Codelivery of sorafenib and GPC3 siRNA with PEI-modified liposomes for hepatoma therapy†
Abstract
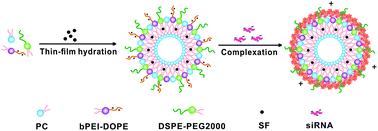
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most common malignancies imposing a serious threat to human health worldwide. To date, the effect of HCC chemotherapy has been limited due to drug resistance. Combination therapy of chemotherapeutic drugs and siRNA represents an emerging strategy that may improve anticancer effects by synergistic actions. The current study was aimed at achieving better HCC treatment via combination therapy, in which PEI-modified liposomes prepared by a thin-film hydration method were used to codeliver sorafenib (SF) and siRNA targeting GPC3 gene (siGPC3). Under optimized experimental conditions, SF and siGPC3 were effectively loaded into liposomes (SF-PL/siGPC3). SF-PL/siGPC3 with selected sizes and zeta potentials effectively accumulated at tumor sites and entered HCC cells. The two codelivered therapeutic agents exerted good anticancer effects by jointly suppressing the expression of the anti-apoptotic GPC3 gene and the proliferative cyclin D1 gene in HCC. Consequently, the intravenous injection of SF-PL/siGPC3 into nude mice bearing subcutaneous human HepG2 xenografts effectively inhibited tumor growth and also increased the survival rates of animals. These results revealed the great potential of the PEI-modified liposomal nanomedicine carrying SF and siGPC3 to improve HCC treatment.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...