contemporary MXene-based hybrid electrode materials in different alkali ion batteries.
Energy Adv., 2022,1, 950-979
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2YA00212D
Tailored nonwoven supported non-flammable quasi-solid electrolyte enables an ultra-stable sodium metal battery
We present an easily scalable approach to developing a nonwoven-supported PVDF-HFP polymer-based quasi-solid-state flexible non-flammable electrolyte, with a conductivity of 1.16 × 10−4 S cm−1 at RT with a transfer number of 0.68.

Energy Adv., 2024,3, 419-423
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3YA00435J
Anodic dissolution of aluminum in non-aqueous electrolyte solutions for sodium-ion batteries
The respective impact of the electrolyte and solvent, during anodic dissolution or passivation of aluminum was investigated in electrolyte solutions developed for sodium-ion batteries.

Energy Adv., 2024,3, 143-148
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3YA00233K
The role of specific and active surface areas in optimizing hard carbon irreversible capacity loss in sodium ion batteries
The hard carbon irreversible capacity loss in Na-ion cells can be reduced by decreasing the total surface area and the active surface area (defects).
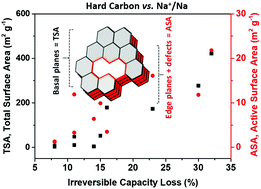
Energy Adv., 2022,1, 185-190
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2YA00004K
Fluorine-free “solvent-in-salt” sodium battery electrolytes: solvation structure and dynamics
Most “solvent-in-salt” (SIS) electrolytes are based on heavily fluorinated anions. Here we create fluorine-free SIS electrolytes with many promising basic characteristics for future sodium battery application.

Energy Adv., 2024,3, 564-573
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4YA00002A
Probing electrochemical strain generation in sodium chromium oxide (NaCrO2) cathode in Na-ion batteries during charge/discharge
Operando electrochemical strain generations in NaCrO2 cathode electrode during cycling are monitored using a digital image correlation.

Energy Adv., 2024,3, 601-608
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3YA00563A
Virtual screening of organic quinones as cathode materials for sodium-ion batteries
The discovery of quinone-based compounds that are commercially accessible and can function as cathode materials in sodium ion batteries.

Energy Adv., 2023,2, 820-828
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2YA00282E
Additive-free red phosphorus/Ti3C2Tx MXene nanocomposite anodes for metal–ion batteries
We report an environmentally benign, and additive-free red P/Ti3C2Tx MXene nanocomposites as high-performance anodes for alkali-metal–ion batteries (MIBs where M = Li+, Na+, K+).
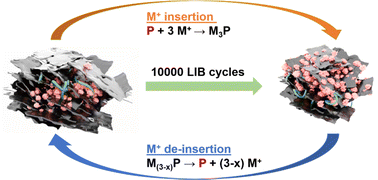
Energy Adv., 2022,1, 999-1008
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2YA00168C
High voltage and superior cyclability of indium hexacyanoferrate cathodes for aqueous Na-ion batteries enabled by superconcentrated NaClO4 electrolytes
Highly-concentrated aqueous NaClO4 electrolyte enables the high working voltage and superior cyclability of NaIn[Fe(CN)6]. Furthermore, a guideline for tuning the working potential of Prussian Blue Analogs is demonstrated.
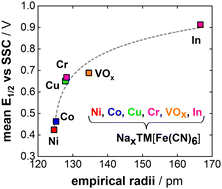
Energy Adv., 2022,1, 623-631
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2YA00130F
Facile surface engineering of bio-waste derived amorphous carbon with SnO2 nanowires to enhance the efficacy of Li/Na storage
A wet chemical dispersion followed by annealing synthesis strategy enables the development of a low-cost metal oxide-based composite anode material.

Energy Adv., 2022,1, 205-215
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1YA00021G
About this collection
Energy Advances features cutting-edge science at the forefront of energy technology with a particular focus on emerging materials and methods. This collection highlights some of our recent publications on sodium-ion batteries.
Our multidisciplinary journal publishes research across a broad scope of energy topics. To contribute your work, please visit our submission platform.