Thixotropic silk nanofibril-based hydrogel with extracellular matrix-like structure†
Abstract
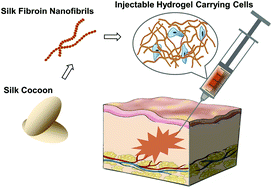
Silk fibroin (SF) based materials have been widely studied and applied in bio-related areas due to their excellent structural and biological properties. Here, we present an injectable hydrogel formed by SF nanofibrils via simple fibrillation and centrifugation approach. The hydrogels with extracellular matrix-like structure not only perform the sufficient mechanical properties, but also show outstanding thixotropic character, whose storage modulus (G′) can recover to 93% within 40 seconds after a large shearing strain (5000 %). More importantly, the injectable hydrogel exhibits significant biocompatibility for L929 cells cultured in hydrogel after injection, illustrated by cell viability and cytotoxicity assays. All of these results indicate that such SF nanofibril-based hydrogel has promise in application such as a cell therapy carrier.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Silk and silk-inspired materials

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...