Improving methanol assimilation in Yarrowia lipolytica via systematic metabolic engineering combined with compartmentalization†
Abstract
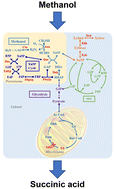
Renewable methanol is an attractive non-food feedstock that can replace sugar-based materials for biochemical production. However, the metabolic construction of a synthetic methylotroph to achieve methanol conversion for cell growth and chemical production remains a challenge due to toxic intermediates and complicated metabolic pathways. Herein, we rationally engineered the oleaginous yeast Yarrowia lipolytica for the achievement of methanol utilization and value-added chemicals (mainly succinic acid) production. The artificially constructed methylotrophic Y. lipolytica showed 3.40 g L−1 consumption of methanol when synergistically using methanol and xylose as carbon sources. Then, through the rewiring of the peroxisomal Xu5P recycle pathway to improve precursor supply, the recombinant strain showed enhanced cell growth and methanol utilization. Transcriptome analysis revealed that the downregulation of key genes in the glycolysis pathway and upregulation of key genes in the amino acid biosynthesis pathway and TCA cycle can rebalance the methylotrophic metabolism. Furthermore, the heat shock protein 70 (hsp70) was found to enable the recombinant Y. lipolytica to efficiently use methanol for cell growth and metabolism. After the inactivation of the succinate dehydrogenase subunit 5 (sdh5), 0.92 g L−1 of succinic acid can be synthesized from methanol on its own, demonstrating its great potential for bioconversion of methanol into valuable chemicals. This study represents a successful example for the biological conversion of methanol to value-added chemicals.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...