Themed collection Functional Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications

Functional nanoparticles for biomedical applications
Editorial for the themed issue “Functional nanoparticles for biomedical applications”.
Nanoscale, 2013,5, 11338-11338
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3NR90095A
Tracking stem cells in tissue-engineered organs using magnetic nanoparticles
We review the use of magnetic nanoparticles for stem cell tracking by MRI and propose a novel strategy with active targeting of nanoparticles towards specific cell populations.

Nanoscale, 2013,5, 11362-11373
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3NR03861K
Upconverting and NIR emitting rare earth based nanostructures for NIR-bioimaging
The high potential of up-converting and near-infrared emitting lanthanide (Ln3+)-based nanomaterials such as Y2O3:Ln3+ or Gd2O3:Ln3+ for bioimaging is demonstrated.
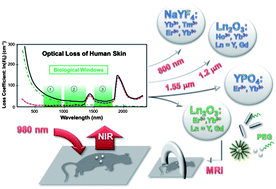
Nanoscale, 2013,5, 11339-11361
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3NR02286B
Programmed assembly of polymer–DNA conjugate nanoparticles with optical readout and sequence-specific activation of biorecognition
Display of a biorecognition signal may be controlled by addition of DNA in a sequence specific manner.
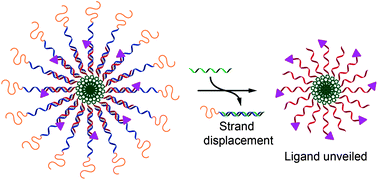
Nanoscale, 2014,6, 2368-2374
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3NR04952C
Manganese-impregnated mesoporous silica nanoparticles for signal enhancement in MRI cell labelling studies
Mesoporous silica nanoparticles (MSNs) are labeled with manganese to provide high relaxivities and strong positive MRI contrast enhancement in cell tracking studies.
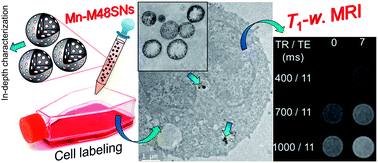
Nanoscale, 2013,5, 11499-11511
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3NR02969G
Feasibility and constraints of particle targeting using the antigen–antibody interaction
Silica nanoparticles with covalently coupled antibody M75 specifically bind to the PG domain of carbonic anhydrase IX under a variety of flow conditions.
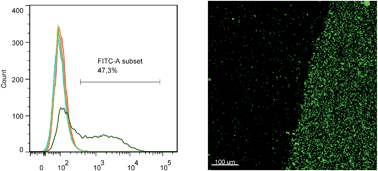
Nanoscale, 2013,5, 11490-11498
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3NR04340A
Optimized multimodal nanoplatforms for targeting αvβ3 integrins
This work describes the design and optimization of multimodal MRI and fluorescent nanoplatforms targeting integrins overexpressed by tumor cells.
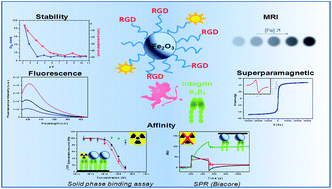
Nanoscale, 2013,5, 11478-11489
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3NR03763K
Highly stable monodisperse PEGylated iron oxide nanoparticle aqueous suspensions: a nontoxic tracer for homogeneous magnetic bioassays
25 nm Brownian iron oxide nanoparticles were PEGylated and labeled with Herceptin via mild conjugation chemistry.
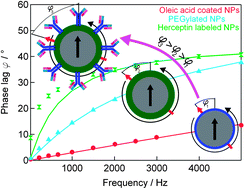
Nanoscale, 2013,5, 11447-11455
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3NR02197A
Poly(acrylic acid)-block-poly(vinyl alcohol) anchored maghemite nanoparticles designed for multi-stimuli triggered drug release
Original core/corona nanoparticles were assessed as drug delivery systems sensitive to pH, ionic strength and/or temperature variations.
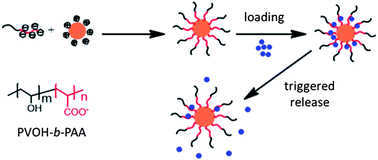
Nanoscale, 2013,5, 11464-11477
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3NR02861E
Functionalization of PEGylated Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles with tetraphosphonate cavitand for biomedical application
Tetraphosphonate cavitand and PEG were anchored onto magnetic nanoparticles using phosphonic linkers. Obtained multifunctional nanoparticles combined biocompatibility with good magnetic and complexation properties.
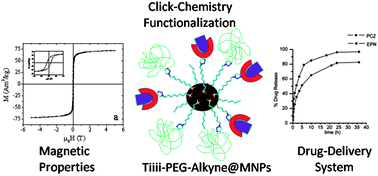
Nanoscale, 2013,5, 11438-11446
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3NR02188B
Direct intercalation of cisplatin into zirconium phosphate nanoplatelets for potential cancer nanotherapy
Cisplatin was intercalated into zirconium phosphate nanoparticles and tested in vitro for cytotoxicity in human breast cancer cells showing anti-cancer activity.
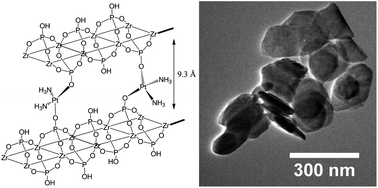
Nanoscale, 2013,5, 11456-11463
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3NR02206D
Different cell responses induced by exposure to maghemite nanoparticles
Cell responses to maghemite nanoparticles significantly vary depending on the physicochemical properties resulting from their coating and the cell type.
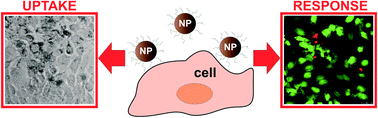
Nanoscale, 2013,5, 11428-11437
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3NR02148C
Modulation of the pharmacokinetics of zinc oxide nanoparticles and their fates in vivo
ZnO (−) NPs are better absorbed by the systemic circulation in both particulate and zinc ionic forms, localize in tissue primarily as Zn2+ ions, and then are eliminated from the body in the same manner as zinc ions, regardless of particle size or gender.
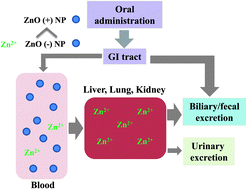
Nanoscale, 2013,5, 11416-11427
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3NR02140H
Cytotoxicity and DNA cleavage with core–shell nanocomposites functionalized by a KH domain DNA binding peptide
Photoexcitation DNA targeted Fe3O4@TiO2 nanocomposites using hnRNPK protein as a targeting moiety resulted in production of ROS close to the DNA which initiated significant DNA cleavage and apoptosis.
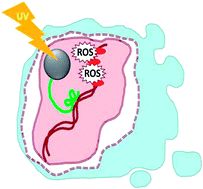
Nanoscale, 2013,5, 11394-11399
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3NR02203J
Paramagnetic nanoparticles to track and quantify in vivo immune human therapeutic cells
Hybrid multimodal core–shell FITC–gadolinium oxide nanoparticles to sensitively detect and quantify in vivo immune human therapeutic cells with MRI via bright spots.
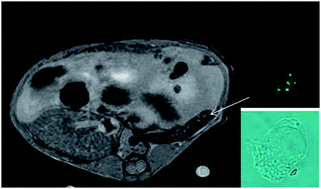
Nanoscale, 2013,5, 11409-11415
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3NR34240A
Continuously manufactured magnetic polymersomes – a versatile tool (not only) for targeted cancer therapy
Micromixer technology enables continuous manufacturing of multifunctional magnetic and drug-loaded polymersomes for cancer theranostics.
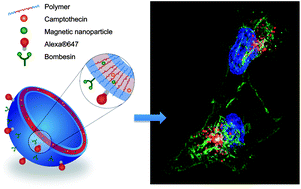
Nanoscale, 2013,5, 11385-11393
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3NR02190D
Biodistribution and pharmacokinetics of uniform magnetite nanoparticles chemically modified with polyethylene glycol
Magnetic and non-magnetic methods for determination of the metabolic routes for iron oxide nanoparticles chemically modified with DMSA and PEG in rats.
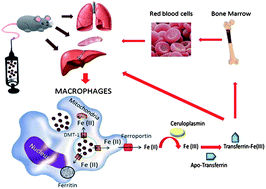
Nanoscale, 2013,5, 11400-11408
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3NR01412F
Cell-derived vesicles as a bioplatform for the encapsulation of theranostic nanomaterials
Cell-released vesicles are engineered to camouflage iron oxide nanoparticles, nanocubes, quantum dots, gold-based nanoparticles and gold-iron oxide nanodimers, either single or multiple components. These hybrid vesicles can be monitored by MRI and/or fluorescence imaging methods, while acting as efficient nano-heaters.

Nanoscale, 2013,5, 11374-11384
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3NR01541F
About this collection
The themed issue on Functional Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications covers nanoparticle research with many potential applications, especially in biomedicine, by exploiting the fundamental physical properties of materials at the nanoscale. Guest edited by Nguyen T. K. Thanh.