Anion-exchange membrane water electrolyzers and fuel cells†
Abstract
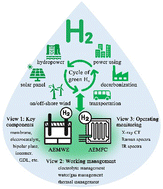
Anion-exchange membrane (AEM) water electrolyzers (AEMWEs) and fuel cells (AEMFCs) are technologies that, respectively, achieve transformation and utilization of renewable resources in the form of green hydrogen (H2) energy. The significantly reduced cost of their key components (membranes, electrocatalysts, bipolar plates, etc.), quick reaction kinetics, and fewer corrosion problems endow AEM water electrolyzers and fuel cells with overwhelming superiority over their conventional counterparts (e.g., proton-exchange membrane water electrolyzer/fuel cells and alkaline water electrolyzer/fuel cells). Limitations in our fundamental understanding of AEM devices, however, specifically in key components, working management, and operation monitoring, restrict the improvement of cell performance, and they further impede the deployment of AEM water electrolyzers and fuel cells. Therefore, a panoramic view to outline the fundamentals, technological progress, and future perspectives on AEMWEs and AEMFCs is presented. The objective of this review is to (1) present a timely overview of the market development status of green hydrogen technology that is closely associated with AEMWEs (hydrogen production) and AEMFCs (hydrogen utilization); (2) provide an in-depth and comprehensive analysis of AEMWEs and AEMFCs from the viewpoint of all key components (e.g., membranes, ionomers, catalysts, gas diffusion layers, bipolar plates, and membrane electrode assembly (MEA)); (3) summarize the state-of-the-art technologies for working management of AEMWEs and AEMFCs, including electrolyte engineering (electrolyte selection and feeding), water management, gas and heat management, etc.; (4) outline the advances in monitoring the operations of AEMWEs and AEMFCs, which include microscopic and spectroscopic techniques and beyond; and (5) present key aspects that need to be further studied from the perspective of science and engineering to accelerate the deployment of AEMWEs and AEMFCs.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...