β and γ-Cyclodextrin dimers: design, characterization and in silico studies to explore the cooperative effect of the cavities†
Abstract
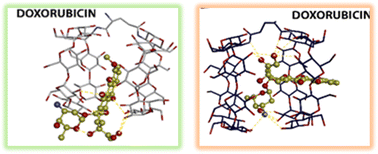
Cyclodextrins can encapsulate various molecules and have exciting applications in supramolecular, pharmaceutical, material, food and environmental chemistry. Typically, the encapsulation into the cyclodextrin cavity confers to the guest improved solubility, stability, bioavailability and organoleptic properties. In recent years, cyclodextrin multi-cavity systems have also been studied to encapsulate biomolecules or drugs. This context has inspired us to synthesize and characterize two new β and γ-cyclodextrin dimers and compare their complexation behavior. The two cavities in the same molecule significantly improve the stability of inclusion complexes. Particularly we investigated cholic acid, cholesterol and doxorubicin as guests. The extent of binding between a guest molecule and β and γ-cyclodextrin dimers was established by molecular docking. Cholic acid at physiological pH was chosen as a water-soluble cholesterol analog for the investigation in water by isothermal calorimetry. We found that dimers can include cholate species, cholesterol and doxorubicin better than native cyclodextrins, and the cyclodextrin type tunes the stability of inclusion complexes.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...