Current status of research on composite bipolar plates for proton exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs): nanofillers and structure optimization
Abstract
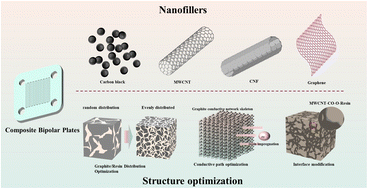
The proton exchange membrane fuel cell (PEMFC) is an efficient and clean energy source with promising applications. However, drawbacks such as high cost and low durability limit its application. Bipolar plates are an important component of PEMFCs, which not only account for a large proportion of the price and quality, but also affect the performance and durability of PEMFCs. Unlike traditional graphite and metal bipolar plates, composite bipolar plates have the advantages of easy processing, low cost, and corrosion resistance, but their lower performance limits their practical applications. This paper firstly summarizes the current research progress of various nanofillers used to improve the performance of composite bipolar plates, and discusses the improvement of the performance of composite bipolar plates by different forms and types of nanofillers. The morphological characteristics of different types of nanofillers and their effects on the improvement of conductive pathways are also analyzed. Subsequently, the means of structural optimization of composite bipolar plates are summarized, and specific optimization methods for phase interface, graphite/resin dispersion morphology, and conductive network structure are discussed in detail. Finally, challenges are discussed. Overall, this review can provide a reference for future research on composite bipolar plates.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2024 Reviews in RSC Advances


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...