Development of an improved and greener HPLC-DAD method for the determination of fecal sterols in sediment and water samples using ultrasonic-assisted derivatization with benzoyl isocyanate
Abstract
The analysis of sterols by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) with UV detection presents a challenge, owing to the intrinsically low molar absorptivity of these compounds. In this study, we developed a novel derivatization method for sterols (7-dehydrocholesterol, cholesterol, and coprostanol), which serve as indicators of fecal pollution, for analysis by HPLC-DAD. We proposed benzoyl isocyanate as the derivatization reagent, as isocyanates are characterized by a functional group containing –N![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C
C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O, which reacts with the hydroxyl (–OH) groups present in the structure of sterols, thereby introducing the chromophore group of benzoyl isocyanate to the sterols. This method is more environmentally friendly compared to previously published derivatization techniques. The conditions for sterol derivatization were optimized using chemometric tools, including a 22 factorial design with a central point and central composite design for the variables of molar ratio (sterol/benzoyl isocyanate = 0.046, equivalent to 1.57 × 10−5 mols of sterol and 3.39 × 10−4 mols of benzoyl isocyanate) and ultrasonic bath time (32.1 minutes). The chromatographic parameters
O, which reacts with the hydroxyl (–OH) groups present in the structure of sterols, thereby introducing the chromophore group of benzoyl isocyanate to the sterols. This method is more environmentally friendly compared to previously published derivatization techniques. The conditions for sterol derivatization were optimized using chemometric tools, including a 22 factorial design with a central point and central composite design for the variables of molar ratio (sterol/benzoyl isocyanate = 0.046, equivalent to 1.57 × 10−5 mols of sterol and 3.39 × 10−4 mols of benzoyl isocyanate) and ultrasonic bath time (32.1 minutes). The chromatographic parameters 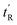 , k, α, Rs, N, and As were determined. The quantification limits were established at 0.6 mg L−1 for 7-dehydrocholesteryl-N-benzoylcarbamate and 0.5 mg L−1 for cholesteryl-N-benzoylcarbamate and coprostanolyl-N-benzoylcarbamate. The feasibility of the proposed method was confirmed by analysing water and sediment samples from lakes in Londrina, Paraná, Brazil, yielding recovery values ranging from 91 to 108%.
, k, α, Rs, N, and As were determined. The quantification limits were established at 0.6 mg L−1 for 7-dehydrocholesteryl-N-benzoylcarbamate and 0.5 mg L−1 for cholesteryl-N-benzoylcarbamate and coprostanolyl-N-benzoylcarbamate. The feasibility of the proposed method was confirmed by analysing water and sediment samples from lakes in Londrina, Paraná, Brazil, yielding recovery values ranging from 91 to 108%.



 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...