Solvatochromism and fluorescence response of a halogen bonding anion receptor†
Abstract
Herein, we present two 2,6-bis(4-ethynylpyridinyl)-4-fluoroaniline receptors that display solvatochromic absorption and emission. Neutral derivatives displayed opposite solvatochromic behavior as compared to the alkylated receptors. Adding anions induced changes in the absorption and emission spectra. In general, the fluorescence of the halogen bonding receptor was quenched less efficiently when compared to the hydrogen bonding receptor.
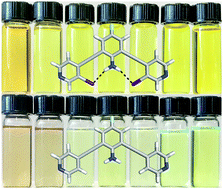
- This article is part of the themed collection: The halogen bond: a new avenue in recognition and self-assembly


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...
