Sensitive and specific capture of polystyrene and polypropylene microplastics using engineered peptide biosensors†
Abstract
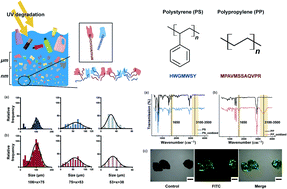
Owing to increased environmental pollution, active research regarding microplastics circulating in the ocean has attracted significant interest in recent times. Microplastics accumulate in the bodies of living organisms and adversely affect them. In this study, a new method for the rapid detection of microplastics using peptides was proposed. Among the various types of plastics distributed in the ocean, polystyrene and polypropylene were selected. The binding affinity of the hydrophobic peptides suitable for each type of plastic was evaluated. The binding affinities of peptides were confirmed in unoxidized plastics and plasma-oxidized plastics in deionised or 3.5% saline water. Also, the detection of microplastics in small animals' intestine extracts were possible with the reported peptide biosensors. We expect plastic-binding peptides to be used in sensors to increase the detection efficiency of microplastics and potentially help separate microplastics from seawater.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...