Novel tetrahydropyrimidinyl-substituted benzimidazoles and benzothiazoles: synthesis, antibacterial activity, DNA interactions and ADME profiling†
Abstract
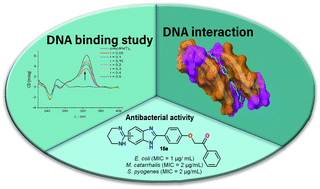
A series of tetrahydropyrimidinyl-substituted benzimidazoles attached to various aliphatic or aromatic residues via phenoxymethylene were synthesised to investigate their antibacterial activities against selected Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. The influence of the type of substituent at the C-3 and C-4 positions of the phenoxymethylene linker on the antibacterial activity was observed, showing that the aromatic moiety improved the antibacterial potency. Of all the evaluated compounds, benzoyl-substituted benzimidazole derivative 15a was the most active compound, particularly against the Gram-negative pathogens E. coli (MIC = 1 μg mL−1) and M. catarrhalis (MIC = 2 μg mL−1). Compound 15a also exhibited the most promising antibacterial activity against sensitive and resistant strains of S. pyogenes (MIC = 2 μg mL−1). Significant stabilization effects and positive induced CD bands strongly support the binding of the most biologically active benzimidazoles inside the minor grooves of AT-rich DNA, in line with docking studies. The predicted physico-chemical and ADME properties lie within drug-like space except for low membrane permeability, which needs further optimization. Our findings encourage further development of novel structurally related 5(6)-tetrahydropyrimidinyl substituted benzimidazoles in order to optimize their antibacterial effect against common respiratory pathogens.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...