Themed collection VI International Conference on Polyphenols and Health

Interactions of flavan-3-ols and procyanidins with membranes: mechanisms and the physiological relevance
Procyanidin–lipid interactions decrease the potentiality of deleterious agents to incorporate in the membrane and disrupt membrane organization and functions.
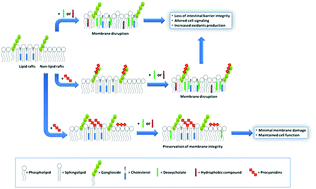
Food Funct., 2015,6, 32-40
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4FO00647J
The pleiotropic flavonoid quercetin: from its metabolism to the inhibition of protein kinases in chronic lymphocytic leukemia
Quercetin inhibits the key protein kinases active in chronic lymphocytic leukemia, ameliorating anticancer therapy.
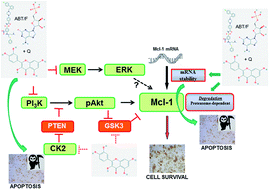
Food Funct., 2014,5, 2393-2401
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4FO00413B
A shortcut to wide-ranging biological actions of dietary polyphenols: modulation of the nitrate–nitrite–nitric oxide pathway in the gut
Dietary polyphenols are complex, natural compounds with recognized health benefits.
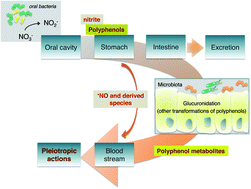
Food Funct., 2014,5, 1646-1652
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4FO00124A
Modulation of nitric oxide by flavonoids
One of the main mechanisms by which dietary flavonoids are thought to influence cardiovascular disease is via protection of the bioactivity of the endothelium-derived nitric oxide (NO).
Food Funct., 2014,5, 1653-1668
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4FO00144C
Coffee: biochemistry and potential impact on health
This article reviews the diversity of compounds found in coffee beans, the effect of roasting and the potential impact of coffee beverage on health.

Food Funct., 2014,5, 1695-1717
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4FO00042K
(−)-Epicatechin prevents alterations in the metabolism of superoxide anion and nitric oxide in the hearts of L-NAME-treated rats
The aim of this work was to evaluate the effects of (−)-epicatechin administration in the heart of a rat model with reduced NO production that follows a short-term treatment with L-NAME.
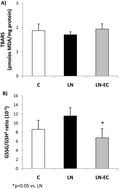
Food Funct., 2015,6, 154-160
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4FO00554F
Oolong, black and pu-erh tea suppresses adiposity in mice via activation of AMP-activated protein kinase
It is well known that tea has a variety of beneficial impacts on human health, including anti-obesity effects.

Food Funct., 2014,5, 2420-2429
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4FO00095A
Phenolic metabolites and substantial microbiome changes in pig feces by ingesting grape seed proanthocyanidins
Proanthocyanidin (PAC) consumption has been linked to better colonic health, but PACs are poorly absorbed, making them a target for colonic metabolism.
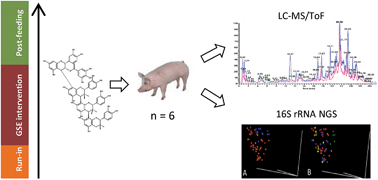
Food Funct., 2014,5, 2298-2308
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4FO00325J
Red wine extract decreases pro-inflammatory markers, nuclear factor-κB and inducible NOS, in experimental metabolic syndrome
Alibernet red wine extract (AWE) decreased p65 NF-κB and iNOS expressions elevated due to the development of metabolic syndrome in SHR/N-cp rats.
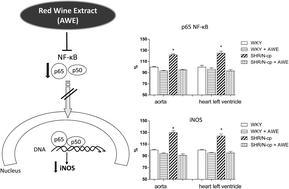
Food Funct., 2014,5, 2202-2207
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4FO00097H
Anti-inflammatory activity and molecular mechanism of Oolong tea theasinensin
Oolong tea theasinensins are a group of tea polyphenols different from green tea catechins and black tea theaflavins, and they are considered as bioactive compounds in oolong tea.
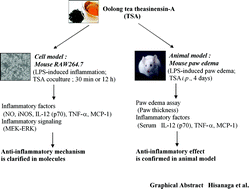
Food Funct., 2014,5, 1891-1897
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4FO00152D
High levels of Bifidobacteria are associated with increased levels of anthocyanin microbial metabolites: a randomized clinical trial
The health benefits associated with the consumption of polyphenol-rich foods have been studied in depth, however, the full mechanism of action remains unknown.
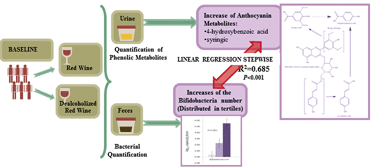
Food Funct., 2014,5, 1932-1938
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4FO00029C
Description of urolithin production capacity from ellagic acid of two human intestinal Gordonibacter species
This is the first time that the urolithin production capacity of pure strains has been demonstrated, which can indirectly affect the health benefits of ellagitannin consumption (cardiovascular protection, anti-inflammatory and anticarcinogenic properties).
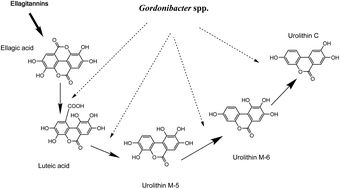
Food Funct., 2014,5, 1779-1784
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4FO00092G
Virgin olive oil phenolics extract inhibit invasion of HT115 human colon cancer cells in vitro and in vivo
A virgin olive oil phenolics extract (OVP) inhibited invasion of HT115 colon cancer cells in vitro. In vivo, OVP by gavage significantly decreased tumour volume and the number of metastases in SCID mice.
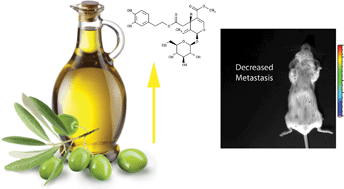
Food Funct., 2014,5, 1513-1519
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4FO00090K
Differential protective effects of red wine polyphenol extracts (RWEs) on colon carcinogenesis
Various epidemiological studies have shown that a regular and moderate consumption of red wine is correlated with a decreased relative risk of developing coronary heart disease and cancer.
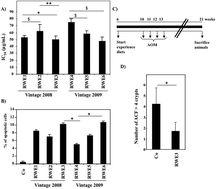
Food Funct., 2014,5, 663-670
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3FO60417A
About this collection
This web collection contains selected contributions from the VI International Conference on Polyphenols and Health (ICPH-6), which took place in Buenos Aires, Argentina, in October 2013. The Conference covered a prolific area of research from basic chemistry to the medical aspects of polyphenols. The overall goal was to improve the understanding of why fruits and vegetables benefit human health. Editors of the collection were Food & Function Board members, Professors Kevin Croft, Gary Williamson, Aedin Cassidy and Cesar G. Fraga who was also President of the Conference.