Coupled nickel–cobalt nanoparticles/N,P,S-co-doped carbon hybrid nanocages with high performance for catalysis and protein adsorption†
Abstract
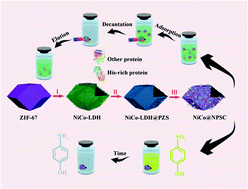
Carbon-supported bimetallic NiCo nanoparticles (NPs) have emerged as attractive catalysts and adsorbents for the reduction of 4-nitrophenol (4-NP) and separation of histidine-rich (His-rich) protein recently due to their low cost, high catalytic activity and good affinity for His-rich protein. In this study, new strongly coupled nickel–cobalt alloy/N,P,S co-doped carbon (NPSC) nanocages are rationally designed via chemical etching of the ZIF-67 dodecahedron with Ni2+ under sonication at room temperature, followed by poly(cyclotriphosphazene-co-4,4′-sulfonyldiphenol) (PZS) coating and subsequent carbonization treatment in a nitrogen atmosphere. When evaluated as a catalyst for 4-NP or an adsorbent for His-rich protein, the as-prepared NiCo@NPSC nanocages obtained at 700 °C show better performance than those obtained at other temperatures (500 and 900 °C). This improved catalytic effect is attributed to the controllable size and fine distribution of the NiCo NPs together with the effective contact between the catalysts and the N,P,S co-doped carbon matrix, leading to a superior catalytic effect on the reduction of 4-NP and the adsorption of His-rich protein. This catalyst design principle can be easily extended to other catalysis research fields.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...