Themed collection Perovskites: from materials science to devices

Perovskites: from materials science to devices
An introduction to the Journal of Materials Chemistry C themed collection on perovskite materials.

J. Mater. Chem. C, 2024,12, 10244-10245
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4TC90109F
Optical and optoelectronic properties of 2D, quasi-2D and 3D metal halide perovskites
Metal halide perovskites have emerged as highly promising semiconductor materials owing to their versatility across a broad spectrum of optoelectronic applications. Through dimensional engineering one can tune their properties to facilitate their use in specific device applications.

J. Mater. Chem. C, 2025,13, 13620-13646
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4TC04864D
Unlocking the potential of perovskite-based nanomaterials for revolutionary smartphone-based sensor applications
The use of perovskite-based nanomaterials in smartphone sensors, which enhance accessibility and efficiency in health diagnostics, and their potential in the integration with wearable technology for improved health monitoring is explored.

J. Mater. Chem. C, 2024,12, 4544-4561
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3TC04505F
Interplay between connectivity and passivating agents in perovskite quantum dot networks
Different treatments (comprising polymeric encasement and different atmospheres) are applied to quantum dot solids in order to modify their defect landscape. The role of the latter in both, carrier recombination and stability, is unveiled.

J. Mater. Chem. C, 2024,12, 16683-16690
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4TC02362E
Femtosecond laser direct writing of CsPb(I/Br)3 quantum dot films for displays and holography
To expand the application of perovskite quantum dots (QDs) in next-generation displays and holography, it is quite significant to develop an efficient and advanced QD patterning technology.

J. Mater. Chem. C, 2025,13, 12707-12713
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5TC01283J
High stability of robust anti-thermal-quenching lead-free double perovskite crystals for optoelectronic devices and high-performance fibers
Sb3+-doped Cs2NaHoCl6 perovskite crystals were synthesized through an efficient and energy-saving method. The flexible luminescent fibers prepared from Sb3+-doped Cs2NaHoCl6 exhibit excellent luminescent stability in high-temperature environments.

J. Mater. Chem. C, 2025,13, 456-464
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4TC03773A
MXenes as a hole transport interfacial layer for efficient and air-stable quasi-2D perovskite solar cells
This work demonstrates the utilization of MXenes as a hole transport interfacial layer for performance and stability improvement in regular device (n–i–p) structures.

J. Mater. Chem. C, 2024,12, 8357-8367
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4TC00466C
Mixed ionic-electronic conduction in Ruddlesden–Popper and Dion–Jacobson layered hybrid perovskites with aromatic organic spacers
Mixed ionic-electronic conduction is revealed in Dion–Jacobson (DJ) and Ruddlesden–Popper phases based on aromatic spacer cations, with higher activation energies for ion migration and thermal stability for DJ systems, relevant to their application.

J. Mater. Chem. C, 2024,12, 7909-7915
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4TC01010H
Anti-solvent engineering enables efficient ambient-processed halide perovskite solar cells
Ambient solution-processed halide perovskite thin films are susceptible to oxygen and moisture. Composition and morphology control of the films via anti-solvents treatment, i.e., DCB, EtOH, and CB affect their crystallization and solar cell performance.

J. Mater. Chem. C, 2024,12, 7562-7571
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4TC01305K
Chemically driven dimensionality modulation of hybrid tin(II) halide perovskite microcrystals
Synthesis conditions determine the dimensionality of TEA–Sn perovskites from low emissive 2D structures to highly luminescent 0D structures. Br-derivatives can be tuned to form 0D and 2D structures, 0D Cl and 2D I-based cannot be dimensional tuned.

J. Mater. Chem. C, 2024,12, 7605-7614
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4TC00623B
Reactive spin coating based on real-time in situ feedback for improved control of perovskite thin film fabrication
This work presents a novel perovskite thin film fabrication approach based on an optical in situ spectroscopy setup and a live closed-loop feedback system to improve the reproducibility of the layer properties independent of external parameters.

J. Mater. Chem. C, 2024,12, 6415-6422
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3TC04361D
Perovskite quantum dots embedded paper photodetectors with high flexibility and self-powered operation
Hybrid MAPbBr3 quantum dot cellulose papers are fabricated via a one-step, oleic acid/oleylamine-free vacuum filtration method, and the corresponding photodetectors demonstrate self-powered capability, high flexibility, and exceptional stability.

J. Mater. Chem. C, 2024,12, 5784-5792
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4TC00508B
Ionic liquid-regulated PbI2 layers and defect passivation for efficient perovskite solar cells
In this work, formamidine acetate (FAAc) was introduced in the two-step method to regulate perovskite crystallization and passivate defects, which resulted in achieving the PCE of device exceeding 24% with notable improvements in stability.

J. Mater. Chem. C, 2024,12, 5175-5183
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4TC00500G
Thermal degradation in methylammonium–formamidinium–guanidinium lead iodide perovskites
Thermal degradation experiments in GAxFAyMA1−x−yPbI3 perovskites show that mixed compositions are generally more stable, but not always. Large GA+ cations may decrease the stability and even change the order of the degradation kinetics.

J. Mater. Chem. C, 2024,12, 5138-5149
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4TC00395K
Thermodynamic study of CsCaCl3 using neutron diffraction
The structural behaviour of CsCaCl3 has been investigated using neutron diffraction as a function of pressure and temperature.
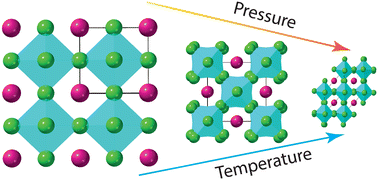
J. Mater. Chem. C, 2024,12, 4800-4808
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4TC00592A
Metal co-doped cesium manganese chlorine nanocrystals with high efficiency and tunable red emission
Metal co-doped cesium manganese halide nanocrystals are synthesized to enhance the red emission depending on the transitional role of Tm3+ ions, and realize tunable red emission from 660 nm to 628 nm by controlling the Pb doping contents.

J. Mater. Chem. C, 2024,12, 3573-3578
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3TC04539K
Ionic liquid-assisted growth of high-quality methylammonium lead bromide single crystals for photodetection applications
The addition of a 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium bromide (BMIB) ionic liquid to the MAPbBr3 precursor solution shows a significant influence on the crystal optoelectronic properties and photodetection performance.

J. Mater. Chem. C, 2024,12, 2953-2960
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3TC04511K
All-inorganic copper-halide perovskites for large-Stokes shift and ten-nanosecond-emission scintillators
Demonstration of how rational design affects self-trapped emission characteristics and scintillation properties in mechanochemically synthesised caesium copper halide perovskites.

J. Mater. Chem. C, 2024,12, 2398-2409
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3TC03977C
About this collection
A perovskite name is applied to the class of compounds which have the same type of crystal structure as CaTiO3 discovered in Ural mountains in 1839 by Gustav Rose. The ABX3 perovskite structure can accommodate a wide variety of different cations and anions. Depending on the chemical composition it can exhibit extremely different properties such like colossal magnetoresistance, ferroelectricity, superconductivity, light absorption, charge ordering, spin dependent transport, high thermopower, to name a few. Thanks to that, a variety of different devices can be constructed using this crystal structure.
This Journal of Materials Chemistry C themed collection brings together manuscripts related to all aspects of the cutting-edge innovations in the development of organic, inorganic and/or hybrid perovskite materials and devices with the focus on potential applications in memories, solar cells, sensors, catalyst electrodes and superconducting ceramic materials.
Guest Editors:
Malgorzata Kot
(Brandenburg University of Technology, Germany)
Chittaranjan Das
(University of Stuttgart, Germany)
Clara P. Aranda Alonso
(Universidad Pablo de Olavide, Spain)
Daniel Prochowicz
(Polish Academy of Sciences, Poland)