Natural deep eutectic solvent assisted synthesis and applications of chiral carbon dots†
Abstract
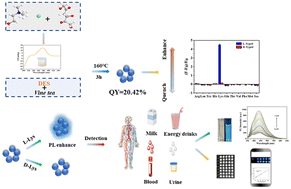
Chiral recognition has attracted extensive attention in the field of pharmaceutical science as it plays an important role in understanding biological and pharmaceutical mechanisms. Chiral carbon dots (CCDs), which integrate the advantages of fluorescence properties and the unique chiral properties, have great potential in chiral recognition. However, the synthetic method, chirality, and optical enantioselective sensing performance of CCDs have been scarcely investigated. Herein, N,Cl-doped CCDs were prepared for the first time through a one-step hydrothermal method using vine tea as the precursor, and a natural deep eutectic solvent (NADES) as the eco-friendly solvent, doping agent, and chiral source. In this synthesis strategy of CCDs, the NADES integrates multiple functions to prepare novel CCDs without adding organic solvents, additional chiral sources and doping agents, providing a new method for the green synthesis of CCDs. The obtained N,Cl-doped CCDs exhibit a high quantum yield, great enantioselective recognition ability, outstanding enantiomeric percentage detection performance, and satisfactory sensitivity to L-lysine (L-Lys). The chiral sensing system of CCDs reported here is simpler for the detection of L-Lys by directly recording the change in fluorescence intensity without any other indicators. The enantioselectivity (FL/FD) reaches 5.46 and the detection limit for L-Lys is 10 nM, which are better than those previously reported. Interestingly, the fabricated CCD-based paper micro-sensor system with a smartphone shows good sensitivity and excellent storage stability for L-Lys detection. Both the CCD dispersion-based method and CCD paper microchip-based visual method can accurately determine L-Lys in actual samples with satisfactory recoveries (96.19–109.65% and 86.74–114.10%, respectively). Furthermore, by combining experiments with theoretical calculation, the response mechanism and the chiral optical activity of CCDs were elucidated in detail. This work opens up a new avenue not only for developing nanomaterials using green methods, but also for broadening the application prospects of chiral nanomaterials in clinical diagnosis and drug screening.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...