A sulfonyl hydrazone cholesterol conjugate: gelation, anion interaction and its application in dye adsorption†
Abstract
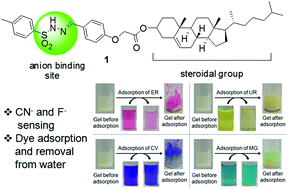
Cholesterol appended sulfonyl hydrazone derivative 1 was designed and synthesized as a supramolecular gelator for anionic sensing and dye adsorption. Gelator 1 forms a stable gel in DMSO–H2O. The intermolecular H-bonding involving the sulfonamide moieties and the hydrophobic interactions between the cholesterol units encourage gelation. The SEM images of the xerogels show tiny rod-like fibrous structures. The rheological studies of the gel reveal the viscoelastic nature of the material. The gels of 1 exhibit a sharp and selective response toward CN− and F− ions causing gel-to-sol transformation. The gels of 1 also show potential for application in adsorption and removal of anionic dyes, such as erythrosine B and uranine, from water. Preparation of a gel column was done with the gel of 1 which shows reasonably high one-time erythrosine B removal efficiency establishing its potential and promising real-life applicability in water purification.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...