Dipolar pathways in dipolar EPR spectroscopy†
Abstract
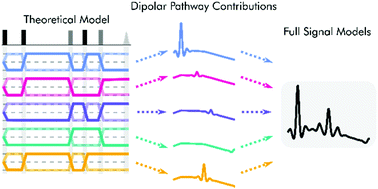
Dipolar electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) experiments such as double electron–electron resonance (DEER) measure distributions of nanometer-scale distances between unpaired electrons, which provide valuable information for structural characterization of proteins and other macromolecular systems. To determine these distributions from the experimental signal, it is critical to employ an accurate model of the signal. For dilute samples of doubly spin-labeled molecules, the signal is a product of an intramolecular and an intermolecular contribution. We present a general model based on dipolar pathways valid for dipolar EPR experiments with spin-1/2 labels. Our results show that the intramolecular contribution consists of a sum and the intermolecular contribution consists of a product over individual dipolar pathway contributions. We examine several commonly used dipolar EPR experiments in terms of dipolar pathways and show experimental results confirming the theoretical predictions. This multi-pathway model makes it possible to analyze a wide range of dipolar EPR experiments within a single theoretical framework.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...