Controllable preparation of CuO/Cu2O composite particles with enhanced photocatalytic performance†
Abstract
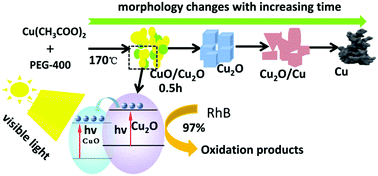
In this paper, copper-based oxide (CuO/Cu2O, Cu2O, Cu2O/Cu, and Cu) nano/micron particles were prepared in polyethylene glycol (PEG)-400 with copper acetate (Cu(CH3COO)2·H2O) as a raw material by a one-step thermal decomposition method. The effects of the reaction time on the valence state, composition, morphology and particle size of the products were investigated. The results show that PEG-400 acted as a modifier and reductant in the system, reducing the copper source from Cu(II) through Cu(I) to elemental Cu. Cu-Based nanocomposites with different valence states were formed at different time points. The photocatalytic activity of the products decreased with the increase of the particle size and the width of the band gap. The CuO/Cu2O composites exhibited as high as 97% (0.0485 g g−1) photocatalytic degradation of rhodamine B (RhB) in 5 minutes under visible light in the presence of H2O2. This simple and green method can be used to tune the composition of copper-based oxide nanocomposites with excellent performance and is suitable for scaling up.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...