Modified acellular nerve-delivering PMSCs improve functional recovery in rats after complete spinal cord transection
Abstract
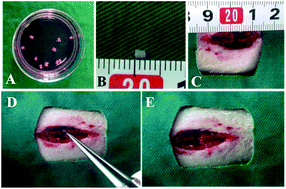
Due to the poor regeneration capacity of neurons and the inhibitory microenvironment, spontaneous regeneration in spinal cord injury (SCI) remains challenging. Tissue engineering is considered a promising approach for enhancing the regeneration of SCI by reconstructing the inherent structure and improving the microenvironment. In this study, the possibility of engineering a nerve complex, which is constructed by acellular nerve delivering placenta mesenchymal stem cells (PMSCs), was assessed for the recovery of a transected spinal cord. Modified acellular nerve grafts were developed, and PMSCs labeled with green fluorescent protein (GFP) were seeded on the graft to construct the engineered nerve complex. Then, the engineered nerve complex was implanted into a 2 mm-length transected gap of the spinal cord. Four weeks after the transplantation, numerous surviving PMSCs were observed in the lesion cavity by immunofluorescence staining. Moreover, co-localization between GFP and neurofilament-200 (NF200) and Neuronal Class III β-Tubulin (Tuj1) was observed at the bridge interface. The PMSCs-graft group exhibited significant function improvement as evaluated by the Basso, Beattie and Bresnahan (BBB) locomotion score and footprint analysis. Eight weeks after surgery, the evoked response was restored in the PMSCs-graft group and numerous thick myelin sheathes were observed compared to that in the control groups. Collectively, our findings suggest that the nerve complex prepared by acellular nerve delivering PMSCs enhanced the structure and function regeneration of the spinal cord after SCI.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...