Choline chloride–ethylene glycol based deep-eutectic solvents as lixiviants for cobalt recovery from lithium-ion battery cathode materials: are these solvents really green in high-temperature processes?†
Abstract
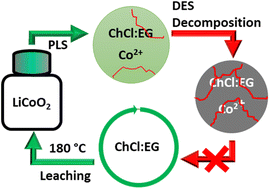
Deep-eutectic solvents (DESs) are often considered to be safe, eco-friendly and non-toxic solvents. Due to these green credentials, they are increasingly being studied for application in metal recycling processes. One example is their use as lixiviants for the recovery of cobalt from lithium cobalt oxide (LiCoO2, LCO), which is a common cathode material in lithium-ion batteries. Here, leaching of cobalt is facilitated by reduction of cobalt(III) to cobalt(II) in the presence of a reducing agent. However, several recent publications report on the use of DESs as lixiviants at high temperatures (180 °C) without addition of a reducing agent. Typical DESs for these applications are based on mixtures of choline chloride and ethylene glycol (ChCl : EG). Unfortunately, these studies ignore the limited thermal stability of ChCl : EG at high temperatures, which limits the recyclability of this DES. In this work, the drawbacks of using ChCl : EG as the lixiviant in high-temperature ionometallurgical processes are demonstrated. Structural analysis confirmed that ChCl : EG is not stable at 180 °C, forming hazardous and toxic decomposition products such as trimethylamine and 2-chloroethanol. It was hypothesized that choline chloride reduces cobalt(III) while simultaneously undergoing a radical β-hydrogen abstraction reaction, thereby decomposing to trimethylamine and other degradation products. The main conclusion is that this type of DES should not be used for high-temperature leaching processes due to their limited stability under such conditions.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...