Iron-based fluorophosphate Na2FePO4F as a cathode for aqueous zinc-ion batteries†
Abstract
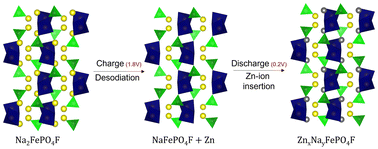
Aqueous zinc-ion batteries form a key post-Li-ion batteries to cater the rising demand for grid storage. Fe-based compounds can be used as economical cathodes for zinc-ion batteries. Herein, we explored iron-based flourophosphate as a potential polyanionic cathode. Involving the Fe3+/2+ redox process, it can reversibly intercalate Zn2+ yielding a capacity of ∼80 mA h g−1, involving a solid-solution mechanism. Polyanionic Fe-based phosphate frameworks can be harnessed as potential low-cost cathodes for secondary zinc-ion batteries.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...