Lycopene ameliorates islet function and down-regulates the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB pathway in diabetic mice and Min6 cells†
Abstract
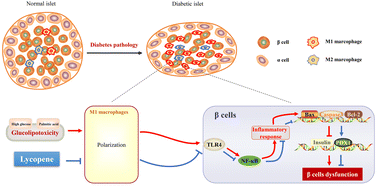
The inflammation of the pancreatic islets triggers β cell dysfunction and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) onset. While dietary lycopene consumption contributes to protection against T2DM in animal studies, the potential mechanism of this compound in the regulation of islet function in T2DM remains largely unclear. In this study, by using anti-diabetic metformin as a positive control, we demonstrated that lycopene treatment suppressed islet inflammation and apoptosis in both high-fat diet (HFD)/streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetic mice and in Min6 cells exposed to high glucose/palmitic acid (HG/PA)-RAW264.7 conditioned medium. Lycopene intervention resulted in M1/M2 macrophage polarization homeostasis, which is associated with increased insulin secretion, decreased fasting blood glucose levels, and improved lipid profiles in diabetic mice. Furthermore, the protective actions of lycopene were associated with the down-regulation of the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway, which is positively related to inflammation in both diabetic mice and Min6 cells. Collectively, our findings indicated that lycopene ameliorates islet function and apoptosis and attenuates hyperglycemia and dyslipidemia by the regulation of the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway. This study highlights dietary lycopene consumption as a novel strategy for the management of patients with diabetes.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...
