Themed collection Engineering Nanoparticles for Sensing and Biomedical Applications

Engineering nanoparticles for sensing and biomedical applications: a themed collection
Guest editors Niveen M. Khashab, Jean-Olivier Durand and Jeffrey I. Zink introduce this themed collection of papers.

Mol. Syst. Des. Eng., 2017,2, 347-348
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7ME90015E
Targeted drug delivery using iRGD peptide for solid cancer treatment
iRGD-mediated nanoparticle transcytosis in a solid tumor.
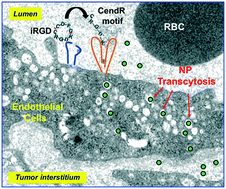
Mol. Syst. Des. Eng., 2017,2, 370-379
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7ME00050B
Advancements on the molecular design of nanoantibiotics: current level of development and future challenges
Numerous antimicrobial drugs have been developed and commercialized to kill and inhibit the growth of pathogenic microbes.
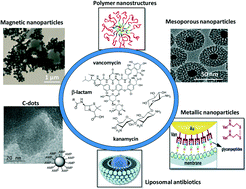
Mol. Syst. Des. Eng., 2017,2, 349-369
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7ME00048K
Degradable gold core–mesoporous organosilica shell nanoparticles for two-photon imaging and gemcitabine monophosphate delivery
The synthesis of degradable gold core–mesoporous organosilica shell nanoparticles is described.
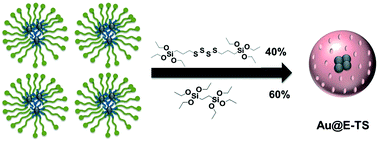
Mol. Syst. Des. Eng., 2017,2, 380-383
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7ME00058H
Monocore vs. multicore magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: uptake by glioblastoma cells and efficiency for magnetic hyperthermia
PEGylated magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (IONPs) were synthesised with the aim to provide proof of concept results of remote cancer cell killing by magnetic fluid hyperthermia.
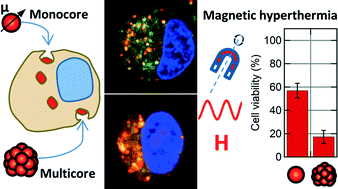
Mol. Syst. Des. Eng., 2017,2, 629-639
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7ME00061H
Modulating the catalytic activity of enzyme-like nanoparticles through their surface functionalization
Surface functional groups of nanozyme ligands dictate their kinetic behavior.
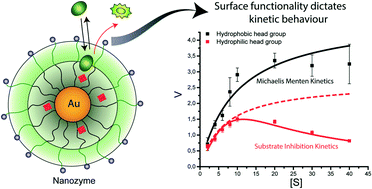
Mol. Syst. Des. Eng., 2017,2, 624-628
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7ME00055C
Design of SERS nanotags for multiplexed lateral flow immunoassays
Surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) can be used to enhance the sensitivity of lateral flow immunoassays.
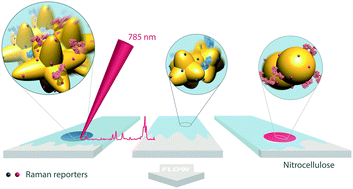
Mol. Syst. Des. Eng., 2017,2, 401-409
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7ME00052A
Influence of mesopore size and peptide aggregation on the adsorption and release of a model antimicrobial peptide onto/from mesoporous silica nanoparticles in vitro
The interplay between mesopore size and degree of peptide aggregation controls both calcitonin adsorption onto and release from mesoporous silica nanoparticles.

Mol. Syst. Des. Eng., 2017,2, 393-400
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7ME00059F
In vitro delivery of calcium ions by nanogated mesoporous silica nanoparticles to induce cancer cellular apoptosis
Calcium ions released by mesoporous silica nanoparticles taken up by cancer cells cause apoptosis.
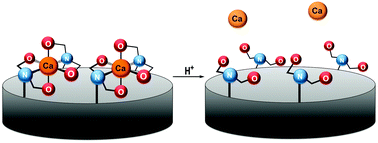
Mol. Syst. Des. Eng., 2017,2, 384-392
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7ME00046D
About this collection
From MSDE
Guest Edited by Professors Niveen M. Khashab (KAUST), Jean-Olivier Durand (Université de Montpellier) and Jeffrey I. Zink (UCLA), this collection showcases some of the major advances in engineering organic and inorganic nanosystems to develop superior biomedical materials.
Smart nanomaterials have taken the research and industry communities by storm, and the field of biomedical applications is no exception. The control of the nanoscale and physicochemical properties of particles, as well as the ability to visualize them via electron microscopy techniques and in cells, has ushered in numerous discoveries. In particular, stimuli-responsive or smart nanomaterials have unique advantages for bioimaging, sensing, and therapeutic applications.
The scale of nanomaterials can be precisely engineered towards specific applications. Stimuli-responsive nanoparticles have involved near-infrared light, magnetic, pH, enzymatic, and cascade actuations which have produced nano-platforms with higher selectivity and efficiency for their biomedical aim than previous nanomaterials.