Structure and Li+ ion transport in a mixed carbonate/LiPF6 electrolyte near graphite electrode surfaces: a molecular dynamics study†
Abstract
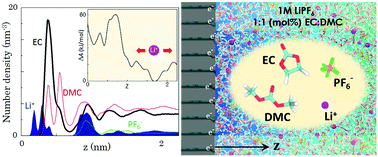
Electrolyte and electrode materials used in lithium-ion batteries have been studied separately to a great extent, however the structural and dynamical properties of the electrolyte–electrode interface still remain largely unexplored despite its critical role in governing battery performance. Using molecular dynamics simulations, we examine the structural reorganization of solvent molecules (cyclic ethylene carbonate : linear dimethyl carbonate 1 : 1 molar ratio doped with 1 M LiPF6) in the vicinity of graphite electrodes with varying surface charge densities (σ). The interfacial structure is found to be sensitive to the molecular geometry and polarity of each solvent molecule as well as the surface structure and charge distribution of the negative electrode. We also evaluated the potential difference across the electrolyte–electrode interface, which exhibits a nearly linear variation with respect to σ up until the onset of Li+ ion accumulation onto the graphite edges from the electrolyte. In addition, well-tempered metadynamics simulations are employed to predict the free-energy barriers to Li+ ion transport through the relatively dense interfacial layer, along with analysis of the Li+ solvation sheath structure. Quantitative analysis of the molecular arrangements at the electrolyte–electrode interface will help better understand and describe electrolyte decomposition, especially in the early stages of solid-electrolyte-interphase (SEI) formation. Moreover, the computational framework presented in this work offers a means to explore the effects of solvent composition, electrode surface modification, and operating temperature on the interfacial structure and properties, which may further assist in efforts to engineer the electrolyte–electrode interface leading to a SEI layer that optimizes battery performance.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...