Microfluidic pressure in paper (μPiP): rapid prototyping and low-cost liquid handling for on-chip diagnostics
Abstract
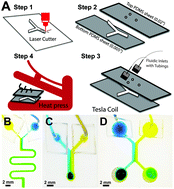
Paper-based microfluidics was initially developed for use in ultra-low-cost diagnostics powered passively by liquid wicking. However, there is significant untapped potential in using paper to internally guide porous microfluidic flows using externally applied pressure gradients. Here, we present a new technique for fabricating and utilizing low-cost polymer-laminated paper-based microfluidic devices using external pressure. Known as microfluidic pressure in paper (μPiP), devices fabricated by this technique are capable of sustaining a pressure gradient for use in precise liquid handling and manipulation applications similar to conventional microfluidic open-channel designs, but instead where fluid is driven directly through the porous paper structure. μPiP devices can be both rapidly prototyped or scalably manufactured and deployed at commercial scale with minimal time, equipment, and training requirements. We present an analysis of continuous pressure-driven flow in porous paper-based microfluidic channels and demonstrate broad applicability of this method in performing a variety of different liquid handling applications, including measuring red blood cell deformability and performing continuous free-flow DNA electrophoresis. This new platform offers a budget-friendly method for performing microfluidic operations for both academic prototyping and large-scale commercial device production.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...