Mechanistic insight into the Dehalococcoides-mediated reductive dechlorination of polychlorinated biphenyls†
Abstract
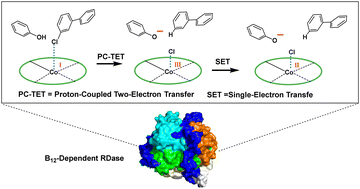
Microbial reductive dechlorination provides a green and highly desirable approach to address the pollution raised by the substantial legacies of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in soil, sediment, and underground water. It has been shown that the reaction event is catalyzed by supernucleophilic cob(I)alamin housed in reductive dehalogenases (RDases). However, the mechanism still remains elusive. Herein, we unravel the mechanism via quantum chemical calculations, considering a general model of RDase and the dechlorination regioselectivity of two representative PCB congeners, 234-236-CB and 2345-236-CB. The B12-catalzyed reductive dechlorination of PCBs starts with the formation of a reactant complex, followed by a proton-coupled two-electron transfer (PC-TET) and a subsequent single-electron transfer (SET). The PC-TET yields a cob(III)alamin-featured intermediate, which is quickly reduced by the latter SET fueled by significant energetic benefits (∼100 kcal mol−1). It rationalizes the exclusive detection and characterization of cob(I/II)alamins in RDase-mediated dehalogenation experiments. The determined mechanism successfully reproduces the experimental dechlorination regioselectivity and reactivity, as observed with Dehalococcoides mccartyi strain CG1.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2023 PCCP HOT Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...