Direct intercalation of cisplatin into zirconium phosphate nanoplatelets for potential cancer nanotherapy†
Abstract
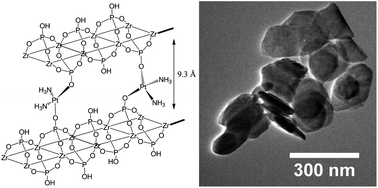
We report the use of zirconium phosphate (ZrP) nanoplatelets for the encapsulation of the anticancer drug cisplatin and its delivery to tumor cells. Cisplatin was intercalated into ZrP by direct ion exchange and was tested in vitro for cytotoxicity in the human breast cancer (MCF-7) cell line. The structural characterization of the intercalated cisplatin in ZrP suggests that during the intercalation process, the chloride ligands of the cisplatin complex were substituted by phosphate groups within the layers. Consequently, a new phosphate phase with the platinum complex directly bound to ZrP (cisPt@ZrP) is produced with an interlayer distance of 9.3 Å. The in vitro release profile of the intercalated drug upon a pH stimulus shows that at low pH under lysosomal conditions the platinum complex is released with simultaneous hydrolysis of the zirconium phosphate material, while at higher pH the complex is not released. Experiments with the MCF-7 cell line show that cisPt@ZrP reduced the cell viability up to 40%. The cisPt@ZrP intercalation product is envisioned as a future nanotherapy agent against cancer. Taking advantage of the shape and sizes of the ZrP particles and controlled release of the drug at low pH, it is intended to exploit the enhanced permeability and retention effect of tumors, as well as their intrinsic acidity, for the destruction of malignant cells.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Functional Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...