Evaluation of MMP substrate concentration and specificity for neovascularization of hydrogel scaffolds
Abstract
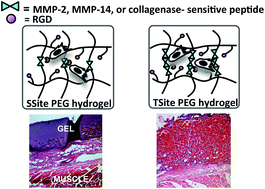
Controlled vascular response in scaffolds following implantation remains a significant clinical challenge. A critical biomaterial design criterion is the synchronization of the rates of scaffold degradation and vascularized tissue formation. Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) are key enzymes that regulate neovascularization and extracellular matrix remodelling. Synthetic protease-sensitive hydrogels offer controllable environments for investigating the role of matrix degradation on neovascularization. In this study, PEG hydrogels containing MMP-sensitive peptides with increased catalytic activity for MMPs expressed during neovascularization were investigated. Scaffolds were functionalized with MMP-2-, MMP-14- or general collagenase-sensitive peptides and with varying peptide concentration using crosslinkers containing one (SSite) or multiple (TSite) repeats of each protease-sensitive sequence. Increasing peptide concentration enhanced the degradation kinetics of scaffolds functionalized with MMP-specific sequences while 80% of the collagenase-sensitive scaffolds remained upon exposure to MMP-2 and MMP-14. In vitro neovascularization was consistent with in vivo tissue invasion with significantly increased invasion occurring within SSite MMP-specific as compared to collagenase-sensitive hydrogels and with further invasion in TSite as compared to SSite hydrogels regardless of peptide specificity. All scaffolds supported in vivo neovascularization; however, this was not dependent on peptide specificity. These findings demonstrate that peptide concentration and specificity regulate in vivo scaffold degradation, neovascularization and matrix remodelling.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...