Mixed-ligand copper(ii) complexes of guanidine derivatives containing ciprofloxacin: synthesis, characterization, DFT calculations, DNA interactions and biological activities†
Abstract
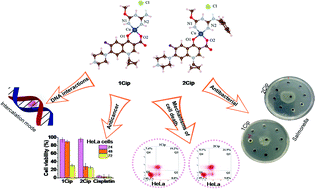
Two mixed-ligand complexes of copper(II) chloride containing guanidine derivatives and ciprofloxacin (HCip), namely [CuL1m(Cip)]Cl (1Cip) and [CuL2m(Cip)]Cl (2Cip) (L1m = amidino-O-methylurea, L2m = N-(benzyl)-amidino-O-methylurea), were synthesized and characterized by elemental analysis and spectroscopic techniques, including density functional theory (DFT) calculations. The possible coordination geometry of 1Cip and 2Cip was predicted to be distorted square planar. The binding mode and strength of the complexes to calf thymus (CT) DNA were explored using absorption titration, viscosity measurements, circular dichroism and fluorescence spectroscopies, which suggested intercalation between the DNA-bases as the most probable binding mode. The intrinsic binding constants (Kb) were determined and found in the trend of 2Cip > 1Cip. Analysis of the cleaving ability of the complexes toward pBR322 plasmid DNA in the absence and presence of hydrogen peroxide was also carried out by gel electrophoresis. The results of our studies suggest that the main cleaving pathway of 1Cip and 2Cip may occur via an oxidative mechanism. Their cytotoxicity was then tested against human cervical cancer (HeLa) and breast cancer (MCF-7) cells in comparison to normal kidney (Vero) cells. The studied complexes showed greater anticancer activity against both cancer cells than HCip and the starting compounds (1 and 2). In addition, the complexes are inactive toward normal cells, probably due to their additional ciprofloxacin. The mechanism of cell death was further investigated by flow cytometry, and it was found that 1Cip and 2Cip may induce the death of the cancer cells via apoptosis pathways in the S phase for HeLa cells, and the G0/G1 phase for MCF-7 cells. The antibacterial activities of the complexes were also tested against three human food poisoning bacteria (E. coli, Salmonella, and Campylobacter). According to the MIC values, the antibacterial activity of 1Cip and 2Cip was the best against Salmonella (1.95 μg mL−1).


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...