Themed collection Injectable Hydrogels

An introduction to injectable hydrogels
Julieta Paez and Khoon Lim introduce the Journal of Materials Chemistry B and Biomaterials Science themed collection on injectable hydrogels.

J. Mater. Chem. B, 2024,12, 5571-5572
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4TB90085E
Injectable organo-hydrogels influenced by click chemistry as a paramount stratagem in the conveyor belt of pharmaceutical revolution
Injectable hydrogels emerging as a significant breakthrough in the myriad of biomedical applications and paving a path towards clinical advancements.

J. Mater. Chem. B, 2023,11, 10761-10777
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3TB01674A
Injectable hydrogels as emerging drug-delivery platforms for tumor therapy
This review summarizes composition and preparation methodologies of injectable hydrogels and highlights the delivery mechanisms of drugs for tumor therapy, along with discussion on the optimal therapeutic efficiency of drugs and provides perspective on challenges and solutions in applications.

Biomater. Sci., 2024,12, 1151-1170
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3BM01840G
Recent advances in fabricating injectable hydrogels via tunable molecular interactions for bio-applications
Fabricating injectable hydrogels via tunable molecular interactions for bio-applications.

J. Mater. Chem. B, 2024,12, 332-349
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3TB02105J
Engineered cyclodextrin-based supramolecular hydrogels for biomedical applications
This review makes a comprehensive summary on the cross-linking mechanism, optimization of mechanical properties, drug loading and release modalities, and recent biological applications of CD-based supramolecular hydrogels.

J. Mater. Chem. B, 2024,12, 39-63
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3TB02101G
Injectable smart stimuli-responsive hydrogels: pioneering advancements in biomedical applications
The synergistic integration of natural and synthetic materials, capitalizing on their respective advantages and mitigating their weaknesses, represents a rational strategy for the development of an ideal injectable smart stimuli-responsive hydrogel.

Biomater. Sci., 2024,12, 8-56
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3BM01352A
Cell or cell derivative-laden hydrogels for myocardial infarction therapy: from the perspective of cell types
Injectable hydrogels and cell-based myocardial infarction (MI) therapy mutually enhance each other. This review focuses on recent studies using hydrogel to deliver cell or cell-derived preparations for MI treatment.

J. Mater. Chem. B, 2023,11, 9867-9888
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3TB01411H
Advances in antimicrobial hydrogels for dental tissue engineering: regenerative strategies for endodontics and periodontics
Multifunctional hydrogels play a pivotal role against infections, inflammation, and oxidative stress, especially for endodontics and periodontics treatment.
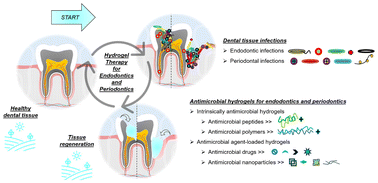
Biomater. Sci., 2023,11, 6711-6747
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3BM00719G
Injectable hydrogels for the delivery of nanomaterials for cancer combinatorial photothermal therapy
Injectable hydrogels intended for cancer combinatorial-photothermal therapy bring forward the possibility of attaining multifunctional systems for an improved and selective treatment for this disease.

Biomater. Sci., 2023,11, 6082-6108
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3BM00845B
Multivalent 2D- and 3D-nanogels as carbohydrate-lectin binders
The development of synthetic glycoarchitectures for targeted bacterial adhesion represents a promising strategy in anti-adhesion therapy.

Biomater. Sci., 2025,13, 4400-4411
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5BM00286A
Photocrosslinkable microgels derived from human platelet lysates: injectable biomaterials for cardiac cell culture
Human-derived methacryloyl platelet lysates (PLMA) have been employed for constructing full human-based 3D cell culture matrices and demonstrated potential for xeno-free applications.

Biomater. Sci., 2024,12, 3112-3123
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3BM01933K
An injectable hydrogel dressing for controlled release of hydrogen sulfide pleiotropically mediates the wound microenvironment
In this work, a hydrogel dressing for controlled release of hydrogen sulfide is developed for the repair of scalded wounds. It exhibits a responsive release of H2S based on ROS concentration, allowing precise modulation of the wound microenvironment.

J. Mater. Chem. B, 2024,12, 5377-5390
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4TB00411F
Tissue-specific gelatin bioink as a rheology modifier for high printability and adjustable tissue properties
This study introduces gelatinized dECM, a tissue-specific rheological modifier, enabling high-resolution printing of flexible tissue constructs with enhanced resilience.
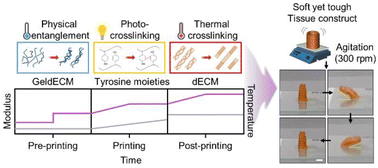
Biomater. Sci., 2024,12, 2599-2613
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3BM02111D
Engineering sulfated polysaccharides and silk fibroin based injectable IPN hydrogels with stiffening and growth factor presentation abilities for cartilage tissue engineering
In this study, we combined the β-sheet mediated self-stiffening ability of silk with growth factor presenting ability of sulphated carboxymethyl cellulose in an injectable interpenetrating network hydrogel for repair of articular cartilage defects.

Biomater. Sci., 2024,12, 2067-2085
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3BM01466E
Injectable polyoxazoline grafted hyaluronic acid thermoresponsive hydrogels for biomedical applications
Injectable thermosensitive hydrogels based on hyaluronic acid (HA) grafted with lower critical solution temperature (LCST) polyoxazoline (copolymers of poly(isopropyl-co-butyl oxazoline)) or P(iPrOx-co-BuOx) have been elaborated with tunable solution/gel temperature transitions and gel state elastic modulus.

J. Mater. Chem. B, 2024,12, 2807-2817
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3TB02108D
Facilely printed silk fibroin hydrogel microparticles as injectable long-lasting fillers
A regenerated silk fibroin hydrogel is facilely printed by a screen to obtain injectable microparticles. The microparticles possess desirable biocompatibility and lasting filling effects and have great potential for facial rejuvenation.

Biomater. Sci., 2024,12, 375-386
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3BM01488F
Photothermal synergistic nitric oxide controlled release injectable self-healing adhesive hydrogel for biofilm eradication and wound healing
A novel injectable self-healing adhesive hydrogel with specific bacteria capture capability and inherent contact antimicrobial activity for mild photothermal therapy and NO controlled release to synergically eliminate biofilm infections and promote wound healing.

J. Mater. Chem. B, 2024,12, 158-175
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3TB02040A
A thermosensitive hydrogel formulation of phage and colistin combination for the management of multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii wound infections
Unlocking the power of synergy: PAS-loaded thermosensitive hydrogel for enhanced skin wound infection management.

Biomater. Sci., 2024,12, 151-163
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3BM01383A
Antibacterial, antioxidant and injectable hydrogels constructed using CuS and curcumin co-loaded micelles for NIR-enhanced infected wound healing
A CuS–curcumin hybrid hydrogel with good biocompatibility, NIR-enhanced antibacterial, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and angiogenesis properties has been developed for infected wound healing.

J. Mater. Chem. B, 2023,11, 11319-11334
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3TB02278A
Combining biomimetic collagen/hyaluronan hydrogels with discogenic growth factors promotes mesenchymal stroma cell differentiation into Nucleus Pulposus like cells
The combination of discogenic factors with biomimetic collagen/hyaluronan hydrogels is promising for disc regeneration; a high content of hyaluronan is responsible for the BM-MSC differentiation into NP like cells.
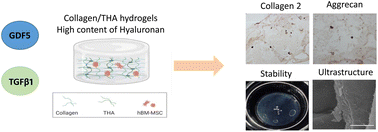
Biomater. Sci., 2023,11, 7768-7783
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3BM01025B
Injectable spontaneously formed asymmetric adhesive hydrogel with controllable removal for wound healing
The mechanism and characteristics of injectable asymmetric hydrogel for large-scale skin trauma repair.

J. Mater. Chem. B, 2023,11, 10845-10858
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3TB02014B
A photocrosslinked methacrylated carboxymethyl chitosan/oxidized locust bean gum double network hydrogel for cartilage repair
Studies in vivo demonstrated that the MCOAC hydrogel exhibited superior performance in promoting cartilage tissue growth in articular cartilage defects. The MCOAC hydrogel is a promising cartilage repair hydrogel with potential for clinical use.

J. Mater. Chem. B, 2023,11, 10464-10481
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3TB01701J
A nanozyme-reinforced injectable photodynamic hydrogel for combating biofilm infection
Here, an oxygen self-supplying nanozyme-based injectable hydrogel is constructed. Both in vitro and in vivo results indicate that the MTC gel has excellent antibiofilm ability with no side effects on normal tissues.

J. Mater. Chem. B, 2023,11, 10108-10120
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3TB01688A
Etamsylate loaded oxidized Konjac glucomannan-ε-polylysine injectable hydrogels for rapid hemostasis and wound healing
Konjac glucomannan was oxidized using NaIO4 and subsequently reacted with ε-polylysine to form a drug-loaded adhesive hydrogel. The hydrogel was then utilized as a hemostatic dressing.

J. Mater. Chem. B, 2023,11, 9950-9960
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3TB01904G
Osteoimmunity-regulating nanosilicate-reinforced hydrogels for enhancing osseointegration
Schematic illustration of osteoimmunity-regulating injectable SA/MMT/HM hydrogel composites for enhanced bone regeneration via M2 macrophage polarization.

J. Mater. Chem. B, 2023,11, 9933-9949
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3TB01509B
An advanced biphasic porous and injectable scaffold displays a fine balance between mechanical strength and remodeling capabilities essential for cartilage regeneration
An important challenge in tissue engineering is the regeneration of functional articular cartilage (AC).

Biomater. Sci., 2023,11, 6801-6822
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3BM00703K
Biomechanical characterization of a fibrinogen–blood hydrogel for human dental pulp regeneration
Biomechanical characterization of a fibrinogen–blood hydrogel for human dental pulp regeneration.

Biomater. Sci., 2023,11, 6919-6930
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3BM00515A
Prodrug-loaded semiconducting polymer hydrogels for deep-tissue sono-immunotherapy of orthotopic glioblastoma
A novel sono-activatable prodrug hydrogel was developed to achieve deep-tissue sono-immunotherapy of orthotopic glioblastoma.

Biomater. Sci., 2023,11, 6823-6833
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3BM00585B
A biodegradable injectable fluorescent polyurethane-oxidized dextran hydrogel for non-invasive monitoring
An injectable fluorescent hydrogel was successfully prepared by fluorescent polyurethane emulsion cross-linked with oxidized dextran for non-invasive monitoring.

J. Mater. Chem. B, 2023,11, 8506-8518
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3TB01488F
3D printable, injectable amyloid-based composite hydrogel of bovine serum albumin and aloe vera for rapid diabetic wound healing
Protein-based biomaterials, particularly amyloids, have sparked considerable scientific interest in recent years due to their exceptional mechanical strength, excellent biocompatibility and bioactivity.

J. Mater. Chem. B, 2023,11, 8142-8158
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3TB01151H
Injectable, antibacterial, and oxygen-releasing chitosan-based hydrogel for multimodal healing of bacteria-infected wounds
This study introduces a novel antibacterial multifunctional hydrogel with synergistic chemodynamic and photothermal features for wound healing applications.

J. Mater. Chem. B, 2023,11, 8056-8068
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3TB01278F
Engineering a platelet-rich plasma-based multifunctional injectable hydrogel with photothermal, antibacterial, and antioxidant properties for skin regeneration
This study presents a novel photothermally active hydrogel that contains platelet-rich plasma for infected wound healing. The hydrogel showed antibacterial, antioxidant, and hemostatic properties, as well as sustained growth factor release.
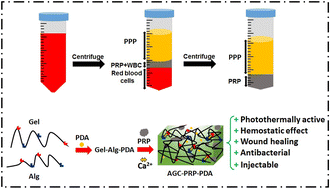
Biomater. Sci., 2023,11, 5872-5892
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3BM00881A
An injectable supramolecular hydrogel as a self-drug-delivery system for local chemoimmunotherapy against melanoma
A unique self-drug-delivery approach providing chemoimmunotherapy in combating deadly melanoma has been developed from a Zn(II)-coordination complex-based hydrogel; M1-macrophages for activating T cells triggering apoptosis was confirmed in in vivo.

Biomater. Sci., 2023,11, 5618-5633
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3BM00758H
About this collection
Injectable hydrogels have emerged as intelligent and versatile materials that have been proven to possess huge potential for many biomedical applications including drug delivery, tissue engineering, and regenerative medicine. Hydrogels are a class of polymers with highly hydrated 3D networks that have microenvironmental properties such as oxygen/nutrient permeability that are similar to the native extracellular matrix. In addition to possessing the typical advantages of conventional hydrogels, injectable hydrogels offer an extra unique feature, which enables minimally invasive injectability and durability for irregularly shaped sites. As such, there has been a growing interest of using injectable hydrogels as scaffolds/carriers for therapeutic agents, including but not limited to drugs, cells, proteins, and bioactive molecules, targeted to treat chronic diseases including cancer, but also to facilitate the repair and regeneration of damaged organs/tissues.
This themed collection across Journal of Materials Chemistry B and Biomaterials Science, Guest Edited by Dr Khoon Lim (University of Sydney, Australia) and Dr Julieta Paez (University of Twente, The Netherlands), aims at providing a platform for recent developments in this rapidly evolving field of injectable hydrogels and aims to inspire future research in this area.