Integrating electrodeposition with electrolysis for closed-loop resource utilization of battery industrial wastewater†
Abstract
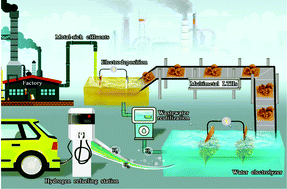
Traditional ab initio industrial wastewater treatment and utilization processes require high energy consumption and have high carbon emissions. Synergistically recovering critical elements, such as metals and hydrogen (H2), from the process is crucial to innovate modern industrial wastewater treatment technologies toward lower carbon emission avenues. Herein, by integrating electrodeposition and water splitting process into battery industrial wastewater management, we have demonstrated a facile metal recycling and wastewater resource reutilization routine. The electrodeposited NiCoMn layered triple hydroxides (LTHs) possess a hierarchical nanoflower structure capable of acting as a bifunctional catalyst for post-electrodeposition (PE) wastewater splitting for H2 production. The optimized wastewater-derived S-3||S-3 couple electrodes outperform the benchmark counterpart, Pt/C||RuO2, for PE wastewater electrolysis, with an H2 production rate of 2.23 vs. 1.78 mg h−1 at an applied potential of 1.8 V. A detailed mechanistic study reveals that metal species with lower valence states in LTHs account for high HER activity, while the in situ evolved amorphous metal (oxy)hydroxides act as the active sites for OER. This report presents an innovative strategy to simultaneously recycle critical metals and produce molecular H2 from industrial wastewater, paving the way for industrial wastewater recycling that ensures optimal resource utilization with low carbon emissions and a modern vision of industrial ecology.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...