Co-liquefaction of sewage sludge with wheat straw in supercritical water – potential for integrating hydrothermal liquefaction with wastewater treatment plants†
Abstract
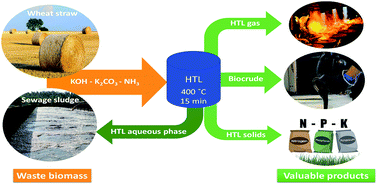
Sewage sludge from wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) represents a source of feedstock for hydrothermal liquefaction (HTL), which in turn offers a sustainable alternative to valorize this societal waste. The co-processing of sewage sludge with other feedstocks might be necessary to ensure a sufficient supply of raw material to commercial scale HTL plants. In this context, the present work investigates the supercritical co-liquefaction of sewage sludge with wheat straw focusing on the effect of biomass composition, alkali catalysts, and ammonia on biocrude production and quality. The results show that the biocrude yield decreases for increasing ratios of straw in the feed, with 41% yield from sewage sludge and 30% from straw. However, the addition of straw reduces the inorganic content of the feed, results in biocrudes with a lower nitrogen content, and does not compromise the phosphorus recovery in the solids (>95%). The addition of KOH, K2CO3, and NH3 enhances the deoxygenation and denitrogenation. KOH leads to the largest biocrude yield from sewage sludge (48%), while K2CO3 in the co-liquefaction (41%). The recirculation of the HTL gas and aqueous phase to the WWTP is proposed in an integrated WWTP-HTL plant based on their compositions and a Sankey diagram investigation. The gas is directed to the burners to produce heat and power increasing the energy output by 11.5%. The aqueous phase, despite showing higher concentrations of carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus, can be recirculated to the inlet flow, as it only represents 0.14% of the total inlet to the WWTP.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...