Controlling the diversity of ion-induced fragmentation pathways by N-methylation of amino acids†
Abstract
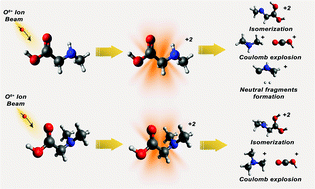
We present a combined experimental and theoretical study of the fragmentation of singly and doubly N-methylated glycine (sarcosine and N,N-dimethyl glycine, respectively) induced by low-energy (keV) O6+ ions. Multicoincidence mass spectrometry techniques and quantum chemistry simulations (ab initio molecular dynamics and density functional theory) allow us to characterise different fragmentation pathways as well as the associated mechanisms. We focus on the fragmentation of doubly ionised species, for which coincidence measurements provide unambiguous information on the origin of the various charged fragments. We have found that single N-methylation leads to a larger variety of fragmentation channels than in no methylation of glycine, while double N-methylation effectively closes many of these fragmentation channels, including some of those appearing in pristine glycine. Importantly, the closure of fragmentation channels in the latter case does not imply a protective effect by the methyl group.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...