Long-range mechanical signaling in biological systems
Abstract
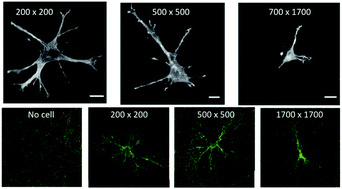
Cells can respond to signals generated by other cells that are remarkably far away. Studies from at least the 1920's showed that cells move toward each other when the distance between them is on the order of a millimeter, which is many times the cell diameter. Chemical signals generated by molecules diffusing from the cell surface would move too slowly and dissipate too fast to account for these effects, suggesting that they might be physical rather than biochemical. The non-linear elastic responses of sparsely connected networks of stiff or semiflexible filament such as those that form the extracellular matrix (ECM) and the cytoskeleton have unusual properties that suggest multiple mechanisms for long-range signaling in biological tissues. These include not only direct force transmission, but also highly non-uniform local deformations, and force-generated changes in fiber alignment and density. Defining how fibrous networks respond to cell-generated forces can help design new methods to characterize abnormal tissues and can guide development of improved biomimetic materials.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Remodelling of Biomembranes


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...
