Rapid, interface-driven domain orientation in bottlebrush diblock copolymer films during thermal annealing†
Abstract
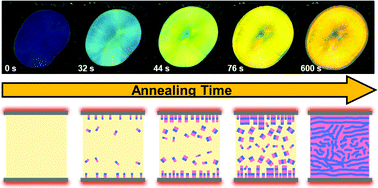
Favorable polymer-substrate interactions induce surface orientation fields in block copolymer (BCP) melts. In linear BCP processed near equilibrium, alignment of domains generally persists for a small number of periods (∼4–6 D0) before randomization of domain orientation. Bottlebrush BCP are an emerging class of materials with distinct chain dynamics stemming from substantial molecular rigidity, enabling rapid assembly at ultrahigh (>100 nm) domain periodicities with strong photonic properties (structural color). This work assesses interface-induced ordering in PS-b-PLA bottlebrush diblock copolymer films during thermal annealing between planar surfaces. To clearly observe the decay in orientational order from surface to bulk, we choose to study micron-scale films spanning greater than 200 lamellar periods. In situ optical microscopy and transmission UV-Vis spectroscopy are used to monitor photonic properties during annealing and paired with ex situ UV-Vis reflection measurement, cross-sectional scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) to probe the evolution of domain microstructure. Photonic properties were observed to saturate within minutes of annealing at 150 °C, with distinct variation in transmission response as a function of film thickness. The depth of the highly aligned surface region was found to vary stochastically in the range of 30–100 lamellar periods, with the sharpness of the orientation gradient decreasing substantially with increasing film thickness. This observation suggests a competition between growth of aligned, heterogeneously nucleated, grains at the surface and orientationally isotropic, homogeneously nucleated, grains throughout the bulk. This work demonstrates the high potential of bottlebrush block copolymers in rapid fabrication workflows and provides a point of comparison for future application of directed self-assembly to BBCP ordering.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Soft Matter Emerging Investigators Series


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...