Fruit juices as a carrier of probiotics to modulate gut phenolics and microbiota†
Abstract
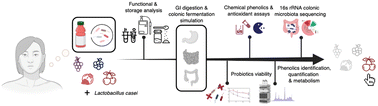
Here we attempted to deliver probiotics to the human gut using fruit juices as a carrier, which is less common despite the newest trend to incorporate probiotics into non-dairy food. Phenolic-rich fruit juices, including blueberry, black cherry, concord grape and pomegranate were fortified with Lactobacillus casei, and then compared and comprehensively assessed to develop novel non-fermented probiotic juices. In black cherry juice, probiotics had the most significant retention of viability after 14 days of storage at 4 °C, the least reduction in phenolics (14.59%) after in vitro gastrointestinal digestion, the highest concentration of phenolic metabolites and a significant increase in anaerobic bacteria after faecal fermentation (48 h). 16s rRNA gene sequencing showed that probiotic-enriched juice treatments were associated with highly distinctive Bacteroidota and Bacteroides vulgatus population. Overall, black cherry juice has the highest potential to be developed as a probiotic carrier with benefits in modulating the gut microbiota.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...