Boric acid catalysed hydrolysis of peroxyacids†
Abstract
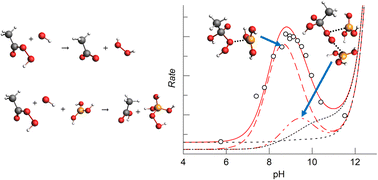
This study shows for the first time that boric acid catalyses the hydrolysis of peroxyacids, resulting in an approximately 12-fold increase in hydrolysis rate for both peracetic acid (PAA) and 3-chloroperbenzoic acid (MCPBA) when 0.1 M boric acid is present. The maximum rate of hydrolysis occurs at pH 9 and pH 8.4 for PAA and MCPBA respectively. In contrast, carbonate buffer does not enhance the rate of PAA hydrolysis. The reaction was followed by measuring the initial rate of hydrogen peroxide formation using a specific Ti(IV) complexation method. The study of the hydrolysis reaction requires the presence of 2 × 10−5 M each of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) and ethylenediamine tetramethylene phosphonic acid (EDTMP) in all solutions in order to chelate metal ions across the full pH range (3 to 13) that would otherwise contribute to peroxyacid decomposition. Catalysis of peroxyacid hydrolysis is most likely effected by the triganol boric acid acting as a Lewis acid catalyst, associating with the peroxide leaving group in the transition state to reduce the leaving group basicity. The products of the reaction are the well characterised monoperoxoborate species and the parent carboxylic acid. Analysis of the pH and borate dependence data reveals that in addition to a catalytic pathway involving a single boric acid molecule, there is a significant pathway involving either (a) two boric acid molecules or (b) the polyborate species, B3O3(OH)4−. Knowledge about catalytic mechanisms for the loss of peroxyacids through hydrolysis is important because they are widely used in reagents in a range of oxidation, bleaching and disinfection applications.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Celebrating the scientific accomplishments of RSC Fellows


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...