Atomically dispersed nanozyme-based synergistic mild photothermal/nanocatalytic therapy for eradicating multidrug-resistant bacteria and accelerating infected wound healing†
Abstract
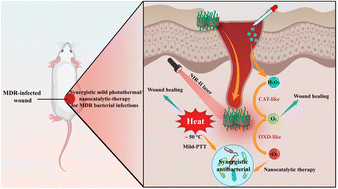
Constructing a synergistic multiple-modal antibacterial platform for multi-drug-resistant (MDR) bacterial eradication and effective treatment of infected wounds remains an important and challenging goal. Herein, we developed a multifunctional Cu/Mn dual single-atom nanozyme (Cu/Mn-DSAzymes)-based synergistic mild photothermal/nanocatalytic-therapy for a MDR bacterium-infected wound. Cu/Mn-DSAzymes with collaborative effects exhibit remarkable dual CAT-like and OXD-like enzyme activities and could efficiently catalyze cascade enzymatic reactions with a low level of H2O2 as an initial reactant to produce reparative O2 and lethal ˙O2−. Moreover, a black N-doped carbon nanosheet supports of Cu/Mn-DSAzymes show superior NIR-II-triggered photothermal performance, endowing them with photothermal-enhanced dual enzyme catalysis. In addition, such enhanced dual enzyme catalysis likely improves the susceptibility and lethality of photothermal effects on MDR bacteria. In vitro and in vivo studies demonstrate that Cu/Mn-DSAzyme-mediated synergistic nanocatalytic and photothermal effects possess dramatic antibacterial outcomes against MDR bacteria and evidently reduced inflammation at wound sites. Moreover, the combined photothermal effect and O2 release mediated by Cu/Mn-DSAzymes promotes macrophage polarization to reparative M2 phenotype, collagen deposition, and angiogenesis, considerably accelerating wound healing. Therefore, Cu/Mn-DSAzyme-based synergetic dual-modal antibacterial therapy is a promising strategy for MDR bacterium-infected wound treatment, owing to their excellent antibacterial ability and significant tissue remodeling effects.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...