Themed collection The Chemistry of Symbiotic Interactions

Mediators of mutualistic microbe–microbe interactions
This viewpoint summarizes recent advances in understanding the role of natural products as regulators of mutualistic microbial interactions.
Nat. Prod. Rep., 2018,35, 303-308
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7NP00035A
Influence of microbial symbionts on insect pheromones
Symbiotic microorganisms can influence the fitness of their insect hosts by modulating pheromone production and perception.
Nat. Prod. Rep., 2018,35, 386-397
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7NP00068E
Ecology and evolution of metabolic cross-feeding interactions in bacteria
The causes and consequences of bacterial metabolic cross-feeding mutualisms.
Nat. Prod. Rep., 2018,35, 455-488
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8NP00009C
Microbial small molecules – weapons of plant subversion
Microbial small molecules subvert plant immunity, and alter plant physiology and development.
Nat. Prod. Rep., 2018,35, 410-433
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7NP00062F
Modulation of plant chemistry by beneficial root microbiota
Beneficial root microbiota modulate plant chemistry and represent an untapped potential to discover new pathways involved in the biosynthesis of high value natural plant products.
Nat. Prod. Rep., 2018,35, 398-409
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7NP00057J
Detoxifying symbiosis: microbe-mediated detoxification of phytotoxins and pesticides in insects
Symbiotic microorganisms degrade natural and artificial toxic compounds, and confer toxin resistance on insect hosts.
Nat. Prod. Rep., 2018,35, 434-454
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7NP00051K
Parallel lives of symbionts and hosts: chemical mutualism in marine animals
Symbiotic microbes interact with animals, often by producing natural products (specialized metabolites; secondary metabolites) that exert a biological role.
Nat. Prod. Rep., 2018,35, 357-378
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7NP00053G
Role of antimicrobial peptides in controlling symbiotic bacterial populations
The review describes the role of antimicrobial peptides in the symbiotic interactions of plants, animals and protists with bacteria.
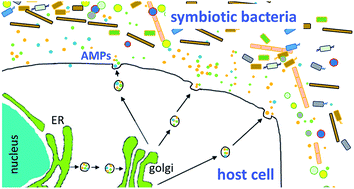
Nat. Prod. Rep., 2018,35, 336-356
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7NP00056A
Chemical language and warfare of bacterial natural products in bacteria–nematode–insect interactions
This review provides a chemical biology perspective on the different confirmed and predicted ecological roles of natural products from Photorhabdus and Xenorhabdus, two genera of entomopathogenic bacteria living in symbiosis with Heterorhabditis and Steinernema nematodes.
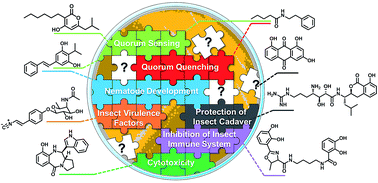
Nat. Prod. Rep., 2018,35, 309-335
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7NP00054E
About this collection
Natural Product Reports is delighted to present a themed issue dedicated to the role natural product chemistry plays in symbiotic interactions, Guest Edited by Professors Martin Kaltenpoth, Mohamed Donia and Martin Heil.
Symbiotic associations are ubiquitous in nature and represent major driving forces of evolutionary innovation. While the theoretical framework and fitness consequences of symbioses for the interacting partners have been studied extensively across taxonomic boundaries, knowledge on the identity and role of chemical signals has long been confined to a few particularly well-studied associations. However, research in the past decades has uncovered the role of primary and secondary metabolites in mediating a plethora of symbiotic interactions between animals, plants, fungi, and bacteria. The aim of the special issue on the is to compile reviews that summarize and synthesize recent findings on chemical compounds governing the establishment, maintenance, and defence of symbioses, the communication between the interacting partners and with their environment, as well as the chemistry underlying manipulation and conflict.
By covering a broad diversity of taxa (bacteria, fungi, plants, animals) and environments, the topics aim to derive general principles that shed light on the chemistry of symbiosis in an ecological and evolutionary context.