Surface oxygenation induced strong interaction between Pd catalyst and functional support for zinc–air batteries†
Abstract
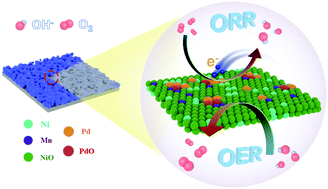
Employing the strong metal-support interaction (SMSI) effect for promoting the catalyst's activity toward the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) is promising due to the electronic structure optimization and high utilization efficiency of platinum group metal (PGM) catalysts. Metal oxides as alternative supports for PGMs facilitate intrinsic activity and improve durability as compared to conventional carbon supports. However, the restricted mass and electron transfer at the metal/support interface need to be addressed. Herein, to strengthen the interaction at the metal/support interfaces and improve the utilization efficiency of PGM, an ultralow loading of Pd was embedded in a surface-oxygenated PdNiMnO porous film. The Mn-doping was designed to promote surface oxygenation using a facile anodization process that created sufficiently exposed interfaces between Pd and the support, strengthening the SMSI effects at the Pd/oxygenated support interface for enhancing ORR performance. Furthermore, the Ni-containing oxygenated catalyst served as both the active component for the oxygen evolution reaction (OER) and the functional support for stabilizing Pd, making PdNiMnO a bifunctional catalyst for zinc–air flow batteries (ZAFB). As a proof-of-concept, the ZAFB (PdNiMnO) shows a maximal power density of 211.6 mW cm−2 and outstanding cycling stability for over 2000 h with a minimal voltage gap of 0.69 V at a current density of 10 mA cm−2, superior to the state-of-the-art catalysts.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...