Themed collection Environmental Science: Nano 2014 Most Accessed Articles

The road to nowhere: equilibrium partition coefficients for nanoparticles
This perspective demonstrates the inapplicability of equilibrium partition coefficients as fate descriptors for nanoparticles.
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2014,1, 317-323
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4EN00043A
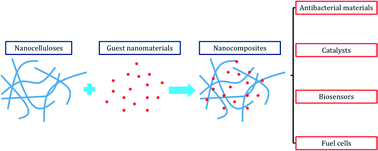
Environmental science and engineering applications of nanocellulose-based nanocomposites
This review summarizes recent progress in the development of nanocellulose-based nanocomposites and in their environmental applications.
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2014,1, 302-316
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4EN00059E
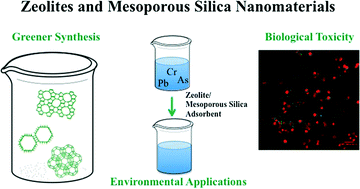
Zeolite and mesoporous silica nanomaterials: greener syntheses, environmental applications and biological toxicity
Zeolites and mesoporous silica nanoparticles are silicate or aluminosilicate nanomaterials with well-defined pore networks.
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2014,1, 200-213
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4EN00031E
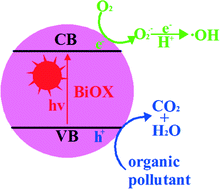
Recent advances in BiOX (X = Cl, Br and I) photocatalysts: synthesis, modification, facet effects and mechanisms
This review gives an overview of the applications of BiOX (X = Cl, Br and I) photocatalysts for environmental remediation.
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2014,1, 90-112
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3EN00098B
Deposition of nanoparticles onto polysaccharide-coated surfaces: implications for nanoparticle–biofilm interactions
While environmental biofilms have recently been implicated as a potential major sink for nanoparticles (NPs), the mechanisms of interactions remain largely unknown.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2014,1, 117-122
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3EN00075C
Sulfidation of copper oxide nanoparticles and properties of resulting copper sulfide
Sulfidation of 40 nm CuO nanoparticles in water yields poorly structured CuxSy and crystalline covellite (CuS) with increasing apparent solubility.
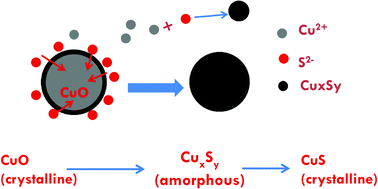
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2014,1, 347-357
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4EN00018H
Surface chemistry, charge and ligand type impact the toxicity of gold nanoparticles to Daphnia magna
Using highly characterized gold nanoparticles this study determined that ligand identity, nanoparticle surface charge and aggregation type alters toxicity of gold nanoparticles to Daphnia magna.
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2014,1, 260-270
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4EN00006D
Iron oxide nanoparticles induce Pseudomonas aeruginosa growth, induce biofilm formation, and inhibit antimicrobial peptide function
It is important to understand any effects that iron-containing nanoparticles have on the environment and human health.
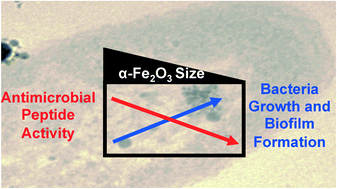
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2014,1, 123-132
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3EN00029J
Green synthesis and formation mechanism of cellulose nanocrystal-supported gold nanoparticles with enhanced catalytic performance
A one-pot and green synthesis of gold nanoparticles deposited on cellulose nanocrystals under hydrothermal conditions using CNs as a reducing agent and stabilizing template for the reduction of 4-nitrophenol.
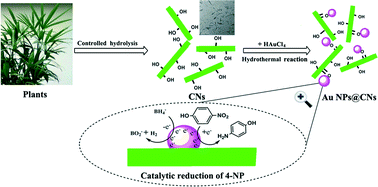
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2014,1, 71-79
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3EN00066D
Natural water chemistry (dissolved organic carbon, pH, and hardness) modulates colloidal stability, dissolution, and antimicrobial activity of citrate functionalized silver nanoparticles
Critical water chemistry parameters (dissolved organic carbon (DOC), pH, and hardness) alter colloidal stability, dissolution dynamics, and antimicrobial activity of citrate-functionalized AgNPs.
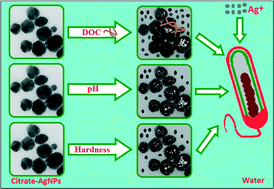
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2014,1, 45-54
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3EN00017F
About this collection
This web collection features the top 10 most downloaded articles published in Environmental Science: Nano in 2014. Congratulations to all of the authors whose articles have been featured!